Chemical Bonding
... uneven distribution of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. • Cohesion is attraction between molecules of the same substance. • Adhesion is an attraction between molecules of different substances. ...
... uneven distribution of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. • Cohesion is attraction between molecules of the same substance. • Adhesion is an attraction between molecules of different substances. ...
CHEMISTRY 3
... Because esters are made by forcing the equilibrium reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol to the right, it should also be possible to split an ester back into its constituents by forcing the same equilibrium to shift itself in the reverse direction, ie to the left. (a) ...
... Because esters are made by forcing the equilibrium reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol to the right, it should also be possible to split an ester back into its constituents by forcing the same equilibrium to shift itself in the reverse direction, ie to the left. (a) ...
BioN01 Introduction, pH and buffer Summer 2014
... [H+] and [OH-] For pure water, there are equal concentrations of [H+] and [OH-], each with a value of 1 x 10-7 M Since Kw is a fixed value, the concentrations of [H+] and [OH-] are inversely changing If the concentration of H+ is high, then the concentration of OH- must be low, and vice versa. For ...
... [H+] and [OH-] For pure water, there are equal concentrations of [H+] and [OH-], each with a value of 1 x 10-7 M Since Kw is a fixed value, the concentrations of [H+] and [OH-] are inversely changing If the concentration of H+ is high, then the concentration of OH- must be low, and vice versa. For ...
Chem 206 Exam 2 Answers
... Therefore, the rate is 2.90 s−1 × 9.2 = 27 M ⋅ s−1 . Note: You must use the equilibrium concentration. Or: Because at equilibrium kf=kr, 3.45 M −1 ⋅ s −1 × 2.8 × 2.8 = 27 M ⋅ s−1 d) After equilibrium is obtained, you add a catalyst and 3.00 additional moles of HCl. What will happen? <8 pts.> The add ...
... Therefore, the rate is 2.90 s−1 × 9.2 = 27 M ⋅ s−1 . Note: You must use the equilibrium concentration. Or: Because at equilibrium kf=kr, 3.45 M −1 ⋅ s −1 × 2.8 × 2.8 = 27 M ⋅ s−1 d) After equilibrium is obtained, you add a catalyst and 3.00 additional moles of HCl. What will happen? <8 pts.> The add ...
Chp 5
... • Naming Oxy Acids have polyatomic ions and end differently • Hydrogen + …-ate = (remove hydrogen)…ic acid • H2CO3(aq) = hydrogen carbonate = carbonic acid • Hydrogen + …-ite = (remove hydrogen)…ous acid • H2SO3(aq) = hydrogen sulphite = sulphurous acid ...
... • Naming Oxy Acids have polyatomic ions and end differently • Hydrogen + …-ate = (remove hydrogen)…ic acid • H2CO3(aq) = hydrogen carbonate = carbonic acid • Hydrogen + …-ite = (remove hydrogen)…ous acid • H2SO3(aq) = hydrogen sulphite = sulphurous acid ...
AP Chemistry Test Review
... 31) Le Chatlier’s principle…(+) or (-) heat; ∆P; ∆V; (+) or (-) reactants and products; inert gases have no effect. 32) Q>K…the reaction goes backwards to the reactants 33) for Ksp, Q>K means a precipitate will form (see topic #45) 34) Calculate K by doing ICE box problems 35) acid/base definitions… ...
... 31) Le Chatlier’s principle…(+) or (-) heat; ∆P; ∆V; (+) or (-) reactants and products; inert gases have no effect. 32) Q>K…the reaction goes backwards to the reactants 33) for Ksp, Q>K means a precipitate will form (see topic #45) 34) Calculate K by doing ICE box problems 35) acid/base definitions… ...
SNC2D – Science 10 Tuesday April 26th, 2010 Mr. Sourlis and Mr
... 3. When a chemical reaction takes place, the total mass of the products is always a. Greater than the total mass of the reactants b. Less than the total mass of the reactants c. Equal to the total mass of the reactants d. Dependent on the type of reaction e. Impossible to determine 4. What is anothe ...
... 3. When a chemical reaction takes place, the total mass of the products is always a. Greater than the total mass of the reactants b. Less than the total mass of the reactants c. Equal to the total mass of the reactants d. Dependent on the type of reaction e. Impossible to determine 4. What is anothe ...
last year`s April exam
... b) Draw a picture that shows how water molecules can interact with an aldehyde through H-bonding, showing all possible interactions. ...
... b) Draw a picture that shows how water molecules can interact with an aldehyde through H-bonding, showing all possible interactions. ...
4 Acid Base Solutions
... You should allocate 30 minutes to finish this portion of the test. No calculator should be used. A periodic table and data table will be provided. Select the answer that best responds to each question. 1. Consider the equilibrium, HF(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + F−(aq). Which pair of substances makes u ...
... You should allocate 30 minutes to finish this portion of the test. No calculator should be used. A periodic table and data table will be provided. Select the answer that best responds to each question. 1. Consider the equilibrium, HF(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + F−(aq). Which pair of substances makes u ...
Chemical Equation Interpretations – Match the chemical equation
... __ 6. C16H30O2(s) + H2(g) C16H32O2(s) __ 7. CaO(s) + H2O(l) Ca(OH)2 (s) ...
... __ 6. C16H30O2(s) + H2(g) C16H32O2(s) __ 7. CaO(s) + H2O(l) Ca(OH)2 (s) ...
Chapters 14
... 7. What is the molarity of a solution made by dissolving 9.1 g of H3PO4 in enough water to make 22.3 L of solution? Assume that H3PO4 ionizes completely in water to H+ and PO43ions. What is the pH of the solution? Find the concentration of OH-? ...
