Atmosphere I
... lower orbital, the emitted photon can travel in any direction. Thus, the observer notices a decrease in the number of photons of this energy (wavelength). Planck’s constant is h, is frequency, and is wavelength. ...
... lower orbital, the emitted photon can travel in any direction. Thus, the observer notices a decrease in the number of photons of this energy (wavelength). Planck’s constant is h, is frequency, and is wavelength. ...
File - Ms. Renfro`s Physical Science Web Class
... S8P2. Scholars will be familiar with the forms and transformations of energy. a. Explain energy transformation in terms of the Law of Conservation of Energy. b. Explain the relationship between potential and kinetic energy. c. Compare and contrast the different forms of energy (heat, light, electric ...
... S8P2. Scholars will be familiar with the forms and transformations of energy. a. Explain energy transformation in terms of the Law of Conservation of Energy. b. Explain the relationship between potential and kinetic energy. c. Compare and contrast the different forms of energy (heat, light, electric ...
Thermal and Statistical Physics (Part II) Examples Sheet 1
... a value of the Boltzmann constant, kB , and compare it with the modern value. 31. The famous ratchet and pawl machine, originally suggested by Smoluchowski in 1912 to be able to extract useful work from a thermal reservoir (against the Laws of Thermodynamics) is shown below. The pawl preventing the ...
... a value of the Boltzmann constant, kB , and compare it with the modern value. 31. The famous ratchet and pawl machine, originally suggested by Smoluchowski in 1912 to be able to extract useful work from a thermal reservoir (against the Laws of Thermodynamics) is shown below. The pawl preventing the ...
Questions
... A9. Which one of the following statements is correct concerning electromagnetic waves traveling through a vacuum? (A) All waves have the same wavelength. (B) All waves have the same frequency. (C) The electric and magnetic fields associated with the waves are parallel to each other but perpendicular ...
... A9. Which one of the following statements is correct concerning electromagnetic waves traveling through a vacuum? (A) All waves have the same wavelength. (B) All waves have the same frequency. (C) The electric and magnetic fields associated with the waves are parallel to each other but perpendicular ...
Q - W
... We generally assume quasi-static processes (slow enough that p and T are well defined at all times): ...
... We generally assume quasi-static processes (slow enough that p and T are well defined at all times): ...
Thermo 2 - WordPress.com
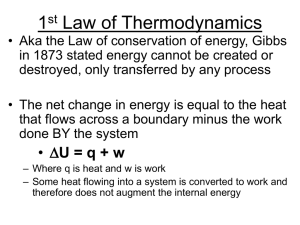
... 0th Law: if two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other. 1st Law: is the law of conservation of energy. Energy can to be created or destroyed. There is function called internal energy that relates work and heat transfer. 2nd Law: E ...
... 0th Law: if two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other. 1st Law: is the law of conservation of energy. Energy can to be created or destroyed. There is function called internal energy that relates work and heat transfer. 2nd Law: E ...
File
... groups or aggregates of molecules within fluids (e.g., liquids, gases) and rheids, either through advection or through diffusion or as a combination of both of them. Convection of mass cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids. D ...
... groups or aggregates of molecules within fluids (e.g., liquids, gases) and rheids, either through advection or through diffusion or as a combination of both of them. Convection of mass cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids. D ...
The Second Law of Thermodynamics
... The problems arise from: 1.Classical thermodynamics is connected with states of equilibrium and various processes connecting them. 2.The exact process by which a system reaches the final state from its initial state is immaterial. i.e. the transition is independent of the particular path taken 3. T ...
... The problems arise from: 1.Classical thermodynamics is connected with states of equilibrium and various processes connecting them. 2.The exact process by which a system reaches the final state from its initial state is immaterial. i.e. the transition is independent of the particular path taken 3. T ...
Powerpoint - Appalachian State University
... The intense solar radiation that charges the dust also causes extreme temperatures which exceed the operating temperatures of lunar exploration equipment. The lack of an atmosphere prevents cooling by convection, so the surfaces of lunar exploration equipment and vehicles are designed with materials ...
... The intense solar radiation that charges the dust also causes extreme temperatures which exceed the operating temperatures of lunar exploration equipment. The lack of an atmosphere prevents cooling by convection, so the surfaces of lunar exploration equipment and vehicles are designed with materials ...
Chapter 12 Study Guide - School District of La Crosse
... States that the total_____________in the thermal energy of a system is the__________of the work done on It and the heat added to it. The first law of thermodynamics is another way of stating the law of ...
... States that the total_____________in the thermal energy of a system is the__________of the work done on It and the heat added to it. The first law of thermodynamics is another way of stating the law of ...
Lecture 5 - Thermodynamics II
... • Entropy is a measure of the disorder (randomness) of a system. The higher the entropy of the system, the more disordered it is. • The second law states that the universe always becomes more disordered in any real process. • The entropy (order) of a system can decrease, but in order for this to hap ...
... • Entropy is a measure of the disorder (randomness) of a system. The higher the entropy of the system, the more disordered it is. • The second law states that the universe always becomes more disordered in any real process. • The entropy (order) of a system can decrease, but in order for this to hap ...
Thermochemistry
... We can define a new state variable (one where the path to its current state does not affect its value) called enthalpy: ...
... We can define a new state variable (one where the path to its current state does not affect its value) called enthalpy: ...
Thermal radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation generated by the thermal motion of charged particles in matter. An object with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. When the temperature of the body is greater than absolute zero, interatomic collisions cause the kinetic energy of the atoms or molecules to change. This results in charge-acceleration and/or dipole oscillation which produces electromagnetic radiation, and the wide spectrum of radiation reflects the wide spectrum of energies and accelerations that occur even at a single temperature.Examples of thermal radiation include the visible light and infrared light emitted by an incandescent light bulb, the infrared radiation emitted by animals and detectable with an infrared camera, and the cosmic microwave background radiation. Thermal radiation is different from thermal convection and thermal conduction—a person near a raging bonfire feels radiant heating from the fire, even if the surrounding air is very cold.Sunlight is part of thermal radiation generated by the hot plasma of the Sun. The Earth also emits thermal radiation, but at a much lower intensity and different spectral distribution (infrared rather than visible) because it is cooler. The Earth's absorption of solar radiation, followed by its outgoing thermal radiation are the two most important processes that determine the temperature and climate of the Earth.If a radiation-emitting object meets the physical characteristics of a black body in thermodynamic equilibrium, the radiation is called blackbody radiation. Planck's law describes the spectrum of blackbody radiation, which depends only on the object's temperature. Wien's displacement law determines the most likely frequency of the emitted radiation, and the Stefan–Boltzmann law gives the radiant intensity.Thermal radiation is one of the fundamental mechanisms of heat transfer.