CHEMISTRY SEC 06 SYLLABUS
... Preparation of hydrogen from action of dilute non-oxdising acids on certain metals, exemplified by dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sulfuric acid on magnesium, zinc or iron. Test for hydrogen. Combustion of hydrogen - its advantages and disadvantages as a fuel. Reducing action of hydrogen with met ...
... Preparation of hydrogen from action of dilute non-oxdising acids on certain metals, exemplified by dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sulfuric acid on magnesium, zinc or iron. Test for hydrogen. Combustion of hydrogen - its advantages and disadvantages as a fuel. Reducing action of hydrogen with met ...
- Kendriya Vidyalaya NKJ Katni
... 18. 50% of the original amount of a reactant was added to the reaction mixture after 40 min. What % of the total amount will be present after 60 min, given that half life period of the reaction is 20 min. ...
... 18. 50% of the original amount of a reactant was added to the reaction mixture after 40 min. What % of the total amount will be present after 60 min, given that half life period of the reaction is 20 min. ...
GCSE ADDITIONAL CHEMISTRY (C2) REVISION BOOKLET
... i) The first level is filled with electrons first and then the second and third ones. j) When atoms bond with other atoms, the number of electrons in their outermost energy level changes. 2 a) In ionic bonding, electrons from one atom are transferred/given to another. b) The charged particles formed ...
... i) The first level is filled with electrons first and then the second and third ones. j) When atoms bond with other atoms, the number of electrons in their outermost energy level changes. 2 a) In ionic bonding, electrons from one atom are transferred/given to another. b) The charged particles formed ...
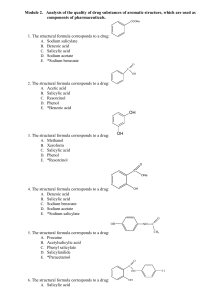
Module 2. Drug substances of aromatic structure
... E. *Bismuth tribromophenol basic with bismuth oxide 82. For synthesis of thymol it is possible to use such initial substance: A. Phenylsalicylate B. Phthalic acid C. Benzol D. Phenol E. *3-Metylphenol (m-cresol) 83. For assay of resorcinol, according to Pharmacopoeia, use method: A. Cerymetry, direc ...
... E. *Bismuth tribromophenol basic with bismuth oxide 82. For synthesis of thymol it is possible to use such initial substance: A. Phenylsalicylate B. Phthalic acid C. Benzol D. Phenol E. *3-Metylphenol (m-cresol) 83. For assay of resorcinol, according to Pharmacopoeia, use method: A. Cerymetry, direc ...
To Study The Harmful Effects Of Food Preservatives On Human Health
... Benzoic acid occurs naturally in many types of berries, plums, prunes, and some spices, As an additive, it is used as benzoic acid or as benzoate.The latter is used more often because benzoic acid is sparsely soluble in water, and sodium benzoate is more soluble. The undissociated form on benzoic ac ...
... Benzoic acid occurs naturally in many types of berries, plums, prunes, and some spices, As an additive, it is used as benzoic acid or as benzoate.The latter is used more often because benzoic acid is sparsely soluble in water, and sodium benzoate is more soluble. The undissociated form on benzoic ac ...
ACP Chemistry Semester 1 Final Exam - Doc-U-Ment
... 6) An ionic bond is best described as A) the sharing of electrons. B) the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. C) the attraction that holds the atoms together in a polyatomic ion. D) the attraction between 2 nonmetal atoms. E) the attraction between 2 metal atoms. 7) Determine the name fo ...
... 6) An ionic bond is best described as A) the sharing of electrons. B) the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. C) the attraction that holds the atoms together in a polyatomic ion. D) the attraction between 2 nonmetal atoms. E) the attraction between 2 metal atoms. 7) Determine the name fo ...
RES6_chem_stretch_challenge
... several marks using a careful approach. The answers have been laid out to show any potential marking points – i.e. if the question carries six marks, the corresponding answer will have six points to it; if the question has been allocated eight marks then the corresponding answer will have eights poi ...
