m5zn_307118e6dc84400
... Examples 1. All cations are Lewis acids since they are able to accept electrons. (e.g., Cu2+, Fe2+ ) 2. An atom, ion, or molecule with an incomplete octet of electrons can act as an Lewis acid (e.g., BF3, AlF3). 3. Molecules that have multiple bonds between two atoms of different electronegativities ...
... Examples 1. All cations are Lewis acids since they are able to accept electrons. (e.g., Cu2+, Fe2+ ) 2. An atom, ion, or molecule with an incomplete octet of electrons can act as an Lewis acid (e.g., BF3, AlF3). 3. Molecules that have multiple bonds between two atoms of different electronegativities ...
No Slide Title
... The charge the atom would have in a molecule (or an ionic compound) if electrons were completely transferred. 1. Free elements (uncombined state) have an oxidation number of zero. ...
... The charge the atom would have in a molecule (or an ionic compound) if electrons were completely transferred. 1. Free elements (uncombined state) have an oxidation number of zero. ...
final exam review chapter 1-4
... 5. If you have 4 g NaOH, and 10 g HBr, what is the limiting reagent and how much salt is produced? In lab if you produce1 g salt, what is the percent yield? ...
... 5. If you have 4 g NaOH, and 10 g HBr, what is the limiting reagent and how much salt is produced? In lab if you produce1 g salt, what is the percent yield? ...
What are reactions? - UTLNET Secure Site
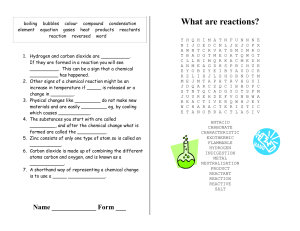
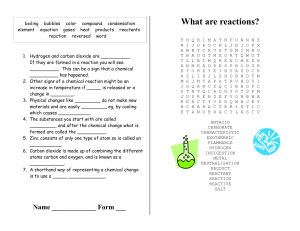
... If they are formed in a reaction you will see __________. This can be a sign that a chemical __________ has happened. 2. Other signs of a chemical reaction might be an increase in temperature if _____ is released or a change in ________. 3. Physical changes like _________ do not make new materials a ...
... If they are formed in a reaction you will see __________. This can be a sign that a chemical __________ has happened. 2. Other signs of a chemical reaction might be an increase in temperature if _____ is released or a change in ________. 3. Physical changes like _________ do not make new materials a ...
What are reactions?
... If they are formed in a reaction you will see __________. This can be a sign that a chemical __________ has happened. 2. Other signs of a chemical reaction might be an increase in temperature if _____ is released or a change in ________. 3. Physical changes like _________ do not make new materials a ...
... If they are formed in a reaction you will see __________. This can be a sign that a chemical __________ has happened. 2. Other signs of a chemical reaction might be an increase in temperature if _____ is released or a change in ________. 3. Physical changes like _________ do not make new materials a ...
Acid and Bases: Alkalinity and pH in Natural Waters.
... acid is strong when its propensity to release protons is high, and weak conversely. Acids that completely dissociate in water are therefore strong acids, e.g., HClO4, HCl, HNO3, and acids that do not have a strong propensity to release protons are therefore weak, e.g. Acetic Acid (Ethanoic: CH3COOH) ...
... acid is strong when its propensity to release protons is high, and weak conversely. Acids that completely dissociate in water are therefore strong acids, e.g., HClO4, HCl, HNO3, and acids that do not have a strong propensity to release protons are therefore weak, e.g. Acetic Acid (Ethanoic: CH3COOH) ...
semester two final review key units 5 and 6 only
... Bases: ionic compounds that break apart to form a negatively charged hydroxide ion (OH-) in water Neutral: A solution that has a pH of 7. It is neither acidic nor basic Amphoteric: a substance that can act as an acid or base under various conditions pH scale: a measure of the strength of acidity or ...
... Bases: ionic compounds that break apart to form a negatively charged hydroxide ion (OH-) in water Neutral: A solution that has a pH of 7. It is neither acidic nor basic Amphoteric: a substance that can act as an acid or base under various conditions pH scale: a measure of the strength of acidity or ...
Microbiology: A Systems Approach
... Proteins take on a variety of shapes due to extensive folding of the molecule. This enable them to perform specific functions and interactions with other molecules. ...
... Proteins take on a variety of shapes due to extensive folding of the molecule. This enable them to perform specific functions and interactions with other molecules. ...
CHEM 2218 Inorganic Chemistry I (Final Exam sample paper)
... Consider the C-H σ bond stretching normal modes in benzene. (10 points) (a) How many such vibration modes does the molecule have? (b) Please draw all the stretching normal modes. (c) Give the symmetry labels to all the normal modes you draw in (b). (d) Point out which are IR active and which are Ram ...
... Consider the C-H σ bond stretching normal modes in benzene. (10 points) (a) How many such vibration modes does the molecule have? (b) Please draw all the stretching normal modes. (c) Give the symmetry labels to all the normal modes you draw in (b). (d) Point out which are IR active and which are Ram ...
TYPES OF SOLUTION CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... a. endpoint- the point (volume of standard) at which the unknown changes color b. equivalence point--# moles of standard solution = # moles of unknown solution. c. standardize- titration the unknown solution with the standard of known concentration. Exercise 14 A student carries out an experiment to ...
... a. endpoint- the point (volume of standard) at which the unknown changes color b. equivalence point--# moles of standard solution = # moles of unknown solution. c. standardize- titration the unknown solution with the standard of known concentration. Exercise 14 A student carries out an experiment to ...
The acidic environment – Acids
... A concentrated solution contains a large amount of solute in a given amount of solution. A 10 mol L-1 solution would be called concentrated. A dilute solution contains a small amount of solute in a given amount of solution. A 0.01 mol L-1 solution would be called dilute. Strong acids essentially com ...
... A concentrated solution contains a large amount of solute in a given amount of solution. A 10 mol L-1 solution would be called concentrated. A dilute solution contains a small amount of solute in a given amount of solution. A 0.01 mol L-1 solution would be called dilute. Strong acids essentially com ...
Atoms, molecules and ions
... • For an oxyacid (general formula HmXOn) it often happens that there are multiple possible values of n for each element X, and as such, within this series of compounds, – There is always an acid in the series that ends with “ic” • Adding another oxygen to the “ic” acid produces the “per….ic” acid • ...
... • For an oxyacid (general formula HmXOn) it often happens that there are multiple possible values of n for each element X, and as such, within this series of compounds, – There is always an acid in the series that ends with “ic” • Adding another oxygen to the “ic” acid produces the “per….ic” acid • ...
Acids and Bases
... The stronger the acid, the weaker the conjugate base The stronger the base, the weaker the conjugate acid ...
... The stronger the acid, the weaker the conjugate base The stronger the base, the weaker the conjugate acid ...
Chapter 4 - Aqueous Reactions
... Lead (Pb) is above H, so is Al. But these metals are not attacked by 6M HCl. They form very protective oxides. Cu reacts with nitric acid (HNO3) because that acid is a strong oxidizing agent in addition to being an acid. Gold (Au) and platinum (Pt) are valuable because they are (a) rare and (b) ...
... Lead (Pb) is above H, so is Al. But these metals are not attacked by 6M HCl. They form very protective oxides. Cu reacts with nitric acid (HNO3) because that acid is a strong oxidizing agent in addition to being an acid. Gold (Au) and platinum (Pt) are valuable because they are (a) rare and (b) ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... 9. How do positive and negative ions form? Positive ions form when an atom loses an electron, negative ions form when an atom gains an electron 10. In the equation,(REACTANT) P4 + O2 P2O3 (PRODUCT) , if there are 20 g of P4 and 15 g of O2, how many grams of P2O3 will form? 35g 11. How many atoms o ...
... 9. How do positive and negative ions form? Positive ions form when an atom loses an electron, negative ions form when an atom gains an electron 10. In the equation,(REACTANT) P4 + O2 P2O3 (PRODUCT) , if there are 20 g of P4 and 15 g of O2, how many grams of P2O3 will form? 35g 11. How many atoms o ...
Chapter 4
... An electrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved in water, results in a solution that can conduct electricity. A nonelectrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved, results in a solution that does not conduct electricity. ...
... An electrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved in water, results in a solution that can conduct electricity. A nonelectrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved, results in a solution that does not conduct electricity. ...
Acid
An acid (from the Latin acidus/acēre meaning sour) is a chemical substance whose aqueous solutions are characterized by a sour taste, the ability to turn blue litmus red, and the ability to react with bases and certain metals (like calcium) to form salts. Aqueous solutions of acids have a pH of less than 7. Non-aqueous acids are usually formed when an anion (negative ion) reacts with one or more positively charged hydrogen cations. A lower pH means a higher acidity, and thus a higher concentration of positive hydrogen ions in the solution. Chemicals or substances having the property of an acid are said to be acidic.There are three common definitions for acids: the Arrhenius definition, the Brønsted-Lowry definition, and the Lewis definition. The Arrhenius definition defines acids as substances which increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), or more accurately, hydronium ions (H3O+), when dissolved in water. The Brønsted-Lowry definition is an expansion: an acid is a substance which can act as a proton donor. By this definition, any compound which can easily be deprotonated can be considered an acid. Examples include alcohols and amines which contain O-H or N-H fragments. A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. Examples of Lewis acids include all metal cations, and electron-deficient molecules such as boron trifluoride and aluminium trichloride.Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (a solution of hydrogen chloride which is found in gastric acid in the stomach and activates digestive enzymes), acetic acid (vinegar is a dilute solution of this liquid), sulfuric acid (used in car batteries), and tartaric acid (a solid used in baking). As these examples show, acids can be solutions or pure substances, and can be derived from solids, liquids, or gases. Strong acids and some concentrated weak acids are corrosive, but there are exceptions such as carboranes and boric acid.