Lec 11 Galileo I Tel..
... Pre-1610 = phases required by Aristotelian cosmology Problem was to explain why they are not seen Post-1610 the phases contradict Aristotle-Ptolemy [A-P]. Huh? The problem: what are the sources of stellar illumination? Aristotle (all celestial bodies, except the moon) Scholastics (pseudo ...
... Pre-1610 = phases required by Aristotelian cosmology Problem was to explain why they are not seen Post-1610 the phases contradict Aristotle-Ptolemy [A-P]. Huh? The problem: what are the sources of stellar illumination? Aristotle (all celestial bodies, except the moon) Scholastics (pseudo ...
How a small scientific spark grew during the Renaissance
... strong lens, and one bigger less strong lens. This type of telescope was first used for seeing enemies from far away, but it was originally Dutch. With it, Galileo was able to see the four major moons of Jupiter (now called the Galilean Satellites in his honour, but he called them the “Medician Sart ...
... strong lens, and one bigger less strong lens. This type of telescope was first used for seeing enemies from far away, but it was originally Dutch. With it, Galileo was able to see the four major moons of Jupiter (now called the Galilean Satellites in his honour, but he called them the “Medician Sart ...
On Epistemology of the Celestial Realm
... 2.2 Breakdown of Scientific Method in Astronomy When the conventional scientific method is applied to astronomy, it is noticed that it does not aid one in constructing reliable theories mainly due to two reasons. Firstly, outer space observations usually consist of rare or one-time phenomena, which ...
... 2.2 Breakdown of Scientific Method in Astronomy When the conventional scientific method is applied to astronomy, it is noticed that it does not aid one in constructing reliable theories mainly due to two reasons. Firstly, outer space observations usually consist of rare or one-time phenomena, which ...
Astronomical Toolkit
... stars. Some appear bright and others very faint as seen from Earth. Some of the faint stars are intrinsically very bright, but are very distant. Some of the brightest stars in the sky are very faint stars that just happen to lie very close to us. When observing, we are forced to stay on Earth or nea ...
... stars. Some appear bright and others very faint as seen from Earth. Some of the faint stars are intrinsically very bright, but are very distant. Some of the brightest stars in the sky are very faint stars that just happen to lie very close to us. When observing, we are forced to stay on Earth or nea ...
the PDF - Vassar`s Special Collections
... or comet while noting the time of the night. The old Observatory, which now houses the Education Department, has an entryway filled with quotes by Maria Mitchell and photographs of her with her students. Orbit calculations were a routine part of Maria’s mathematical astronomy courses that were requi ...
... or comet while noting the time of the night. The old Observatory, which now houses the Education Department, has an entryway filled with quotes by Maria Mitchell and photographs of her with her students. Orbit calculations were a routine part of Maria’s mathematical astronomy courses that were requi ...
9 spectroscopic parallax
... We can measure apparent magnitude and spectral type. The main sequence lets us infer absolute magnitude from spectral type. Comparing apparent magnitude to absolute magnitude gives us distance. ...
... We can measure apparent magnitude and spectral type. The main sequence lets us infer absolute magnitude from spectral type. Comparing apparent magnitude to absolute magnitude gives us distance. ...
Chapter 2 - personal.kent.edu
... Earth is like the planets so the planets are like Earth Sun is a minor Star, so other planetary systems exist Implies humans not unique in God’s eyes Burned at the stake for heresy ...
... Earth is like the planets so the planets are like Earth Sun is a minor Star, so other planetary systems exist Implies humans not unique in God’s eyes Burned at the stake for heresy ...
Mar 2016 - Bays Mountain Park
... monster, Hera sent the Crab to distract him. Cancer grabbed onto ...
... monster, Hera sent the Crab to distract him. Cancer grabbed onto ...
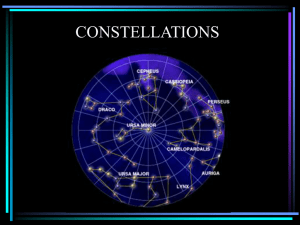
Constellations Overview
... The most famous of all the constellations are the 12 that make up the Zodiac. All planets can be observed only in these 12 constellations as they pass across the sky during the course of their year. This is because the orbits of all the planets lie within ± 8º of the ecliptic. The Sun also moves t ...
... The most famous of all the constellations are the 12 that make up the Zodiac. All planets can be observed only in these 12 constellations as they pass across the sky during the course of their year. This is because the orbits of all the planets lie within ± 8º of the ecliptic. The Sun also moves t ...
May 2017 - Bays Mountain Park
... events are held in Suffern, NY, just outside of New York City. They are both 2 day events. NEAIC has everything that an astro-imager dreams of. Presentations, workshops, vendors, and of course, door prizes. Best of all, you get to meet and talk to the authors of nearly every astro image you have droo ...
... events are held in Suffern, NY, just outside of New York City. They are both 2 day events. NEAIC has everything that an astro-imager dreams of. Presentations, workshops, vendors, and of course, door prizes. Best of all, you get to meet and talk to the authors of nearly every astro image you have droo ...
Here
... • Today, we rarely photograph spectra, but rather plot the intensity vs the wavelength. • The “lines” where there is relatively little light show up as dips in the curves. • These dips tell us about what elements are present in the star! ...
... • Today, we rarely photograph spectra, but rather plot the intensity vs the wavelength. • The “lines” where there is relatively little light show up as dips in the curves. • These dips tell us about what elements are present in the star! ...
What is a Star?
... • Different hemispheres also see different constellations because they see different parts of the sky based on their locations. ...
... • Different hemispheres also see different constellations because they see different parts of the sky based on their locations. ...
ASTR 1101-001 Spring 2008 - Louisiana State University
... • Astronomers determine the mass of a star by examining how strong the gravitational field is around that star. (Isaac Newton’s law of universal gravitation; §4-7) • By studying the motion of planets around our Sun, astronomers have determined that the Sun has a mass of 2 x 1030 kilograms. • We cann ...
... • Astronomers determine the mass of a star by examining how strong the gravitational field is around that star. (Isaac Newton’s law of universal gravitation; §4-7) • By studying the motion of planets around our Sun, astronomers have determined that the Sun has a mass of 2 x 1030 kilograms. • We cann ...
the candidate teachers` perception about basic astronomy concepts
... answers in the fashion that planets are spherical, however most of the candidates were unable to explain why a planet has a shape like that. Please find below an example of explanations by a candidate who asserted what he learned as the reason. A ...
... answers in the fashion that planets are spherical, however most of the candidates were unable to explain why a planet has a shape like that. Please find below an example of explanations by a candidate who asserted what he learned as the reason. A ...
Stellarium Astronomy Software
... projection quality. Star Theater 3.0 works best when it is located between one to six feet from the projection surface. If your ceiling is very high, place the planetarium on a shelf or create a raised platform by piling up books for example. Raise or lower the planetarium until the stars are in sha ...
... projection quality. Star Theater 3.0 works best when it is located between one to six feet from the projection surface. If your ceiling is very high, place the planetarium on a shelf or create a raised platform by piling up books for example. Raise or lower the planetarium until the stars are in sha ...
Lecture02: Astronomical Distance
... Astronomers use angular measure to describe the apparent size of a celestial object - what fraction of the sky that object seems to cover. If you draw lines from your eye to two edges of the Moon, the angle between the lines is the angular size of the Moon. ...
... Astronomers use angular measure to describe the apparent size of a celestial object - what fraction of the sky that object seems to cover. If you draw lines from your eye to two edges of the Moon, the angle between the lines is the angular size of the Moon. ...
NIE10x301Sponsor Thank You (Page 1)
... towards these catalogued “nebulosities” and discover many to have a generally circular, and often spiral-shaped, structure; they called these spiral nebulae, and presumed them objects within our own “island universe”. A famous example would be M51, nicknamed The Whirlpool Galaxy today, which was stu ...
... towards these catalogued “nebulosities” and discover many to have a generally circular, and often spiral-shaped, structure; they called these spiral nebulae, and presumed them objects within our own “island universe”. A famous example would be M51, nicknamed The Whirlpool Galaxy today, which was stu ...