... 7. What is the molarity of a solution made by dissolving 9.1 g of H3PO4 in enough water to make 22.3 L of solution? Assume that H3PO4 ionizes completely in water to H+ and PO43ions. What is the pH of the solution? Find the concentration of OH-? ...
Chapter 2. Atoms, Molecules, and Ion
... If two elements can combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element are in ratios of small whole ...
... If two elements can combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element are in ratios of small whole ...
Amino acids - CMA
... In alkaline (basic) environments, the NH3+ group will donate a proton, reverting to a NH2 group. This leaves the molecule with a net negative charge (on the COO - group). NH3+ reacts as a weak acid and has its own pKa value. In acid environments, the COO- group will accept a proton, reverting to a C ...
... In alkaline (basic) environments, the NH3+ group will donate a proton, reverting to a NH2 group. This leaves the molecule with a net negative charge (on the COO - group). NH3+ reacts as a weak acid and has its own pKa value. In acid environments, the COO- group will accept a proton, reverting to a C ...
Determination of K of Weak Acids
... where each step is characterized by its own equilibrium constant (Ka1, Ka2, etc.). The second reaction (removal of the second acidic hydrogen) always occurs to a much smaller extent than the first reaction, and so Ka2 is always significantly smaller than Ka1. Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and phosphoric aci ...
... where each step is characterized by its own equilibrium constant (Ka1, Ka2, etc.). The second reaction (removal of the second acidic hydrogen) always occurs to a much smaller extent than the first reaction, and so Ka2 is always significantly smaller than Ka1. Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and phosphoric aci ...
HSE Chemistry Questions
... ( iii ) Formic acid is a weaker acid than acetic acid. ( iv ) Both formaldehyde and acetaldehyde give the halo form test. ( v ) The reagent Ag(NH3)2+ can distinguish between ethylene and acetylene. ( vi ) Acetylene is more acidic than thylene. ( vii ) Acetaldehyde can be prepared by distillation ...
... ( iii ) Formic acid is a weaker acid than acetic acid. ( iv ) Both formaldehyde and acetaldehyde give the halo form test. ( v ) The reagent Ag(NH3)2+ can distinguish between ethylene and acetylene. ( vi ) Acetylene is more acidic than thylene. ( vii ) Acetaldehyde can be prepared by distillation ...
Brønsted acid
... An electrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved in water, results in a solution that can conduct electricity. A nonelectrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved, results in a solution that does not conduct electricity. ...
... An electrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved in water, results in a solution that can conduct electricity. A nonelectrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved, results in a solution that does not conduct electricity. ...
X CHEMISTRY-1-2006 TIME-1½ MARKS 80 SECTION
... c. If HX is a weak acid, what particles will be preseut in its dilute solution apart from those of water? d. Cations are formed by ________ (loss/gain)of electron and auions are formed by ________(loss/gain)of electrons [choose correct words to fill in the blanks] e. What ions must be present in a s ...
... c. If HX is a weak acid, what particles will be preseut in its dilute solution apart from those of water? d. Cations are formed by ________ (loss/gain)of electron and auions are formed by ________(loss/gain)of electrons [choose correct words to fill in the blanks] e. What ions must be present in a s ...
Ch. 2 The Chemistry of Life
... - Base – a _____________ that produces _____________ ions in solution - _________, or alkaline, solutions have __________ concentrations of _____ ions than pure ________ & have ____ values _____________ - The ________ the concentration of _____ ions, the _________ the ____ value (up to ___) - Buffer ...
... - Base – a _____________ that produces _____________ ions in solution - _________, or alkaline, solutions have __________ concentrations of _____ ions than pure ________ & have ____ values _____________ - The ________ the concentration of _____ ions, the _________ the ____ value (up to ___) - Buffer ...
Acid-Base Reactions
... (1) strong acid + strong base (2) weak acid + strong base (3) strong acid + weak base [(4) weak acid + weak base] {treated separately with titration} ...
... (1) strong acid + strong base (2) weak acid + strong base (3) strong acid + weak base [(4) weak acid + weak base] {treated separately with titration} ...
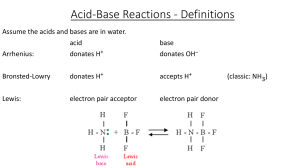
Acid
An acid (from the Latin acidus/acēre meaning sour) is a chemical substance whose aqueous solutions are characterized by a sour taste, the ability to turn blue litmus red, and the ability to react with bases and certain metals (like calcium) to form salts. Aqueous solutions of acids have a pH of less than 7. Non-aqueous acids are usually formed when an anion (negative ion) reacts with one or more positively charged hydrogen cations. A lower pH means a higher acidity, and thus a higher concentration of positive hydrogen ions in the solution. Chemicals or substances having the property of an acid are said to be acidic.There are three common definitions for acids: the Arrhenius definition, the Brønsted-Lowry definition, and the Lewis definition. The Arrhenius definition defines acids as substances which increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), or more accurately, hydronium ions (H3O+), when dissolved in water. The Brønsted-Lowry definition is an expansion: an acid is a substance which can act as a proton donor. By this definition, any compound which can easily be deprotonated can be considered an acid. Examples include alcohols and amines which contain O-H or N-H fragments. A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. Examples of Lewis acids include all metal cations, and electron-deficient molecules such as boron trifluoride and aluminium trichloride.Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (a solution of hydrogen chloride which is found in gastric acid in the stomach and activates digestive enzymes), acetic acid (vinegar is a dilute solution of this liquid), sulfuric acid (used in car batteries), and tartaric acid (a solid used in baking). As these examples show, acids can be solutions or pure substances, and can be derived from solids, liquids, or gases. Strong acids and some concentrated weak acids are corrosive, but there are exceptions such as carboranes and boric acid.