Level General characteristics of language of level 9C Plants and
... use K/U to describe/explain- more than one factor; use appropriate terminology; distinguish between processes; identify differences/similarities; describe some causes; use word equations; use abstract ideas in unfamiliar contexts; give applications of ...
... use K/U to describe/explain- more than one factor; use appropriate terminology; distinguish between processes; identify differences/similarities; describe some causes; use word equations; use abstract ideas in unfamiliar contexts; give applications of ...
Session B
... In the past scientists classified algae as simple plants. Like all plants algae can make their own food by photosynthesis, but they do not have a water transport system. Some scientists think algae should be classified as protists (another kingdom like plants & animals in classification, which child ...
... In the past scientists classified algae as simple plants. Like all plants algae can make their own food by photosynthesis, but they do not have a water transport system. Some scientists think algae should be classified as protists (another kingdom like plants & animals in classification, which child ...
Plant Divisions
... • What did plants have to overcome to live on land? • What is the most primitive division of plants because they have no vascular system? • What is the most common example in this division and how do they reproduce? • Why are mosses so small? • What is the division of plants that contain a vascular ...
... • What did plants have to overcome to live on land? • What is the most primitive division of plants because they have no vascular system? • What is the most common example in this division and how do they reproduce? • Why are mosses so small? • What is the division of plants that contain a vascular ...
flora e fauna/ Animals and plants in Italy
... It has very short legs, but very long and sharp nails On its back there are a lot of big spikes (each one is high 30 centimetres!!) Its head and its belly don’t have a protection It is very shy and it is always scared, this is why it usually goes out during the night! ...
... It has very short legs, but very long and sharp nails On its back there are a lot of big spikes (each one is high 30 centimetres!!) Its head and its belly don’t have a protection It is very shy and it is always scared, this is why it usually goes out during the night! ...
An assortment of Haemanthus
... habitat, and is a particularly desirable and easy to grow garden subject, and suitable as a groundcover in areas of semishade. It is equally at home in deep shade on forest floors, on rocky sea shores exposed to salt spray, in coastal dune forest, on cliff faces in hot river valleys where it clings ...
... habitat, and is a particularly desirable and easy to grow garden subject, and suitable as a groundcover in areas of semishade. It is equally at home in deep shade on forest floors, on rocky sea shores exposed to salt spray, in coastal dune forest, on cliff faces in hot river valleys where it clings ...
Meet the Saratoga Bay Laurel Tree
... tinged red. When crushed, the stems and leaves of this hybrid are strongly aromatic with the typical scent of bay, and can be used for culinary purposes. In late winter or early spring ‘Saratoga’ pr oduces an abundant display of small, pale yellow flower clusters. These male flowers do not produce u ...
... tinged red. When crushed, the stems and leaves of this hybrid are strongly aromatic with the typical scent of bay, and can be used for culinary purposes. In late winter or early spring ‘Saratoga’ pr oduces an abundant display of small, pale yellow flower clusters. These male flowers do not produce u ...
Katydids in Grapes
... Katydids may feed on a few flowers during and shortly before and after bloom. The damaged flowers will fall off, along with many undamaged flowers during shatter. Thus flower damage is of no importance. FTBK nymph with nibbled flower bud in It is not clear whether katydids May. feed on grape berries ...
... Katydids may feed on a few flowers during and shortly before and after bloom. The damaged flowers will fall off, along with many undamaged flowers during shatter. Thus flower damage is of no importance. FTBK nymph with nibbled flower bud in It is not clear whether katydids May. feed on grape berries ...
DESERT PLANTS
... eliminating leaves -- replacing them with thorns, not spines -- or by greatly reducing leaf size to eliminate transpiration (loss of water to the air). Such plants also usually have smooth, green bark on stems and trunks serving to both produce food and seal in moisture. ...
... eliminating leaves -- replacing them with thorns, not spines -- or by greatly reducing leaf size to eliminate transpiration (loss of water to the air). Such plants also usually have smooth, green bark on stems and trunks serving to both produce food and seal in moisture. ...
Ch. 22
... • Each of these minerals constitutes 1% or more of a plant’s dry weight • Plants must absorb these materials, along with water, through their roots the first plants were symbiotically involved with mycorrhizae ...
... • Each of these minerals constitutes 1% or more of a plant’s dry weight • Plants must absorb these materials, along with water, through their roots the first plants were symbiotically involved with mycorrhizae ...
