Invasive Species: Garlic Mustard Alliaria petiolata
... especially if flowers are present, to avoid further infestation. Large Infestations For areas with larger numbers of plants, where hand-pulling plants is not possible, flowering stems can be cut at or a few inches above ground level. This is because plants may still be able to produce flowers at lea ...
... especially if flowers are present, to avoid further infestation. Large Infestations For areas with larger numbers of plants, where hand-pulling plants is not possible, flowering stems can be cut at or a few inches above ground level. This is because plants may still be able to produce flowers at lea ...
Swiss Chard - Portland Nursery
... Swiss Chard Not only is swiss chard a good heatofthesummer spinach substitute, it’s also a looker! Check out varieties like ‘Bright Lights’ that have stunning, almost neon, color contrasts between leaves and stems. PLANTING: CULTURE: ...
... Swiss Chard Not only is swiss chard a good heatofthesummer spinach substitute, it’s also a looker! Check out varieties like ‘Bright Lights’ that have stunning, almost neon, color contrasts between leaves and stems. PLANTING: CULTURE: ...
CHAPTER 26
... plants and grew as tall as modern trees a. Horsetails contributed to the coal deposits 2. Genus Equisetum is the only extant genus and grows in wet habitats 3. Horsetails have true roots, stems, and leaves 4. The stems of the horsetail have silica which makes them abrasive. Pioneers used them to cle ...
... plants and grew as tall as modern trees a. Horsetails contributed to the coal deposits 2. Genus Equisetum is the only extant genus and grows in wet habitats 3. Horsetails have true roots, stems, and leaves 4. The stems of the horsetail have silica which makes them abrasive. Pioneers used them to cle ...
Chapter 2 – Plant Structures and Functions
... move in plants? • Roots – xylem: moves water and minerals up from roots to the stem – phloem: carries sugar from leaves down the stem and into roots ...
... move in plants? • Roots – xylem: moves water and minerals up from roots to the stem – phloem: carries sugar from leaves down the stem and into roots ...
Phylum Tracheophyta: Class Filicinae
... The process of _________________________ requires __________________ in the form of _______________ Photosynthesis is carried out in the __________ ...
... The process of _________________________ requires __________________ in the form of _______________ Photosynthesis is carried out in the __________ ...
Whee! New variegated dogwoods are colorful, fancy and fun
... foliage turns from green, gold, yellow and white to brilliant hot tones of orange, red and burgundy. The fancy foliage of variegated Chinese dogwoods delivers eye-catching color throughout the growing season, making these special cultivars ideally suited for garden center sales. Their hardiness, dis ...
... foliage turns from green, gold, yellow and white to brilliant hot tones of orange, red and burgundy. The fancy foliage of variegated Chinese dogwoods delivers eye-catching color throughout the growing season, making these special cultivars ideally suited for garden center sales. Their hardiness, dis ...
Lec 16 - Development of e
... after transplanting and repeated at 10-12 days interval. Leaf Blight (Blast): Botrytis spp. Symptoms ...
... after transplanting and repeated at 10-12 days interval. Leaf Blight (Blast): Botrytis spp. Symptoms ...
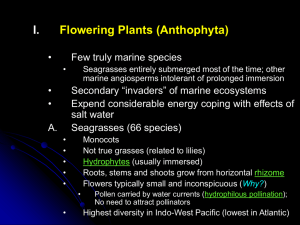
Topic 3: Plant Diversity I (Ch. 29)
... A. probably form a monophyletic group with ferns and whisk ferns; some group these within the fern phylum B. 15 known living species, all in genus Equisetum C. most <1 m tall, some 3 m tall; widely scattered in damp regions throughout the world D. fossil record back to 300 MYA 1. once much more dive ...
... A. probably form a monophyletic group with ferns and whisk ferns; some group these within the fern phylum B. 15 known living species, all in genus Equisetum C. most <1 m tall, some 3 m tall; widely scattered in damp regions throughout the world D. fossil record back to 300 MYA 1. once much more dive ...
Plants Woo Woo! Notes for 4-15
... C. [Water is not required for fertilization] D. [all of the above] ...
... C. [Water is not required for fertilization] D. [all of the above] ...
Lesson 3 How Do Plants Meet Their Needs? Fast Fact Sprouting
... begins to grow downward, and a shoot begins to grow upward. This growth takes place at the tips of the root and shoot. In some plants, branches may grow from side buds as well. As with the roots and shoots, the tips of the side branches grow. The branches produce leaves and more side buds, from whic ...
... begins to grow downward, and a shoot begins to grow upward. This growth takes place at the tips of the root and shoot. In some plants, branches may grow from side buds as well. As with the roots and shoots, the tips of the side branches grow. The branches produce leaves and more side buds, from whic ...
Fungal Plant Pathogen
... fragmentation, fission and budding. With asexual reproduction the repeating cycles of infection can continue throughout the growing season. Asexual spores may be classified as oidia (formed by fragmentation of hyphae into individual cells), conidia (borne on tips or sides of specialized branches of ...
... fragmentation, fission and budding. With asexual reproduction the repeating cycles of infection can continue throughout the growing season. Asexual spores may be classified as oidia (formed by fragmentation of hyphae into individual cells), conidia (borne on tips or sides of specialized branches of ...
Stems - SBI3USpring2014
... •storing water and nutrients for future use (parenchyma) •can also help protect plan (eg. Can be spiny like in a cactus or raspberry plant) ...
... •storing water and nutrients for future use (parenchyma) •can also help protect plan (eg. Can be spiny like in a cactus or raspberry plant) ...
