Temporal variation of δ13C of larch leaves from a montane boreal
... iron tower at the site (Li et al. 2005). Precipitation during the leaf-out period at the tower site was not available and instead precipitation observed at the Mongonmorit Weather Station was used. Additional details about the study site are presented elsewhere (Li et al. 2005, 2006). Sample collect ...
... iron tower at the site (Li et al. 2005). Precipitation during the leaf-out period at the tower site was not available and instead precipitation observed at the Mongonmorit Weather Station was used. Additional details about the study site are presented elsewhere (Li et al. 2005, 2006). Sample collect ...
Chelone glabra
... SPECIAL FEATURES: Each blossom resembles the head of a turtle. The tubular blossoms end with an upper lip having two lobes and a lower lip with three lobes. The lower lip protrudes beyond ...
... SPECIAL FEATURES: Each blossom resembles the head of a turtle. The tubular blossoms end with an upper lip having two lobes and a lower lip with three lobes. The lower lip protrudes beyond ...
Thinleaf or Mountain Alder
... Leaves: 1 to 4 inches (2.5 to 10 cm) long; doubly toothed; to 2.5 inches (6 cm) wide and wrinkled. Leaves alternate but so close together as to appear opposite, and often in clumps of 2 or 3 at end of twigs. Six to nine parallel veins are noticeable. Leaf size is usually about twice water birch leaf ...
... Leaves: 1 to 4 inches (2.5 to 10 cm) long; doubly toothed; to 2.5 inches (6 cm) wide and wrinkled. Leaves alternate but so close together as to appear opposite, and often in clumps of 2 or 3 at end of twigs. Six to nine parallel veins are noticeable. Leaf size is usually about twice water birch leaf ...
Biology 2201 Unit 2
... • Locomotion: Yes. Most are motile at some point in their lifetime. • Animals are divided into two groups: – Vertebrates: with a backbone and 5% of animal ...
... • Locomotion: Yes. Most are motile at some point in their lifetime. • Animals are divided into two groups: – Vertebrates: with a backbone and 5% of animal ...
CHAPTER VIII VEGETABLE SUBSTITUTES FOR SOAP AMONG the
... tree,2 and to the Spanish-speaking people as jaboncillo (little soap). All three species are trees with pinnate leaves (non-deciduous in the first two) and small, white flowers borne in terminal panicles; and all produce fleshy berries about the size of cherries and containing one or two seeds. It i ...
... tree,2 and to the Spanish-speaking people as jaboncillo (little soap). All three species are trees with pinnate leaves (non-deciduous in the first two) and small, white flowers borne in terminal panicles; and all produce fleshy berries about the size of cherries and containing one or two seeds. It i ...
Lec 12- Plant viruses
... Protein forms a protective coat (capsid) around the nucleic acid in a virus. Plant viruses have only one kind of protein. Individual protein subunits are called as capsomers. Protein subunits are spirally arranged in elongated viruses and packed on the side of polyhedral particles of spherical virus ...
... Protein forms a protective coat (capsid) around the nucleic acid in a virus. Plant viruses have only one kind of protein. Individual protein subunits are called as capsomers. Protein subunits are spirally arranged in elongated viruses and packed on the side of polyhedral particles of spherical virus ...
Topic 9 Plant Biology
... 2. Meristem cells are small and go through the cell cycle repeatedly to produce more cells 3. Root apical meristem is responsible for the growth of the root. period. Like, that’s it…roots beget roots 4. Shoot apical meristem is more complex a. It sends off the cells needed for growth of the stem b. ...
... 2. Meristem cells are small and go through the cell cycle repeatedly to produce more cells 3. Root apical meristem is responsible for the growth of the root. period. Like, that’s it…roots beget roots 4. Shoot apical meristem is more complex a. It sends off the cells needed for growth of the stem b. ...
Watsonia Factsheet - Blackwood Basin Group
... herbicides in conjunction with mechanical control methods will give good results for thick infestations. Wipe individual leaves with glyphosate or spray dense infestations. Eradication from an area usually takes two to three years. ...
... herbicides in conjunction with mechanical control methods will give good results for thick infestations. Wipe individual leaves with glyphosate or spray dense infestations. Eradication from an area usually takes two to three years. ...
Herbaceous Cuttings - NAAE Communities of Practice
... Each group should prepare 12 uniform stem cuttings from the same genus, species and if applicable the same cultivar or variety and divide ...