The way something feels to the touch is often referred to as texture
... Any part of the plant can have texture flowers, leaves, stems, roots, seeds, or pods. There may be a variety of textures on a single plant, or even a single part of the plant. A leaf may be smooth on top and rough on the bottom, or a flower can have silky petals and a rough seedhead (coneflower). A ...
... Any part of the plant can have texture flowers, leaves, stems, roots, seeds, or pods. There may be a variety of textures on a single plant, or even a single part of the plant. A leaf may be smooth on top and rough on the bottom, or a flower can have silky petals and a rough seedhead (coneflower). A ...
Lilium humboldtii Duch. subsp. ocellatum (Kellogg) Thorne
... occurring occasionally growing in rich humus in shade of undisturbed southern oak woodland or near streambanks. Leaves of Humboldt lily are commonly described as whorled, with long internodes between the “whorls,” but closer examination reveals that leaves appearing in a whorl actually arise at node ...
... occurring occasionally growing in rich humus in shade of undisturbed southern oak woodland or near streambanks. Leaves of Humboldt lily are commonly described as whorled, with long internodes between the “whorls,” but closer examination reveals that leaves appearing in a whorl actually arise at node ...
Section 21.1 Summary – pages 559
... • Both groups have the same types of chlorophyll used in photosynthesis and store food in the form of starch. ...
... • Both groups have the same types of chlorophyll used in photosynthesis and store food in the form of starch. ...
Forms of Inflorescence: panicle, raceme, spike
... some examples later. • Pictures in books work best for plants with showy flowers. For grasses, keys are a must. • How to decide if a plant is a grass or a forb? How to decide which key to use? • Focus for this class is mostly grasses. ...
... some examples later. • Pictures in books work best for plants with showy flowers. For grasses, keys are a must. • How to decide if a plant is a grass or a forb? How to decide which key to use? • Focus for this class is mostly grasses. ...
Non-Chemical Control - SellingYourScreenplay.com
... height. Quackgrass is a common weed of agronomic crops, turfgrass, lawns, nurseries, and landscapes that may be found in the northern United States from North Carolina to California. Seedling: First leaf is very long and wide and may have hairs or be hairless (glabrous) on the upper surface but are ...
... height. Quackgrass is a common weed of agronomic crops, turfgrass, lawns, nurseries, and landscapes that may be found in the northern United States from North Carolina to California. Seedling: First leaf is very long and wide and may have hairs or be hairless (glabrous) on the upper surface but are ...
Everlasting Garden Moluccella laevis
... Strawflower, probably the best-known of the everlastings. It easy to grow from seed, but not grown for it’s beauty in the garden. The strawflower is great for “glue work” using only the heads. Many sizes and colors. Leaves must be removed and hung in bunches to dry. Stems in most cases are strong en ...
... Strawflower, probably the best-known of the everlastings. It easy to grow from seed, but not grown for it’s beauty in the garden. The strawflower is great for “glue work” using only the heads. Many sizes and colors. Leaves must be removed and hung in bunches to dry. Stems in most cases are strong en ...
Macroscopic and microscopic analysis of stems and seeds of plants
... grows mainly in the piedmont plains, foothills and low mountains, where sometimes forms almost pure thickets. It often occurs as a weed in the non-irrigated fields. Perennial, 60-80 cm in height (pic 1). Stems erect, branched, whitish hairs and brown glands. The stems are used for fiber used to make ...
... grows mainly in the piedmont plains, foothills and low mountains, where sometimes forms almost pure thickets. It often occurs as a weed in the non-irrigated fields. Perennial, 60-80 cm in height (pic 1). Stems erect, branched, whitish hairs and brown glands. The stems are used for fiber used to make ...
sperms Vascular Plants
... • Pollinated by wind • Conifers adapted to cold, dry climate – cones to protect seeds – evergreen – waterproof needle-like leaves – sap does not freeze ...
... • Pollinated by wind • Conifers adapted to cold, dry climate – cones to protect seeds – evergreen – waterproof needle-like leaves – sap does not freeze ...
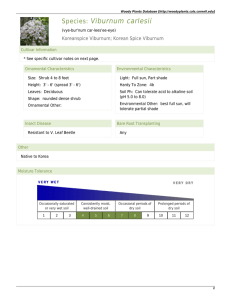
PDF view - Woody Plants Database
... 'Compactum' - compact, slow-growing, rounded form; tolerant of juglone; pink buds open in spring to sweetly fragrant white flowers arranged in snowball-like clusters, to 3" across; fall foliage dull red to wine-red to burgundy; grows 2.5 -4' tall and wide ...
... 'Compactum' - compact, slow-growing, rounded form; tolerant of juglone; pink buds open in spring to sweetly fragrant white flowers arranged in snowball-like clusters, to 3" across; fall foliage dull red to wine-red to burgundy; grows 2.5 -4' tall and wide ...
Quiz 12C
... classify plants is whether they produce seeds. Nonvascular plants – seedless and reproduce by producing gametes in one stage of their life cycle and spores. Vascular plants – some reproduce by gametes and spores & others by gametes and seeds. ...
... classify plants is whether they produce seeds. Nonvascular plants – seedless and reproduce by producing gametes in one stage of their life cycle and spores. Vascular plants – some reproduce by gametes and spores & others by gametes and seeds. ...
Choosing Bamboo for the Garden
... Bamboo is actually a highly evolved grass that spreads by rhizomes (underground stems). Every year, new shoots emerge from the underground rhizomes to form the stems, which are called culms. Basically, there are two types of bamboo: the clumpers and the runners. Clumpers stay close to where they ar ...
... Bamboo is actually a highly evolved grass that spreads by rhizomes (underground stems). Every year, new shoots emerge from the underground rhizomes to form the stems, which are called culms. Basically, there are two types of bamboo: the clumpers and the runners. Clumpers stay close to where they ar ...
BSc.- I Biotech - DAV College Jalandhar
... on each of its 1–5 culms (stems). Height is variable, from about 1.2–1.5 m for 1930s cultivars to about 85 cm for most modern cultivars, with a simultaneous strengthening of the culm so as to bear the increased weight (resulting from the increased grain yield) of the spike. Culms (stems): Hollow wit ...
... on each of its 1–5 culms (stems). Height is variable, from about 1.2–1.5 m for 1930s cultivars to about 85 cm for most modern cultivars, with a simultaneous strengthening of the culm so as to bear the increased weight (resulting from the increased grain yield) of the spike. Culms (stems): Hollow wit ...
Plant Divisions
... • What did plants have to overcome to live on land? • What is the most primitive division of plants because they have no vascular system? • What is the most common example in this division and how do they reproduce? • Why are mosses so small? • What is the division of plants that contain a vascular ...
... • What did plants have to overcome to live on land? • What is the most primitive division of plants because they have no vascular system? • What is the most common example in this division and how do they reproduce? • Why are mosses so small? • What is the division of plants that contain a vascular ...
Anemone (Anomone (a·nem·o·ne) from the Latin anemōnē and from
... • it does produce much sap which was used as a syrup by Inuit people. • The powdered inner cortex was applied to the hands and face to give protection from cold weather • syrup was traditionally extracted from the stems and flowers • in Europe, the fluff was used with cotton for making stockings. • ...
... • it does produce much sap which was used as a syrup by Inuit people. • The powdered inner cortex was applied to the hands and face to give protection from cold weather • syrup was traditionally extracted from the stems and flowers • in Europe, the fluff was used with cotton for making stockings. • ...
Leaf

A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant and is the principal lateral appendage of the stem. The leaves and stem together form the shoot. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves collectively.Typically a leaf is a thin, dorsiventrally flattened organ, borne above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Most leaves have distinctive upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) surfaces that differ in colour, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases) and other features. In most plant species, leaves are broad and flat. Such species are referred to as broad-leaved plants. Many gymnosperm species have thin needle-like leaves that can be advantageous in cold climates frequented by snow and frost. Leaves can also have other shapes and forms such as the scales in certain species of conifers. Some leaves are not above ground (such as bulb scales). Succulent plants often have thick juicy leaves, but some leaves are without major photosynthetic function and may be dead at maturity, as in some cataphylls, and spines). Furthermore, several kinds of leaf-like structures found in vascular plants are not totally homologous with them. Examples include flattened plant stems (called phylloclades and cladodes), and phyllodes (flattened leaf stems), both of which differ from leaves in their structure and origin. Many structures of non-vascular plants, and even of some lichens, which are not plants at all (in the sense of being members of the kingdom Plantae), look and function much like leaves. The primary site of photosynthesis in most leaves (palisade mesophyll) almost always occurs on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of Eucalyptus palisade occurs on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral.