BAS Visit to the Norman Lockyer Observatory, October 2015
... Omicron Ceti, better known as Mira in the constellation Cetus, is a binary star consisting of a red giant and a companion star. The system is approximately 400 light years distant. See page 13 for star map and location. Mira A, a red giant belonging to the spectral type M7 IIIe, is an oscillating va ...
... Omicron Ceti, better known as Mira in the constellation Cetus, is a binary star consisting of a red giant and a companion star. The system is approximately 400 light years distant. See page 13 for star map and location. Mira A, a red giant belonging to the spectral type M7 IIIe, is an oscillating va ...
Option_E_Astrophysics_
... doesn’t really tell us anything about the star itself! We’d really like to know things that are intrinsic properties of the star like: ...
... doesn’t really tell us anything about the star itself! We’d really like to know things that are intrinsic properties of the star like: ...
What do “yellowballs” have to do with the birth of new stars?
... Using a different combination of infrared colors, the yellowballs would not pop out. Ideally, astronomers want to look at as many different colors of light as they can, but the reality is they can not build instruments that do everything. Before building astronomical instruments, scientists need to ...
... Using a different combination of infrared colors, the yellowballs would not pop out. Ideally, astronomers want to look at as many different colors of light as they can, but the reality is they can not build instruments that do everything. Before building astronomical instruments, scientists need to ...
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Lab - Introduction to Astronomy
... This course meets the lab portion of the lab/science general studies requirement for graduation when taken with the lecture (AST 101). This course is provided for students who cannot take lab and lecture during the same semester. The combination of AST 101-102 is equivalent to AST 103. Description I ...
... This course meets the lab portion of the lab/science general studies requirement for graduation when taken with the lecture (AST 101). This course is provided for students who cannot take lab and lecture during the same semester. The combination of AST 101-102 is equivalent to AST 103. Description I ...
rotation of the Earth
... commonly trace out creatures or characters from myths and legends (sometimes using what must be a very active imagination!). Today our stellar atlases divide the sky into distinct regions – some small, some large – so that every star is mapped to one of 88 constellations which are based on, but refi ...
... commonly trace out creatures or characters from myths and legends (sometimes using what must be a very active imagination!). Today our stellar atlases divide the sky into distinct regions – some small, some large – so that every star is mapped to one of 88 constellations which are based on, but refi ...
Star Maps - Astronomy Outreach - The University of Texas at Austin
... The star maps show the position of the zenith, the point overhead. The objects near the zenith will change over time and thus zenith is not shown on star wheels or planispheres. Star maps often show the positions of planets since they are designed for one month's use. Star wheels and planisphere ...
... The star maps show the position of the zenith, the point overhead. The objects near the zenith will change over time and thus zenith is not shown on star wheels or planispheres. Star maps often show the positions of planets since they are designed for one month's use. Star wheels and planisphere ...
o - Salem State University
... 1.Let's say we find a star that is located on the following points or circles in the sky. Then, on the same night we move to a location on Earth that is some significant distance from our first location. There will now be a different star at or on: a. the celestial north pole b. the zenith c. the ce ...
... 1.Let's say we find a star that is located on the following points or circles in the sky. Then, on the same night we move to a location on Earth that is some significant distance from our first location. There will now be a different star at or on: a. the celestial north pole b. the zenith c. the ce ...
Astronomical Distance Ladder
... approximation can be use to determine the distance between the sun and the star. d=206265”/” A.U. ...
... approximation can be use to determine the distance between the sun and the star. d=206265”/” A.U. ...
Famous Constellations
... Orion, the Hunter, famous constellation named from Greek Mythology It is most easily recognized constellation https://img1.etsystatic.com/009/1/5742776/il_570xN.411934929_a84j.jpg Ursa Major is also famous and very important because it points to North Star Ursa Major means Big Bear in Latin http://3 ...
... Orion, the Hunter, famous constellation named from Greek Mythology It is most easily recognized constellation https://img1.etsystatic.com/009/1/5742776/il_570xN.411934929_a84j.jpg Ursa Major is also famous and very important because it points to North Star Ursa Major means Big Bear in Latin http://3 ...
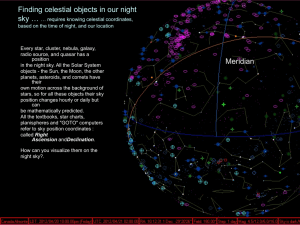
Local Horizon View
... Meridian is the important North/South line through your zenith and also through both celestial poles. We look at our celestial objects while we are oriented along our North/South meridian ...