... Each group should prepare 12 uniform stem cuttings from the same genus, species and if applicable the same cultivar or variety and divide ...
test plants and animal
... 1. Refer to Figure 21-3. Removing which structure would cause this plant to fall over? a. A c. C b. B d. D 2. Refer to Figure 21-3. Which structure is used for the transportation of nutrients? a. A c. C b. B d. D 3. Refer to Figure 21-3. Removing which structure would cause this plant to starve? a. ...
... 1. Refer to Figure 21-3. Removing which structure would cause this plant to fall over? a. A c. C b. B d. D 2. Refer to Figure 21-3. Which structure is used for the transportation of nutrients? a. A c. C b. B d. D 3. Refer to Figure 21-3. Removing which structure would cause this plant to starve? a. ...
Gas Exchange Characteristics as a Basis for Prediction of its
... of 77 ng cm-2 sec-I recorded here, placing it in the same category as some of the more productive C , crop plants (Gifford 1974). The rates of photosynthesis observed at low photon flux in the present study also indicate that P. hysterophorus may compete successfully with many native and exotic past ...
... of 77 ng cm-2 sec-I recorded here, placing it in the same category as some of the more productive C , crop plants (Gifford 1974). The rates of photosynthesis observed at low photon flux in the present study also indicate that P. hysterophorus may compete successfully with many native and exotic past ...
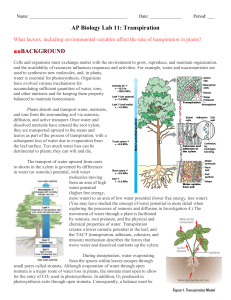
AP Biology Lab 11: Transpiration
... c. What predictions and/or hypotheses can you make about the number of stomata per mm2 and the rate of transpiration? d. Is the leaf surface area directly related to the rate of transpiration? e. What predictions can you make about the rate of transpiration in plants with smaller or fewer leaves? f ...
... c. What predictions and/or hypotheses can you make about the number of stomata per mm2 and the rate of transpiration? d. Is the leaf surface area directly related to the rate of transpiration? e. What predictions can you make about the rate of transpiration in plants with smaller or fewer leaves? f ...
Managing for pests on Managing for pests on
... Symptoms: white or yellow spots on leaves, scales concentrated on stems, females overwinter Management: plant further from buildings for better air circulation, insecticidal soap, horticulture oils ...
... Symptoms: white or yellow spots on leaves, scales concentrated on stems, females overwinter Management: plant further from buildings for better air circulation, insecticidal soap, horticulture oils ...
English
... pupae or adults. The larval period is the most damaging period, usually completed within ...
... pupae or adults. The larval period is the most damaging period, usually completed within ...
Seedless Vascular Plants
... Leaves capture more sunlight with their increased surface area by employing more chloroplasts to trap light energy and convert it to chemical energy, which is then used to x atmospheric carbon dioxide into carbohydrates. The carbohydrates are exported to the rest of the plant by the conductive cell ...
... Leaves capture more sunlight with their increased surface area by employing more chloroplasts to trap light energy and convert it to chemical energy, which is then used to x atmospheric carbon dioxide into carbohydrates. The carbohydrates are exported to the rest of the plant by the conductive cell ...
Exam III Review
... 35. Name the male and female gametophytes. 36. Why do the bryophytes require water for fertilization? 37. Name two differences between bryophytes and ferns. 38. Name the two types of vascular tissue and their functions. 39. Name the two other examples of vascular seedless plants. ...
... 35. Name the male and female gametophytes. 36. Why do the bryophytes require water for fertilization? 37. Name two differences between bryophytes and ferns. 38. Name the two types of vascular tissue and their functions. 39. Name the two other examples of vascular seedless plants. ...
Medicinal uses of the plants that have been the most listed
... vasicine, and an essential oil. The chief use of vasaka is as an expectorant; it is given in the form of juice, syrup or decocation, It softens the thick sputum, facilitates its coming out and thus bring about quick relief in bronchitis. The expectorant activity is due to stimulation of bronchial gl ...
... vasicine, and an essential oil. The chief use of vasaka is as an expectorant; it is given in the form of juice, syrup or decocation, It softens the thick sputum, facilitates its coming out and thus bring about quick relief in bronchitis. The expectorant activity is due to stimulation of bronchial gl ...
