The concept of pH and pKa
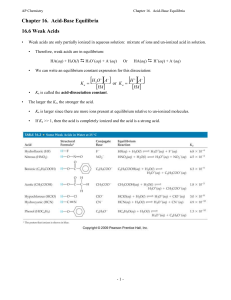
... • An acid (often represented by the generic formula HA [H+A-]) any chemical compound that, when dissolved in water, gives a solution with a hydrogen ion activity greater than in pure water (a pH less than 7.0) • an acid as a compound which donates a hydrogen ion (H+) to another compound (called a ...
... • An acid (often represented by the generic formula HA [H+A-]) any chemical compound that, when dissolved in water, gives a solution with a hydrogen ion activity greater than in pure water (a pH less than 7.0) • an acid as a compound which donates a hydrogen ion (H+) to another compound (called a ...
6.5 Main Group
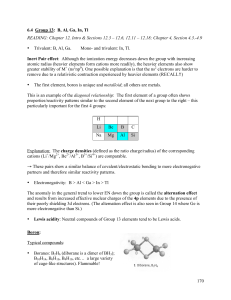
... Amphoterism and Isopolyoxo Ions Amphoterism: Being able to do two opposite things at the same time. In chemistry: Acid/Base amphoterism, Redox amphoterism ...
... Amphoterism and Isopolyoxo Ions Amphoterism: Being able to do two opposite things at the same time. In chemistry: Acid/Base amphoterism, Redox amphoterism ...
acids and bases - sukgr11chemistry
... Introduction of the topic Acids and bases are chemical compounds that have distinctive properties in water solution. The sour taste of a lemon, lime, or grapefruit, for example, is caused by citric acid. The slippery feel of ammonia, a common base, is characteristic of all bases. Bases tend to tast ...
... Introduction of the topic Acids and bases are chemical compounds that have distinctive properties in water solution. The sour taste of a lemon, lime, or grapefruit, for example, is caused by citric acid. The slippery feel of ammonia, a common base, is characteristic of all bases. Bases tend to tast ...
Document
... An electrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved in water, results in a solution that can conduct electricity. A nonelectrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved, results in a solution that does not conduct electricity. ...
... An electrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved in water, results in a solution that can conduct electricity. A nonelectrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved, results in a solution that does not conduct electricity. ...
Chapter 4 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry Chemical Reactions in
... <<100% ionization in water = weak base Most common weak bases: NH3 and amines Reaction of Acids with Bases: Neutralization neutralization reaction: the reaction of ionizable H+ ions on acid molecules with OH1- or other anions (such as HCO3 1- or CO3 2-) on base “molecules” Example. We represent an a ...
... <<100% ionization in water = weak base Most common weak bases: NH3 and amines Reaction of Acids with Bases: Neutralization neutralization reaction: the reaction of ionizable H+ ions on acid molecules with OH1- or other anions (such as HCO3 1- or CO3 2-) on base “molecules” Example. We represent an a ...
Slide 1
... Acidic proton on a hydroxyl group bonded or coordinated to a central atom on which there is an oxo (=O) group ...
... Acidic proton on a hydroxyl group bonded or coordinated to a central atom on which there is an oxo (=O) group ...
Chemical Reactions
... Calculate Molarity. Calculate molality. Calculate % by mass Calculate changes in freezing point and boiling point Calculate the solute and solvent necessary for a dilution Calculate the volume necessary to neutralize an acid/base ...
... Calculate Molarity. Calculate molality. Calculate % by mass Calculate changes in freezing point and boiling point Calculate the solute and solvent necessary for a dilution Calculate the volume necessary to neutralize an acid/base ...
Dr. Arrington Exam 3
... (c) pH is determined in three ways during a titration: (i) pH calculated from the excess concentration of H+ or OH− in solution. (ii) pH calculated from the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation (buffer equation) (iii) pH calculated from a weak acid or weak base equilibrium calculation. Place the calculati ...
... (c) pH is determined in three ways during a titration: (i) pH calculated from the excess concentration of H+ or OH− in solution. (ii) pH calculated from the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation (buffer equation) (iii) pH calculated from a weak acid or weak base equilibrium calculation. Place the calculati ...
Acids and Bases - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Finding [OH-] in Acids and [H+] in Bases Remember Kw from the previous section? Now we learn why it is important. When we need to determine ion concentrations of an acid, you should immediately realize you will be finding the concentration of hydrogen ion (H+) and some anion (Cl- and C2H3O2- in our ...
... Finding [OH-] in Acids and [H+] in Bases Remember Kw from the previous section? Now we learn why it is important. When we need to determine ion concentrations of an acid, you should immediately realize you will be finding the concentration of hydrogen ion (H+) and some anion (Cl- and C2H3O2- in our ...
Ka or Kb - RangerCalculus
... EQUILIBRIUM REVIEW #2 (Ka/Kb) Ka or Kb Here are some things in common with most Ka/Kb problems. 1. Many of them will ask for you to determine pH or pOH. To do this, you obviously need to know [H+] or [OH-]. If you have a strong acid or strong base, you can determine [H+] or [OH-] directly from the a ...
... EQUILIBRIUM REVIEW #2 (Ka/Kb) Ka or Kb Here are some things in common with most Ka/Kb problems. 1. Many of them will ask for you to determine pH or pOH. To do this, you obviously need to know [H+] or [OH-]. If you have a strong acid or strong base, you can determine [H+] or [OH-] directly from the a ...
Sections 6.4 - 6.5
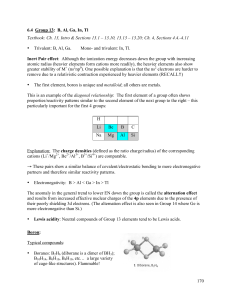
... Amphoterism and Isopolyoxo Ions Amphoterism: Being able to do two opposite things at the same time. In chemistry: Acid/Base amphoterism, Redox amphoterism ...
... Amphoterism and Isopolyoxo Ions Amphoterism: Being able to do two opposite things at the same time. In chemistry: Acid/Base amphoterism, Redox amphoterism ...
Chapter 1 - TamAPChemistryHart
... Weak bases generally fall into one of two categories. 1. Neutral substances with a lone pair of electrons that can accept protons. • Most neutral weak bases contain nitrogen. • Amines are related to ammonia and have one or more N–H bonds replaced with N–C bonds (e.g., CH3NH2 is methylamine). ...
... Weak bases generally fall into one of two categories. 1. Neutral substances with a lone pair of electrons that can accept protons. • Most neutral weak bases contain nitrogen. • Amines are related to ammonia and have one or more N–H bonds replaced with N–C bonds (e.g., CH3NH2 is methylamine). ...
CHEMISTRY NOTES – CHAPTERS 20 AND 21
... bases are substances which yield hydroxide (OH-) ions in aqueous solution. Examples of Arrhenius acids are hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), and phosphoric acid (H3PO4). Examples of Arrhenius bases are sodium hydroxide (NaOH), calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2), and aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH) ...
... bases are substances which yield hydroxide (OH-) ions in aqueous solution. Examples of Arrhenius acids are hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), and phosphoric acid (H3PO4). Examples of Arrhenius bases are sodium hydroxide (NaOH), calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2), and aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH) ...
Document
... As stated above, a buffer solution resists changes in pH by consuming and countering the effects of strong acids and bases. A brief overview of how a buffer is made and how it serves to counteract changes in pH can be seen at the link below. (If this link does not open, just double-click on the Powe ...
... As stated above, a buffer solution resists changes in pH by consuming and countering the effects of strong acids and bases. A brief overview of how a buffer is made and how it serves to counteract changes in pH can be seen at the link below. (If this link does not open, just double-click on the Powe ...
Honors Chemistry II Review 1. Express the following in scientific
... monoxide to yield metallic iron and carbon dioxide. Write a balanced chemical equation and predict how many moles of CO will react with 0.5 moles of iron (III) oxide. 18. Dichloromethane (CH2Cl2), a solvent used in the decaffeination of coffee beans, is prepared by the reaction of methane (CH4) with ...
... monoxide to yield metallic iron and carbon dioxide. Write a balanced chemical equation and predict how many moles of CO will react with 0.5 moles of iron (III) oxide. 18. Dichloromethane (CH2Cl2), a solvent used in the decaffeination of coffee beans, is prepared by the reaction of methane (CH4) with ...
Strong and weak acids and bases
... – methanoic acid (CHOOH) – ethanoic (acetic) acid • CH3COOH(l) + H2O(l) ⇌ CH3COO-(aq) + H3O+ – carbonic acid: (CO2 in water) • CO2(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H2CO3(aq) ...
... – methanoic acid (CHOOH) – ethanoic (acetic) acid • CH3COOH(l) + H2O(l) ⇌ CH3COO-(aq) + H3O+ – carbonic acid: (CO2 in water) • CO2(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H2CO3(aq) ...
Chemical laboratories Dipl.-Ing.(FH) Giovanna
... Automated Determination of ammonium, phosphate, nitrate and nitrite by flow injection analysis (FIA) ...
... Automated Determination of ammonium, phosphate, nitrate and nitrite by flow injection analysis (FIA) ...
CHEM 101 1st Major (Term 161)
... 1. A weather balloon filled with helium has a diameter of 3.50 ft. What is the mass in grams of the helium in the balloon? The density of the helium is 0.166 g/L. The volume can be calculated as (4/3)r3. [1 ft =12 in; 1 in = 2.54 cm] A) 106 g B) 271 g C) 21.3 g D) 79.9 g E) 63.6 g ...
... 1. A weather balloon filled with helium has a diameter of 3.50 ft. What is the mass in grams of the helium in the balloon? The density of the helium is 0.166 g/L. The volume can be calculated as (4/3)r3. [1 ft =12 in; 1 in = 2.54 cm] A) 106 g B) 271 g C) 21.3 g D) 79.9 g E) 63.6 g ...
unit 4 practice
... hydroxide solutions of the same concentration. Which statement is correct? A. The initial pH values of both acids are equal. B. At the equivalence points, the solutions of both titrations have pH values ...
... hydroxide solutions of the same concentration. Which statement is correct? A. The initial pH values of both acids are equal. B. At the equivalence points, the solutions of both titrations have pH values ...
2A Final Exam Review Worksheet
... A. If there is 10.0 g of P4O10, find the mass of phosphoric acid formed. B. If there is also 10.0 g of perchloric acid, find the mass of phosphoric acid formed. C. Considering A & B, how much of the excess reactant remains after the reaction is complete. D. Find the number of phosphorus atoms in 10. ...
... A. If there is 10.0 g of P4O10, find the mass of phosphoric acid formed. B. If there is also 10.0 g of perchloric acid, find the mass of phosphoric acid formed. C. Considering A & B, how much of the excess reactant remains after the reaction is complete. D. Find the number of phosphorus atoms in 10. ...
Chapter 4 - Aqueous Reactions
... Acid - a substance that ionizes in water to form hydrogen ions H+. HCl (aq) H+ (aq) + Cl(aq) What is H+? A hydrogen atom without its electron - a bare proton. ...
... Acid - a substance that ionizes in water to form hydrogen ions H+. HCl (aq) H+ (aq) + Cl(aq) What is H+? A hydrogen atom without its electron - a bare proton. ...
Acid
An acid (from the Latin acidus/acēre meaning sour) is a chemical substance whose aqueous solutions are characterized by a sour taste, the ability to turn blue litmus red, and the ability to react with bases and certain metals (like calcium) to form salts. Aqueous solutions of acids have a pH of less than 7. Non-aqueous acids are usually formed when an anion (negative ion) reacts with one or more positively charged hydrogen cations. A lower pH means a higher acidity, and thus a higher concentration of positive hydrogen ions in the solution. Chemicals or substances having the property of an acid are said to be acidic.There are three common definitions for acids: the Arrhenius definition, the Brønsted-Lowry definition, and the Lewis definition. The Arrhenius definition defines acids as substances which increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), or more accurately, hydronium ions (H3O+), when dissolved in water. The Brønsted-Lowry definition is an expansion: an acid is a substance which can act as a proton donor. By this definition, any compound which can easily be deprotonated can be considered an acid. Examples include alcohols and amines which contain O-H or N-H fragments. A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. Examples of Lewis acids include all metal cations, and electron-deficient molecules such as boron trifluoride and aluminium trichloride.Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (a solution of hydrogen chloride which is found in gastric acid in the stomach and activates digestive enzymes), acetic acid (vinegar is a dilute solution of this liquid), sulfuric acid (used in car batteries), and tartaric acid (a solid used in baking). As these examples show, acids can be solutions or pure substances, and can be derived from solids, liquids, or gases. Strong acids and some concentrated weak acids are corrosive, but there are exceptions such as carboranes and boric acid.