Celestial Navigation in 60 min
... We found a mathematical relation between what we know (delta, GHA, h) and what we are looking for (latitude, longitude). With 2 observations, we get a system of 2 equations with 2 unknowns that we are able to solve. The celestial navigation problem is thus resolved. What? You don't like my equation ...
... We found a mathematical relation between what we know (delta, GHA, h) and what we are looking for (latitude, longitude). With 2 observations, we get a system of 2 equations with 2 unknowns that we are able to solve. The celestial navigation problem is thus resolved. What? You don't like my equation ...
The universe is composed mostly of
... classes. Excused absences will receive a bonus deduct of four points for the first absence and three points thereafter until a zero is attained. Students with additional excused absences will see no further reduction in points. To avoid penalty, pupils who receive an excused absence will be expected ...
... classes. Excused absences will receive a bonus deduct of four points for the first absence and three points thereafter until a zero is attained. Students with additional excused absences will see no further reduction in points. To avoid penalty, pupils who receive an excused absence will be expected ...
February 13
... Radiative zone – inner 71 percent of the Sun’s Interior were all atoms are ionized. Takes a photon 170,000 years to reach the convective zone. Each time a photon is absorbed ...
... Radiative zone – inner 71 percent of the Sun’s Interior were all atoms are ionized. Takes a photon 170,000 years to reach the convective zone. Each time a photon is absorbed ...
Discovering the Universe for Yourself
... What have we learned? • What does the universe look like from Earth? – We can see over 2000 stars and the Milky Way with our naked eyes, and each position on the sky belongs to one of 88 constellations. – We can specify the position of an object in the local sky by its altitude above the horizon ...
... What have we learned? • What does the universe look like from Earth? – We can see over 2000 stars and the Milky Way with our naked eyes, and each position on the sky belongs to one of 88 constellations. – We can specify the position of an object in the local sky by its altitude above the horizon ...
1B11 Foundations of Astronomy Star names and magnitudes
... • Parsec – One parsec is equivalent to 3.26 light years, or 3.1x1013 km. A star at a distance of 1 parsec has a parallax of 1 arcsecond. • Parallax – Nearby objects appear to move faster with respect to more distant objects as you go past them. This effect is called parallax and is used to measure t ...
... • Parsec – One parsec is equivalent to 3.26 light years, or 3.1x1013 km. A star at a distance of 1 parsec has a parallax of 1 arcsecond. • Parallax – Nearby objects appear to move faster with respect to more distant objects as you go past them. This effect is called parallax and is used to measure t ...
naap_motion1_sg
... Dragging the stick figure allows one to very conveniently change latitude. Dragging the stick figure on top of the subsolar point effectively puts the observer at the latitude where the direct rays of the sun are hitting. ...
... Dragging the stick figure allows one to very conveniently change latitude. Dragging the stick figure on top of the subsolar point effectively puts the observer at the latitude where the direct rays of the sun are hitting. ...
What We Know About Stars So Far
... waves – help us to create images of distant objects that cannot be seen. ...
... waves – help us to create images of distant objects that cannot be seen. ...
Chinese astronomy

Astronomy in China has a very long history, with historians indicating that the Chinese were the most persistent and accurate observers of celestial phenomena anywhere in the world before the Arabs. Star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the middle Shang Dynasty (Chinese Bronze Age), and the mansion (xiù:宿) system's nucleus seems to have taken shape by the time of the ruler Wu Ding (1339-1281 BC).Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BC) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered as it was on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those prevailing in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework.Some elements of Indian astronomy reached China with the expansion of Buddhism after the Eastern Han Dynasty (25–220 AD), but the most detailed incorporation of Indian astronomical thought occurred during the Tang Dynasty (618-907), when numerous Indian astronomers took up residence in the Chinese capital, and Chinese scholars, such as the great Tantric Buddhist monk and mathematician Yi Xing, mastered its system. Islamic astronomers collaborated closely with their Chinese colleagues during the Yuan Dynasty, and, after a period of relative decline during the Ming Dynasty, astronomy was revitalized under the stimulus of Western cosmology and technology after the Jesuits established their missions. The telescope was introduced in the seventeenth century. In 1669, the Peking observatory was completely redesigned and refitted under the direction of Ferdinand Verbiest. Today, China continues to be active in astronomy, with many observatories and its own space program.