Plant ID Group #9
... needles of this two-needle Pine are held on the tree for more than four years making this one of the more dense Pines suitable for a screen planting – Flowers: 1-2 inch pine cone – Height: 4 to 10 feet – Form: shrub or small, round or broad pyramidal plant – Leaf Arrangement: Alternate – Landscape U ...
... needles of this two-needle Pine are held on the tree for more than four years making this one of the more dense Pines suitable for a screen planting – Flowers: 1-2 inch pine cone – Height: 4 to 10 feet – Form: shrub or small, round or broad pyramidal plant – Leaf Arrangement: Alternate – Landscape U ...
PPCP-VEG-003
... affects all parts of the shoot tissue including stems, leaves and on cv. Genovese flower bracts. Leaves first turn yellow in the areas between major veins (Figure 1) and within a few days entire leaves turn yellow and begin to drop off of the plant. Irregular shaped black specks appear on the upper ...
... affects all parts of the shoot tissue including stems, leaves and on cv. Genovese flower bracts. Leaves first turn yellow in the areas between major veins (Figure 1) and within a few days entire leaves turn yellow and begin to drop off of the plant. Irregular shaped black specks appear on the upper ...
Garlic Mustard - Ontario`s Invading Species Awareness Program
... Garlic mustard has two distinct life stages over its first two years. In the first year, it grows only a cluster of leaves shaped like a rosette, while a strong root system develops. Plants that survive the winter produce flowers and hundreds of seeds in their second year. Dense stands produce more ...
... Garlic mustard has two distinct life stages over its first two years. In the first year, it grows only a cluster of leaves shaped like a rosette, while a strong root system develops. Plants that survive the winter produce flowers and hundreds of seeds in their second year. Dense stands produce more ...
Mid North Coast Noxious Weeds Guide
... (Hypericum perforatum) An erect perennial herb or small shrub with a creeping rootstock. Leaves when viewed against light show characteristic oil glands. Flowers in spring, early summer bearing bright yellow flowers. The dead brown flower stalks are clearly visible at other times during the year. To ...
... (Hypericum perforatum) An erect perennial herb or small shrub with a creeping rootstock. Leaves when viewed against light show characteristic oil glands. Flowers in spring, early summer bearing bright yellow flowers. The dead brown flower stalks are clearly visible at other times during the year. To ...
Plant Divisions - World of Teaching
... • What did plants have to overcome to live on land? • What is the most primitive division of plants because they have no vascular system? • What is the most common example in this division and how do they reproduce? • Why are mosses so small? • What is the division of plants that contain a vascular ...
... • What did plants have to overcome to live on land? • What is the most primitive division of plants because they have no vascular system? • What is the most common example in this division and how do they reproduce? • Why are mosses so small? • What is the division of plants that contain a vascular ...
Biology
... An example of thigmotropism is the growth of vines and climbing plants. The stems of these plants do not grow straight up. The growing tip of each stem points sideways and twists in circles as the shoot grows. When the tip encounters an object, it quickly wraps around it. Slide 5 of 32 Copyright Pea ...
... An example of thigmotropism is the growth of vines and climbing plants. The stems of these plants do not grow straight up. The growing tip of each stem points sideways and twists in circles as the shoot grows. When the tip encounters an object, it quickly wraps around it. Slide 5 of 32 Copyright Pea ...
Leaf

A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant and is the principal lateral appendage of the stem. The leaves and stem together form the shoot. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves collectively.Typically a leaf is a thin, dorsiventrally flattened organ, borne above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Most leaves have distinctive upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) surfaces that differ in colour, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases) and other features. In most plant species, leaves are broad and flat. Such species are referred to as broad-leaved plants. Many gymnosperm species have thin needle-like leaves that can be advantageous in cold climates frequented by snow and frost. Leaves can also have other shapes and forms such as the scales in certain species of conifers. Some leaves are not above ground (such as bulb scales). Succulent plants often have thick juicy leaves, but some leaves are without major photosynthetic function and may be dead at maturity, as in some cataphylls, and spines). Furthermore, several kinds of leaf-like structures found in vascular plants are not totally homologous with them. Examples include flattened plant stems (called phylloclades and cladodes), and phyllodes (flattened leaf stems), both of which differ from leaves in their structure and origin. Many structures of non-vascular plants, and even of some lichens, which are not plants at all (in the sense of being members of the kingdom Plantae), look and function much like leaves. The primary site of photosynthesis in most leaves (palisade mesophyll) almost always occurs on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of Eucalyptus palisade occurs on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral.