Key concepts
... -understand the differences between the 3 states of matter, particularly for water -know what salinity is -know the sources of the salts dissolved in the ocean (weathering of surface rocks and outgassing) -Understand Forschammer’s Principle or the Principle of constant proportions -know what the mai ...
... -understand the differences between the 3 states of matter, particularly for water -know what salinity is -know the sources of the salts dissolved in the ocean (weathering of surface rocks and outgassing) -Understand Forschammer’s Principle or the Principle of constant proportions -know what the mai ...
Chapter 16
... prevention and response. C. Toxic pollutants can contaminate seafood. 1. Mercury is a toxic heavy metal emitted from coal combustion, mine tailings, and other sources. 2. After settling onto land and water, mercury bioaccumulates in animals’ tissues and biomagnifies as it makes its way up the food c ...
... prevention and response. C. Toxic pollutants can contaminate seafood. 1. Mercury is a toxic heavy metal emitted from coal combustion, mine tailings, and other sources. 2. After settling onto land and water, mercury bioaccumulates in animals’ tissues and biomagnifies as it makes its way up the food c ...
2nd Nine Weeks Review Science
... When the Earth, Moon and Sun line up as in the picture above, the area of the oceans shown by the star experience high tides low tides no tides tsunamis ...
... When the Earth, Moon and Sun line up as in the picture above, the area of the oceans shown by the star experience high tides low tides no tides tsunamis ...
Continental Drift
... • The north magnetic pole had clearly wandered over time. • More surprisingly, the path it seemed to have followed was different in Europe than in North America. • The two paths could be turned into one consistent path, but only by slowly closing the Atlantic Ocean as older and older rocks were comp ...
... • The north magnetic pole had clearly wandered over time. • More surprisingly, the path it seemed to have followed was different in Europe than in North America. • The two paths could be turned into one consistent path, but only by slowly closing the Atlantic Ocean as older and older rocks were comp ...
Methodology Study area Results Introduction Conclusion Abstract
... control them. The enhanced biogenic flux at SBBT during summer monsoon could be explained with the help of bottom-up control wherein the physical processes controlled chlorophyll biomass through nutrient supply. The mismatch between the lack of seasonality of biogenic flux at EIOT and seasonality in ...
... control them. The enhanced biogenic flux at SBBT during summer monsoon could be explained with the help of bottom-up control wherein the physical processes controlled chlorophyll biomass through nutrient supply. The mismatch between the lack of seasonality of biogenic flux at EIOT and seasonality in ...
Geological Features
... There are many steep-sided canyons and deep, narrow valleys in the bottom of the ocean. Ocean trenches are the deepest part of the ocean basin and are deeper than any valley found on land. Ocean basin Located on either side of the mid-ocean ridge is the ocean basin. It is made up of low hill ...
... There are many steep-sided canyons and deep, narrow valleys in the bottom of the ocean. Ocean trenches are the deepest part of the ocean basin and are deeper than any valley found on land. Ocean basin Located on either side of the mid-ocean ridge is the ocean basin. It is made up of low hill ...
AllanRP_DEEPC_Reading_2013
... • Previously highlighted “missing energy” explained by ocean heat content uncertainty combined with inappropriate net radiation satellite products • Heating of Earth continues at rate of ~0.5 Wm-2 – Negative radiative forcing does not appear to contribute strongly ...
... • Previously highlighted “missing energy” explained by ocean heat content uncertainty combined with inappropriate net radiation satellite products • Heating of Earth continues at rate of ~0.5 Wm-2 – Negative radiative forcing does not appear to contribute strongly ...
Mountain Belts formed at Divergent and Convergent Boundaries
... landmasses and are caused by convective upwelling of mantle beneath weak ...
... landmasses and are caused by convective upwelling of mantle beneath weak ...
The Oceans and Climate
... giant flywheel to the climate system, moderating change but prolonging it once change commences. The ocean also stores vast amounts of carbón dioxide. In 1897 Svante Arrhenius discovered that the amount of carbón dioxide in the atmosphere affected the global temperature through the greenhouse effect ...
... giant flywheel to the climate system, moderating change but prolonging it once change commences. The ocean also stores vast amounts of carbón dioxide. In 1897 Svante Arrhenius discovered that the amount of carbón dioxide in the atmosphere affected the global temperature through the greenhouse effect ...
The Most Effective Antacid - California State Science Fair
... However, we were wrong and we chose Zantac to be the fastest because it had the quickest drop in pH and took the least amount of acid to have a change of 2 in the pH levels. Conclusions/Discussion This concept is not only applied towards the use of antacids to help reduce the pain in the stomach due ...
... However, we were wrong and we chose Zantac to be the fastest because it had the quickest drop in pH and took the least amount of acid to have a change of 2 in the pH levels. Conclusions/Discussion This concept is not only applied towards the use of antacids to help reduce the pain in the stomach due ...
DECISION Disclaimer Posted as adopted subject to copy
... acidification, oxygen loss, dust inputs) on e.g., productivity, species distribution and exclusion, habitat compression, food webs ...
... acidification, oxygen loss, dust inputs) on e.g., productivity, species distribution and exclusion, habitat compression, food webs ...
A Pacific Ocean Legacy Embracing Tradition
... legacy: the protection of 4 million square kilometers (1,544,400 square miles) of ocean waters by 2016 through the establishment of large, highly protected marine reserves. Around the world, Global Ocean Legacy works with local communities and indigenous peoples, fishermen, scientists, governments, ...
... legacy: the protection of 4 million square kilometers (1,544,400 square miles) of ocean waters by 2016 through the establishment of large, highly protected marine reserves. Around the world, Global Ocean Legacy works with local communities and indigenous peoples, fishermen, scientists, governments, ...
Biogeochemical Cycles
... COMMONALITIES AMONG THE CYCLES: >exist in the hydro-, litho-, biosphere, & sometimes the atmosphere >there are “pools” or reservoirs >they are changed chemically or biochemically >there are “fluxes”, or movement between pools >transformations (changes) are important & can lead to positive or negativ ...
... COMMONALITIES AMONG THE CYCLES: >exist in the hydro-, litho-, biosphere, & sometimes the atmosphere >there are “pools” or reservoirs >they are changed chemically or biochemically >there are “fluxes”, or movement between pools >transformations (changes) are important & can lead to positive or negativ ...
Chapter 3: Marine Provinces
... Continental margins Passive or active Passive (Atlantic-type) Not close to any plate boundary No major tectonic activity ...
... Continental margins Passive or active Passive (Atlantic-type) Not close to any plate boundary No major tectonic activity ...
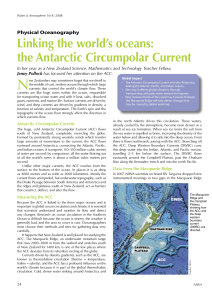
Linking the world`s oceans: the Antarctic Circumpolar Current
... My home is in Nelson so I have spent the year going between the NIWA campuses in Nelson and Wellington where Mike is based. The year has been varied and interesting and has included attending lectures given by Mike and Lionel Carter, formerly at NIWA and now a professor at Victoria University, and d ...
... My home is in Nelson so I have spent the year going between the NIWA campuses in Nelson and Wellington where Mike is based. The year has been varied and interesting and has included attending lectures given by Mike and Lionel Carter, formerly at NIWA and now a professor at Victoria University, and d ...
Document
... Alfred Wegener, a German who was educated as a meteorologist and geologist, was one of the first scientists to theorize about tectonic plates. Wegener suggested that past continents had drifted apart over time to form the present continents. This rearrangement of continents is known as continental d ...
... Alfred Wegener, a German who was educated as a meteorologist and geologist, was one of the first scientists to theorize about tectonic plates. Wegener suggested that past continents had drifted apart over time to form the present continents. This rearrangement of continents is known as continental d ...
An International GEOTRACES study
... This PhD project will use novel Si and N stable isotope measurements of dissolved silicic acid and nitrate to understand silicic acid and nitrate cycling in the Arctic Ocean and processes that govern nutrient exchange to the Atlantic Ocean. Project background The Arctic is currently the most rapidly ...
... This PhD project will use novel Si and N stable isotope measurements of dissolved silicic acid and nitrate to understand silicic acid and nitrate cycling in the Arctic Ocean and processes that govern nutrient exchange to the Atlantic Ocean. Project background The Arctic is currently the most rapidly ...
Let`s Review
... Take notes on the 3 types Erosion (Characteristics of each) What type of erosion is most likely to occur here in the greater Houston area? ...
... Take notes on the 3 types Erosion (Characteristics of each) What type of erosion is most likely to occur here in the greater Houston area? ...
Message from the OCCI Director Terry Joyce
... This project combines elements of geology, chemistry and physics, and is probably the most interdisciplinary project presently supported by the OCCI. Scott Doney has been an OCCI Fellow for the past three years. His report deals with an important aspect of biology and climate change due to gradual a ...