Feb 19 - University of San Diego
... Succulent leaves, cuticle help to retain water Pickleweed (Salicornia) ...
... Succulent leaves, cuticle help to retain water Pickleweed (Salicornia) ...
Plant WebQuest - Balfour Collegiate
... Different types of plants have different characteristics. In this activity, you will find out just how different they are by gathering information on plant diversity. ...
... Different types of plants have different characteristics. In this activity, you will find out just how different they are by gathering information on plant diversity. ...
Cornus kousa - Environmental Horticulture
... Scales can build up to large numbers before being detected. Aphids on small trees may be partially controlled by spraying them with a strong stream of water from the garden hose. ...
... Scales can build up to large numbers before being detected. Aphids on small trees may be partially controlled by spraying them with a strong stream of water from the garden hose. ...
PDF - Mission Monarch
... alternate on the stem (not opposite each other), lance-shaped, 5 to 10 cm long, smooth on top and downy ...
... alternate on the stem (not opposite each other), lance-shaped, 5 to 10 cm long, smooth on top and downy ...
Watercress (Nasturtium officinale L.)
... Watercress, which has a peppery taste with high concentrations of vitamins and minerals, has been used in salads since at least Roman times. In 1750 it was grown commercially in Germany. It is still used in salads as well as in sandwiches, soups and oriental stirfry dishes.. Ducks and deer enjoy eat ...
... Watercress, which has a peppery taste with high concentrations of vitamins and minerals, has been used in salads since at least Roman times. In 1750 it was grown commercially in Germany. It is still used in salads as well as in sandwiches, soups and oriental stirfry dishes.. Ducks and deer enjoy eat ...
Peanut Disease Photos - Extension Plant Pathology
... Large irregular spots are found on the upper leaf surface. Young spots are grayish brown to dark brown with lighter margins. Older spots may be light brown. ...
... Large irregular spots are found on the upper leaf surface. Young spots are grayish brown to dark brown with lighter margins. Older spots may be light brown. ...
MOUNTAIN PEPPER (leaf) - in
... • Flavonne Glycosides - Isovitexin, Rutin, Chlorogenic acid & Polygodial are major peaks ...
... • Flavonne Glycosides - Isovitexin, Rutin, Chlorogenic acid & Polygodial are major peaks ...
Name: Form: Date: Teacher: INSTRUCTIONS This workbook forms
... Native plants prefer soils that are low in phosphorus so be careful not to add too much fertilizer containing this. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION - 1. PROPAGATION BY RUNNERS (OR STOLONS) The main stem of a plant grows straight up. It gives the plant support. Some plants have other kinds of stems too. They ar ...
... Native plants prefer soils that are low in phosphorus so be careful not to add too much fertilizer containing this. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION - 1. PROPAGATION BY RUNNERS (OR STOLONS) The main stem of a plant grows straight up. It gives the plant support. Some plants have other kinds of stems too. They ar ...
Indian Laurel - Trees from Seeds
... and are between 10 – 15 cm long and 5 – 7 cm wide. The leaf apex is blunt and often notched and lateral leaf veins are prominent, numerous and parallel. When the leaves are picked, a yellowish sap is seen. ...
... and are between 10 – 15 cm long and 5 – 7 cm wide. The leaf apex is blunt and often notched and lateral leaf veins are prominent, numerous and parallel. When the leaves are picked, a yellowish sap is seen. ...
Club Mosses, Whisk Fern and Horsetails
... fortuitous, for botanists are not convinced that Psilotum should really be classified with the fossil general Rhynia and Psilophyton. Some even think they may represent primitive ferns! Psilotum has no true leaves or roots, consisting of little more than stems. The underground stems are rhizomes equ ...
... fortuitous, for botanists are not convinced that Psilotum should really be classified with the fossil general Rhynia and Psilophyton. Some even think they may represent primitive ferns! Psilotum has no true leaves or roots, consisting of little more than stems. The underground stems are rhizomes equ ...
Horticulture
... • The process of temporarily covering the plant roots when a tree has to be out of the ground for transplanting. The purpose is to retain the moisture around the roots with an organic material such as straw, mulch or soil during transplanting. ...
... • The process of temporarily covering the plant roots when a tree has to be out of the ground for transplanting. The purpose is to retain the moisture around the roots with an organic material such as straw, mulch or soil during transplanting. ...
Leaf

A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant and is the principal lateral appendage of the stem. The leaves and stem together form the shoot. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves collectively.Typically a leaf is a thin, dorsiventrally flattened organ, borne above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Most leaves have distinctive upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) surfaces that differ in colour, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases) and other features. In most plant species, leaves are broad and flat. Such species are referred to as broad-leaved plants. Many gymnosperm species have thin needle-like leaves that can be advantageous in cold climates frequented by snow and frost. Leaves can also have other shapes and forms such as the scales in certain species of conifers. Some leaves are not above ground (such as bulb scales). Succulent plants often have thick juicy leaves, but some leaves are without major photosynthetic function and may be dead at maturity, as in some cataphylls, and spines). Furthermore, several kinds of leaf-like structures found in vascular plants are not totally homologous with them. Examples include flattened plant stems (called phylloclades and cladodes), and phyllodes (flattened leaf stems), both of which differ from leaves in their structure and origin. Many structures of non-vascular plants, and even of some lichens, which are not plants at all (in the sense of being members of the kingdom Plantae), look and function much like leaves. The primary site of photosynthesis in most leaves (palisade mesophyll) almost always occurs on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of Eucalyptus palisade occurs on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral.