succession
... The Healthy Forest Restoration Act • On December 3, 2003, President Bush signed into law the Healthy Forests Restoration Act of 2003 to reduce the threat of destructive wildfires while upholding environmental standards and encouraging early public input during review and planning processes. The Hea ...
... The Healthy Forest Restoration Act • On December 3, 2003, President Bush signed into law the Healthy Forests Restoration Act of 2003 to reduce the threat of destructive wildfires while upholding environmental standards and encouraging early public input during review and planning processes. The Hea ...
What Shapes an Ecosystem
... Ecosystems are constantly changing in response to natural and human disturbances. As an ecosystem changes, older inhabitants gradually die out and new organisms move in, causing further changes in the community. This series of predictable changes that occurs in a community over time is called Ecolog ...
... Ecosystems are constantly changing in response to natural and human disturbances. As an ecosystem changes, older inhabitants gradually die out and new organisms move in, causing further changes in the community. This series of predictable changes that occurs in a community over time is called Ecolog ...
Ecological Succession
... species that live in an area • The gradual replacement of one plant/animal community by another through natural processes over time • Can be primary or secondary ...
... species that live in an area • The gradual replacement of one plant/animal community by another through natural processes over time • Can be primary or secondary ...
Ecological Succession
... species that live in an area • The gradual replacement of one plant/animal community by another through natural processes over time • Can be primary or secondary ...
... species that live in an area • The gradual replacement of one plant/animal community by another through natural processes over time • Can be primary or secondary ...
Study Notes for Chapter 1-2: Environmental Science
... 14. Organisms that can make their own food from sunlight are called _____________. producers ...
... 14. Organisms that can make their own food from sunlight are called _____________. producers ...
Ecological Succession
... destroyed • Can occur in ecosystems that have been disturbed or disrupted by humans, animals, or by natural process such as storms, floods, earthquakes, or volcanic eruptions ...
... destroyed • Can occur in ecosystems that have been disturbed or disrupted by humans, animals, or by natural process such as storms, floods, earthquakes, or volcanic eruptions ...
Gateway Science Mid Unit Ecology Review
... iii. Zebras, giraffes, and grass in the same area 3. Energy Flow a. The ____________ is the primary source of energy in most ecosystems. b. Organisms that can convert sunlight into food (glucose) are called __________________ or _________________________ c. Organisms that CANNOT make their own food ...
... iii. Zebras, giraffes, and grass in the same area 3. Energy Flow a. The ____________ is the primary source of energy in most ecosystems. b. Organisms that can convert sunlight into food (glucose) are called __________________ or _________________________ c. Organisms that CANNOT make their own food ...
Mid Ecology Unit Test Review
... iii. Zebras, giraffes, and grass in the same area 3. Energy Flow a. The ____________ is the primary source of energy in most ecosystems. b. Organisms that can convert sunlight into food (glucose) are called __________________ or _________________________ c. Organisms that CANNOT make their own food ...
... iii. Zebras, giraffes, and grass in the same area 3. Energy Flow a. The ____________ is the primary source of energy in most ecosystems. b. Organisms that can convert sunlight into food (glucose) are called __________________ or _________________________ c. Organisms that CANNOT make their own food ...
Succession ppt
... • On December 3, 2003, President Bush signed into law the Healthy Forests Restoration Act of 2003 to reduce the threat of destructive wildfires while upholding environmental standards and encouraging early public input during review and planning processes. The Healthy Forests Restoration Act: • Stre ...
... • On December 3, 2003, President Bush signed into law the Healthy Forests Restoration Act of 2003 to reduce the threat of destructive wildfires while upholding environmental standards and encouraging early public input during review and planning processes. The Healthy Forests Restoration Act: • Stre ...
CH-4 Sect 4
... a. They generally weaken but do not kill their host. b. They obtain all or part of their nutritional needs from the host. c. They neither help nor harm the host. d. They are usually smaller than the host. 16. What is ecological succession? (pg 94-97)__________________________________________________ ...
... a. They generally weaken but do not kill their host. b. They obtain all or part of their nutritional needs from the host. c. They neither help nor harm the host. d. They are usually smaller than the host. 16. What is ecological succession? (pg 94-97)__________________________________________________ ...
Succession - Amazing World of Science with Mr. Green
... Seral Stages: Early Successional Plant Species ...
... Seral Stages: Early Successional Plant Species ...
Ecological Succession
... community living within it occurs by a process called PRIMARY SUCCESSION. • An example of an area in which a community has never lived before, would be a new lava or rock from a volcano that makes a new island. ...
... community living within it occurs by a process called PRIMARY SUCCESSION. • An example of an area in which a community has never lived before, would be a new lava or rock from a volcano that makes a new island. ...
Ecological Succession
... Secondary Succession • Begins in a place that already has soil and was once the home of living organisms • Occurs faster and has different pioneer species than primary succession • Example: after forest fires ...
... Secondary Succession • Begins in a place that already has soil and was once the home of living organisms • Occurs faster and has different pioneer species than primary succession • Example: after forest fires ...
Environmental Problems, Their Causes, and the Issue of
... Writing Assignment The town council has observed that the frog population of a local stream has been dwindling. This stream receives storm water from a new development that has been planting and fertilizing the lawns of the new homes being built. The town council is looking to limit the amount of p ...
... Writing Assignment The town council has observed that the frog population of a local stream has been dwindling. This stream receives storm water from a new development that has been planting and fertilizing the lawns of the new homes being built. The town council is looking to limit the amount of p ...
Succession and Stability
... individual species can change substantially. – Stability depends on resolution an area is investigated at. ...
... individual species can change substantially. – Stability depends on resolution an area is investigated at. ...
Succession _ Biomes
... • As these species die, they create soil for further species • Shrubs, ferns, grasses come next • Pines, beeches and maples colonize after that • When the community stabilizes, a climax community is established – How can you tell? ...
... • As these species die, they create soil for further species • Shrubs, ferns, grasses come next • Pines, beeches and maples colonize after that • When the community stabilizes, a climax community is established – How can you tell? ...
Chapter 4: Ecosystems and Communities
... 5. Become extinct in that area What type of species overcome this more easily? ...
... 5. Become extinct in that area What type of species overcome this more easily? ...
Dynamics
... Contributions of Gleason • Major works published in mid 1920’s, but not acknowledged for 30 years because of the shadow of Clements • Contributed to development of non-equilibrium ecology • His work allowed for a much richer possibility of new and ...
... Contributions of Gleason • Major works published in mid 1920’s, but not acknowledged for 30 years because of the shadow of Clements • Contributed to development of non-equilibrium ecology • His work allowed for a much richer possibility of new and ...
Environmental Science
... When a farmer stops ______________________________________, grasses and weeds quickly grow and cover the abandoned land. Over time, ______________________________, such as perennial grasses, shrubs, and trees take over the area. Primary succession can occur on _______________________________________ ...
... When a farmer stops ______________________________________, grasses and weeds quickly grow and cover the abandoned land. Over time, ______________________________, such as perennial grasses, shrubs, and trees take over the area. Primary succession can occur on _______________________________________ ...
Lesson 1: Biodiversity TEK: 7.10 (A) (B) (10) Organisms and
... • How does biodiversity affect an ecosystem? • How does biodiversity support different varieties of organisms? Different environments support different organisms. • How do different ecosystems support different organisms? • What are some biotic components of an ecosystem? • What adaptations help org ...
... • How does biodiversity affect an ecosystem? • How does biodiversity support different varieties of organisms? Different environments support different organisms. • How do different ecosystems support different organisms? • What are some biotic components of an ecosystem? • What adaptations help org ...
Gateway Preparation Class: June 2, Thursday 1
... Bottom Line: Ecological changes refer to the growth or regrowth of species in an ecosystem over time. A common term associated with this concept is ecological succession. In ecological succession, the trend is an ecosystem moves from early stages where only pioneer species, such as small plants, mos ...
... Bottom Line: Ecological changes refer to the growth or regrowth of species in an ecosystem over time. A common term associated with this concept is ecological succession. In ecological succession, the trend is an ecosystem moves from early stages where only pioneer species, such as small plants, mos ...
Succession and Stability
... individual species can change substantially. – Stability depends on resolution an area is investigated at. ...
... individual species can change substantially. – Stability depends on resolution an area is investigated at. ...
Ecological Succession
... • Natural, gradual changes in the types of species that live in an area; can be primary or secondary • The gradual replacement of one plant community by another through natural processes over time ...
... • Natural, gradual changes in the types of species that live in an area; can be primary or secondary • The gradual replacement of one plant community by another through natural processes over time ...
TRADITIONAL SUCCESSION AND CLIMAX CONCEPTS
... 5. Biogenic mechanisms of succession refer to a sudden change in the biota which has a major influence on succession (e.g., introduction of a plant disease which removes a major plant species, introduction of an herbivore which significantly affects plant populations). 6. A sere is a sequence of pl ...
... 5. Biogenic mechanisms of succession refer to a sudden change in the biota which has a major influence on succession (e.g., introduction of a plant disease which removes a major plant species, introduction of an herbivore which significantly affects plant populations). 6. A sere is a sequence of pl ...
Chapter 3.1
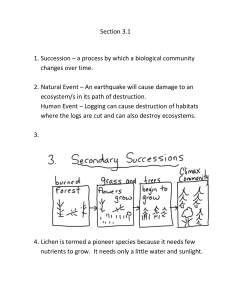
... 4. Lichen is termed a pioneer species because it needs few nutrients to grow. It needs only a little water and sunlight. ...
... 4. Lichen is termed a pioneer species because it needs few nutrients to grow. It needs only a little water and sunlight. ...
Ecological succession
Ecological succession is the observed process of change in the species structure of an ecological community over time. The time scale can be decades (for example, after a wildfire), or even millions of years after a mass extinction.The community begins with relatively few pioneering plants and animals and develops through increasing complexity until it becomes stable or self-perpetuating as a climax community. The ʺengineʺ of succession, the cause of ecosystem change, is the impact of established species upon their own environments. A consequence of living is the sometimes subtle and sometimes overt alteration of one's own environment.It is a phenomenon or process by which an ecological community undergoes more or less orderly and predictable changes following a disturbance or the initial colonization of a new habitat. Succession may be initiated either by formation of new, unoccupied habitat, such as from a lava flow or a severe landslide, or by some form of disturbance of a community, such as from a fire, severe windthrow, or logging. Succession that begins in new habitats, uninfluenced by pre-existing communities is called primary succession, whereas succession that follows disruption of a pre-existing community is called secondary succession.Succession was among the first theories advanced in ecology. The study of succession remains at the core of ecological science. Ecological succession was first documented in the Indiana Dunes of Northwest Indiana which led to efforts to preserve the Indiana Dunes. Exhibits on ecological succession are displayed in the Hour Glass, a museum in Ogden Dunes.