... several marks using a careful approach. The answers have been laid out to show any potential marking points – i.e. if the question carries six marks, the corresponding answer will have six points to it; if the question has been allocated eight marks then the corresponding answer will have eights poi ...
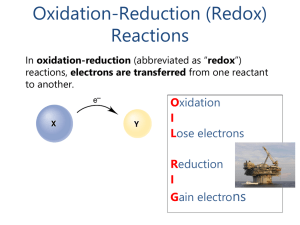
ALE 23. Balancing Redox Reactions
... The Model Oxidation-reduction or Redox reactions involve the transfer of one or more electrons from one chemical species to another. Redox reactions are involved in the corrosion of metals, the combustion of fuels, the generation of electricity from batteries and many biological processes including ...
... The Model Oxidation-reduction or Redox reactions involve the transfer of one or more electrons from one chemical species to another. Redox reactions are involved in the corrosion of metals, the combustion of fuels, the generation of electricity from batteries and many biological processes including ...
Chapter 4: Solution Chemistry and the Hydrosphere
... 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is the charge on the ion. Examples: Na3N, the ions are Na+ and N3–, so oxidation #’s: Na = +1 and N = -3. In Al2O3, the ions are Al+3 and O2–, so oxidation #’s: Al = +3 and O = -2 3. In a compound or polyatomic ion, – Group I elements are always +1. – Group ...
... 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is the charge on the ion. Examples: Na3N, the ions are Na+ and N3–, so oxidation #’s: Na = +1 and N = -3. In Al2O3, the ions are Al+3 and O2–, so oxidation #’s: Al = +3 and O = -2 3. In a compound or polyatomic ion, – Group I elements are always +1. – Group ...
CONDUCTOMETRY
... renewed, this eliminates the poisoning effect. Mercury forms amalgams (solid solution) with many metals. The diffusion current assumed a steady value immediately after each change of applied potential and is reproducible. The large hydrogen over-potential of mercury renders possible deposition of ...
... renewed, this eliminates the poisoning effect. Mercury forms amalgams (solid solution) with many metals. The diffusion current assumed a steady value immediately after each change of applied potential and is reproducible. The large hydrogen over-potential of mercury renders possible deposition of ...
WHAT YOU EAT - Montana State University Extended University
... parts for growth and repair. Respiration is the main way your cells get energy, most all the cells in your body prefer to burn fat and respiration is required for fat burning. ...
... parts for growth and repair. Respiration is the main way your cells get energy, most all the cells in your body prefer to burn fat and respiration is required for fat burning. ...
Page 1
... 57. Compare fission and fusion. (define and identify uses) Fission: the splitting of a nucleus into fragments Fusion: the combining of atomic nuclei 58. Compare alpha, beta and gamma particles. Alpha: a particle with twp protons and two neutrons, with a 2+ charge; is equivalent to a helium -4 nucleu ...
... 57. Compare fission and fusion. (define and identify uses) Fission: the splitting of a nucleus into fragments Fusion: the combining of atomic nuclei 58. Compare alpha, beta and gamma particles. Alpha: a particle with twp protons and two neutrons, with a 2+ charge; is equivalent to a helium -4 nucleu ...
Print out Reviews # 1 through # 17
... 3. Indicate which element in each of the following pairs has the larger atomic radius. (A) sodium , lithium (B) selenium , oxygen (C) strontium , magnesium (D) nitrogen , fluorine (E) carbon , germanium (F) zinc , bromine 4. Arrange each set of elements in order of increasing ionization energy. (A) ...
... 3. Indicate which element in each of the following pairs has the larger atomic radius. (A) sodium , lithium (B) selenium , oxygen (C) strontium , magnesium (D) nitrogen , fluorine (E) carbon , germanium (F) zinc , bromine 4. Arrange each set of elements in order of increasing ionization energy. (A) ...