... Meridian is the important North/South line through your zenith and also through both celestial poles. We look at our celestial objects while we are oriented along our North/South meridian ...
Regulus, June-July 1990 - RASC Kingston Centre
... discovery. It was fairly difficult in the 20 cm at 63X, at first, and I had to use averted vision, but later I saw it more easily. More recently, on 03-09, I found this supernova much more difficult under similar conditions and could, in fact, scarcely see it at all. I had to conclude that it was fa ...
... discovery. It was fairly difficult in the 20 cm at 63X, at first, and I had to use averted vision, but later I saw it more easily. More recently, on 03-09, I found this supernova much more difficult under similar conditions and could, in fact, scarcely see it at all. I had to conclude that it was fa ...
www.aavso.org
... are devices with an array of picture elements called pixels. A typical CCD camera can have tens of thousands to millions of pixels. The accumulated charge in each pixel from photons falling on is measured. CCDs are very sensitive, respond to light over a wide range of wavelengths and can measure man ...
... are devices with an array of picture elements called pixels. A typical CCD camera can have tens of thousands to millions of pixels. The accumulated charge in each pixel from photons falling on is measured. CCDs are very sensitive, respond to light over a wide range of wavelengths and can measure man ...
Using Star Charts
... the north to an angle of 44o. Imagine yourself at the centre of the cylinder looking up at it. A horizontal plane through your position marks the horizon where it cuts the chart. During the night the chart rotates around its axis, causing some stars to rise and some to set. If the positions of the p ...
... the north to an angle of 44o. Imagine yourself at the centre of the cylinder looking up at it. A horizontal plane through your position marks the horizon where it cuts the chart. During the night the chart rotates around its axis, causing some stars to rise and some to set. If the positions of the p ...
Lecture 1 - Simon P Driver
... – RA overhead on 1st Feb is ~8.5h (2hr per month so ~0.5hr per week) – Object therefore overhead on 1st Feb at half past midnight • Rises 3.6hrs earlier = 8.9pm or 8:54pm • Sets 3.6hrs later ...
... – RA overhead on 1st Feb is ~8.5h (2hr per month so ~0.5hr per week) – Object therefore overhead on 1st Feb at half past midnight • Rises 3.6hrs earlier = 8.9pm or 8:54pm • Sets 3.6hrs later ...
Abrams Planetarium Galileo & the Telescope—Sept 12 • Sky preview 2008-2009
... Nearly full only Crescent and nearly full ...
... Nearly full only Crescent and nearly full ...
Navigating the Night Sky – Teacher Guide Argos Online Subject
... o Do the constellations near the horizon on the star map look like the constellations in the sky? If not, how do they look different? -If you are using the star maps in Stardate Magazine, the answer is obviously No. If you are using the star maps from Starmaps.com, the distortion isn’t as obvious, b ...
... o Do the constellations near the horizon on the star map look like the constellations in the sky? If not, how do they look different? -If you are using the star maps in Stardate Magazine, the answer is obviously No. If you are using the star maps from Starmaps.com, the distortion isn’t as obvious, b ...
Chinese astronomy

Astronomy in China has a very long history, with historians indicating that the Chinese were the most persistent and accurate observers of celestial phenomena anywhere in the world before the Arabs. Star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the middle Shang Dynasty (Chinese Bronze Age), and the mansion (xiù:宿) system's nucleus seems to have taken shape by the time of the ruler Wu Ding (1339-1281 BC).Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BC) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered as it was on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those prevailing in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework.Some elements of Indian astronomy reached China with the expansion of Buddhism after the Eastern Han Dynasty (25–220 AD), but the most detailed incorporation of Indian astronomical thought occurred during the Tang Dynasty (618-907), when numerous Indian astronomers took up residence in the Chinese capital, and Chinese scholars, such as the great Tantric Buddhist monk and mathematician Yi Xing, mastered its system. Islamic astronomers collaborated closely with their Chinese colleagues during the Yuan Dynasty, and, after a period of relative decline during the Ming Dynasty, astronomy was revitalized under the stimulus of Western cosmology and technology after the Jesuits established their missions. The telescope was introduced in the seventeenth century. In 1669, the Peking observatory was completely redesigned and refitted under the direction of Ferdinand Verbiest. Today, China continues to be active in astronomy, with many observatories and its own space program.