... This project combines elements of geology, chemistry and physics, and is probably the most interdisciplinary project presently supported by the OCCI. Scott Doney has been an OCCI Fellow for the past three years. His report deals with an important aspect of biology and climate change due to gradual a ...
Ocean Bottom - PAMS-Doyle
... Plant and animal life in the ocean is affect by three factors: amount of sunlight, temperature, and pressure Plants and animals can be classified into three major groups according to their habitats of the water in which they live ...
... Plant and animal life in the ocean is affect by three factors: amount of sunlight, temperature, and pressure Plants and animals can be classified into three major groups according to their habitats of the water in which they live ...
F2007_311_summary_V
... Connection between CO2 levels and climate – CO2 higher -> higher surface temp. There are also positive feedbacks (higher surface temp -> more wv evaporating -> more GH effect -> even higher temp). CO2 concentrations would need to have been a lot higher than today – maybe even 1000x higher. What regu ...
... Connection between CO2 levels and climate – CO2 higher -> higher surface temp. There are also positive feedbacks (higher surface temp -> more wv evaporating -> more GH effect -> even higher temp). CO2 concentrations would need to have been a lot higher than today – maybe even 1000x higher. What regu ...
Worksheet 2
... 4. Rock samples taken neat ocean ridges are older than rock samples taken near deep sea trenches 5. The thickness of ocean floor sediments decreases with distance from an ocean ridge ...
... 4. Rock samples taken neat ocean ridges are older than rock samples taken near deep sea trenches 5. The thickness of ocean floor sediments decreases with distance from an ocean ridge ...
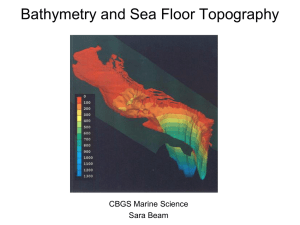
Bathymetry
... trench is easily seen here This is an area of intense subduction where the Nazca plate is being detroyed and is pushing up the Andes mountains in the process. Note the very narrow continental shelf at the active coastal margin, wide shelf at passive margin ...
... trench is easily seen here This is an area of intense subduction where the Nazca plate is being detroyed and is pushing up the Andes mountains in the process. Note the very narrow continental shelf at the active coastal margin, wide shelf at passive margin ...
Ocean acidification

Ocean acidification is the ongoing decrease in the pH of the Earth's oceans, caused by the uptake of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. An estimated 30–40% of the carbon dioxide from human activity released into the atmosphere dissolves into oceans, rivers and lakes. To achieve chemical equilibrium, some of it reacts with the water to form carbonic acid. Some of these extra carbonic acid molecules react with a water molecule to give a bicarbonate ion and a hydronium ion, thus increasing ocean acidity (H+ ion concentration). Between 1751 and 1994 surface ocean pH is estimated to have decreased from approximately 8.25 to 8.14, representing an increase of almost 30% in H+ ion concentration in the world's oceans. Since current and projected ocean pH levels are above 7.0, the oceans are technically alkaline now and will remain so; referring to this effect as ""decreasing ocean alkalinity"" would be equally correct if less politically useful. Earth System Models project that within the last decade ocean acidity exceeded historical analogs and in combination with other ocean biogeochemical changes could undermine the functioning of marine ecosystems and disrupt the provision of many goods and services associated with the ocean.Increasing acidity is thought to have a range of possibly harmful consequences, such as depressing metabolic rates and immune responses in some organisms, and causing coral bleaching. This also causes decreasing oxygen levels as it kills off algae.Other chemical reactions are triggered which result in a net decrease in the amount of carbonate ions available. This makes it more difficult for marine calcifying organisms, such as coral and some plankton, to form biogenic calcium carbonate, and such structures become vulnerable to dissolution. Ongoing acidification of the oceans threatens food chains connected with the oceans. As members of the InterAcademy Panel, 105 science academies have issued a statement on ocean acidification recommending that by 2050, global CO2 emissions be reduced by at least 50% compared to the 1990 level.Ocean acidification has been called the ""evil twin of global warming"" and ""the other CO2 problem"".Ocean acidification has occurred previously in Earth's history. The most notable example is the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which occurred approximately 56 million years ago. For reasons that are currently uncertain, massive amounts of carbon entered the ocean and atmosphere, and led to the dissolution of carbonate sediments in all ocean basins.