File
... Select the one lettered choice that best fits each of sodium hydroxide. statement and then blacken the corresponding space on 13. No precipitate is formed when a dilute solution of the answer sheet. A choice may be used once, more H2SO4 is added to a sample of the solution. than once, or not at all ...
... Select the one lettered choice that best fits each of sodium hydroxide. statement and then blacken the corresponding space on 13. No precipitate is formed when a dilute solution of the answer sheet. A choice may be used once, more H2SO4 is added to a sample of the solution. than once, or not at all ...
Homework Solutions Week 6
... calcium from 97 to 99% precipitated, silver ion goes from 0 to 41% precipitated. 9-17 a) Why do many rivers in Box 9-1. lie on the line [HCO3-] = 2[Ca2+]? According to Box 9-1, the source of calcium in the rivers is the mineral calcite, which dissolves by reacting with carbon dioxide in the river wa ...
... calcium from 97 to 99% precipitated, silver ion goes from 0 to 41% precipitated. 9-17 a) Why do many rivers in Box 9-1. lie on the line [HCO3-] = 2[Ca2+]? According to Box 9-1, the source of calcium in the rivers is the mineral calcite, which dissolves by reacting with carbon dioxide in the river wa ...
Use the following answers for questions 10
... (C) Solubility of glucose in water (D) Degree of dissociation of glucose (E) Density of the solution 38. The radioactive decay of 6-C-14 to 7-N-14 occurs by the process of (A) beta particle emission (B) alpha particle emission (C) positron emission (D) electron capture (E) neutron capture 39. Equal ...
... (C) Solubility of glucose in water (D) Degree of dissociation of glucose (E) Density of the solution 38. The radioactive decay of 6-C-14 to 7-N-14 occurs by the process of (A) beta particle emission (B) alpha particle emission (C) positron emission (D) electron capture (E) neutron capture 39. Equal ...
THE STUDY OF INTERMEDIARY METABOLISM OF
... atoms. Many compounds when treated with hot concentrated DzSO4 exchange otherwise stable hydrogen atoms (59). A number of deuterium-containing fatty acids and amino acids have thus been prepared by this procedure (60, 61). The method introduces deuterium into fatty acids only at the a-carbon atom. A ...
... atoms. Many compounds when treated with hot concentrated DzSO4 exchange otherwise stable hydrogen atoms (59). A number of deuterium-containing fatty acids and amino acids have thus been prepared by this procedure (60, 61). The method introduces deuterium into fatty acids only at the a-carbon atom. A ...
Acid
An acid (from the Latin acidus/acēre meaning sour) is a chemical substance whose aqueous solutions are characterized by a sour taste, the ability to turn blue litmus red, and the ability to react with bases and certain metals (like calcium) to form salts. Aqueous solutions of acids have a pH of less than 7. Non-aqueous acids are usually formed when an anion (negative ion) reacts with one or more positively charged hydrogen cations. A lower pH means a higher acidity, and thus a higher concentration of positive hydrogen ions in the solution. Chemicals or substances having the property of an acid are said to be acidic.There are three common definitions for acids: the Arrhenius definition, the Brønsted-Lowry definition, and the Lewis definition. The Arrhenius definition defines acids as substances which increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), or more accurately, hydronium ions (H3O+), when dissolved in water. The Brønsted-Lowry definition is an expansion: an acid is a substance which can act as a proton donor. By this definition, any compound which can easily be deprotonated can be considered an acid. Examples include alcohols and amines which contain O-H or N-H fragments. A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. Examples of Lewis acids include all metal cations, and electron-deficient molecules such as boron trifluoride and aluminium trichloride.Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (a solution of hydrogen chloride which is found in gastric acid in the stomach and activates digestive enzymes), acetic acid (vinegar is a dilute solution of this liquid), sulfuric acid (used in car batteries), and tartaric acid (a solid used in baking). As these examples show, acids can be solutions or pure substances, and can be derived from solids, liquids, or gases. Strong acids and some concentrated weak acids are corrosive, but there are exceptions such as carboranes and boric acid.