Lecture_1_ Heat and - Arizona State University
... Sign convention: The work is taken negative if it increases the energy in the system. If the volume of the system is decreased work is done on the system, increasing its energy; hence the positive sign in the equation W pdV . The unusual convention was established to fit the behavior of heat engi ...
... Sign convention: The work is taken negative if it increases the energy in the system. If the volume of the system is decreased work is done on the system, increasing its energy; hence the positive sign in the equation W pdV . The unusual convention was established to fit the behavior of heat engi ...
Chapter 27 - Houston ISD
... does the warmth of the sun reach the Earth? In this section, you will learn about another type of heat transfer known as radiation that is responsible for the way the sun warms our planet. Radiation is a type of heat transfer that does not require matter to travel through. ...
... does the warmth of the sun reach the Earth? In this section, you will learn about another type of heat transfer known as radiation that is responsible for the way the sun warms our planet. Radiation is a type of heat transfer that does not require matter to travel through. ...
Week 4 - Earth & Planetary Sciences
... radioactive decay (K,U,Th at present day) • For some bodies (e.g. Io, Europa) the principle heat source is tidal deformation (friction) • Radioactive heat production declines with time • Present-day terrestrial value ~5x10-12 W kg-1 (or ~1.5x10-8 W m-3) • Radioactive decay accounts for only about ha ...
... radioactive decay (K,U,Th at present day) • For some bodies (e.g. Io, Europa) the principle heat source is tidal deformation (friction) • Radioactive heat production declines with time • Present-day terrestrial value ~5x10-12 W kg-1 (or ~1.5x10-8 W m-3) • Radioactive decay accounts for only about ha ...
Exam # 3 Fall 2009
... 1.) The product of the average force and the time interval over which it acts is the __________. (impulse) 2.) Ft = mv is the equation for __________. (impulse momentum) 3.) Under what conditions is momentum conserved? (in a closed, isolated system) 4.) An astronaut at rest fires a thruster pistol ...
... 1.) The product of the average force and the time interval over which it acts is the __________. (impulse) 2.) Ft = mv is the equation for __________. (impulse momentum) 3.) Under what conditions is momentum conserved? (in a closed, isolated system) 4.) An astronaut at rest fires a thruster pistol ...
nupoc study guide - UC Berkeley NROTC
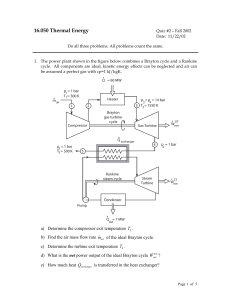
... 1-2 Reversible adiabatic compression of the working fluid until it reaches the temperature TH of the high-temperature reservoir. 2-3 Reversible isothermal expansion during which heat QH is transferred from the high-temperature reservoir TH to the working fluid. 3-4 Reversible adiabatic expansion of ...
... 1-2 Reversible adiabatic compression of the working fluid until it reaches the temperature TH of the high-temperature reservoir. 2-3 Reversible isothermal expansion during which heat QH is transferred from the high-temperature reservoir TH to the working fluid. 3-4 Reversible adiabatic expansion of ...
Lecture Notes
... where k is the thermal conductivity of the material. It has units as W/m.K. Metals have k values in the range 20-400, ceramics 2-50, while polymers have in order of 0.3. Heat energy in solids in transported by two mechanisms: lattice vibrations (phonons) and free electrons. However, usually only one ...
... where k is the thermal conductivity of the material. It has units as W/m.K. Metals have k values in the range 20-400, ceramics 2-50, while polymers have in order of 0.3. Heat energy in solids in transported by two mechanisms: lattice vibrations (phonons) and free electrons. However, usually only one ...
Raman Spectroscopy - Harlem Children Society
... During charge transfer, some vibrations will be altered due to a molecule's interaction with the surface, resulting in some of the SER bands being shifted in respect to the normal Raman Spectrum. SER spectra of a different small peptides and proteins were obtained from a roughened surface using a Ra ...
... During charge transfer, some vibrations will be altered due to a molecule's interaction with the surface, resulting in some of the SER bands being shifted in respect to the normal Raman Spectrum. SER spectra of a different small peptides and proteins were obtained from a roughened surface using a Ra ...
LECTURE NOTES ON PHS 222 (THERMAL PHYSICS) BY DR. V.C.
... put in contact. One system A is said to be hotter than another B if heat flows from the former (A) to the latter (B) when they are in thermal contact. This then allows us to introduce a parameter, called an empirical temperature, which is the same for all bodies that are in thermal equilibrium with ...
... put in contact. One system A is said to be hotter than another B if heat flows from the former (A) to the latter (B) when they are in thermal contact. This then allows us to introduce a parameter, called an empirical temperature, which is the same for all bodies that are in thermal equilibrium with ...
Thermal energy
... to another. • The rate at which heating occurs depends on the difference in temperatures between the objects. ...
... to another. • The rate at which heating occurs depends on the difference in temperatures between the objects. ...
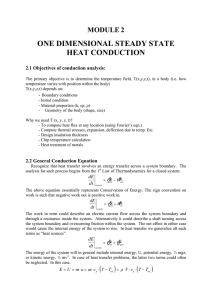
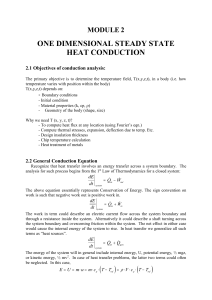
one dimensional steady state heat conduction
... will give us T(x,y,z). Solution depends on boundary conditions (BC) and initial conditions (IC). How many BC’s and IC’s ? - Heat equation is second order in spatial coordinate. Hence, 2 BC’s needed for each coordinate. * 1D problem: 2 BC in x-direction * 2D problem: 2 BC in x-direction, 2 in y-direc ...
... will give us T(x,y,z). Solution depends on boundary conditions (BC) and initial conditions (IC). How many BC’s and IC’s ? - Heat equation is second order in spatial coordinate. Hence, 2 BC’s needed for each coordinate. * 1D problem: 2 BC in x-direction * 2D problem: 2 BC in x-direction, 2 in y-direc ...
2002 - thephysicsteacher.ie
... Using Newton’s first law of motion, explain what would happen to the passengers if they were not wearing seatbelts while the aircraft was landing. (W = Fs; v = u + at; F = ma) ...
... Using Newton’s first law of motion, explain what would happen to the passengers if they were not wearing seatbelts while the aircraft was landing. (W = Fs; v = u + at; F = ma) ...
Lecture 2 Intro to Heat Flow
... This is the famous ‘diffusion equation’. Wheee! It can be expressed most efficiently as ...
... This is the famous ‘diffusion equation’. Wheee! It can be expressed most efficiently as ...
Chemistry Websites of key interest Electron Arrangements Aufbau
... a. In quantum physics, the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, sometimes called the Heisenberg indeterminacy principle, expresses a limitation on accuracy of (nearly) simultaneous measurement of observables such as the position and the momentum of a particle. It furthermore precisely quantifies the im ...
... a. In quantum physics, the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, sometimes called the Heisenberg indeterminacy principle, expresses a limitation on accuracy of (nearly) simultaneous measurement of observables such as the position and the momentum of a particle. It furthermore precisely quantifies the im ...
2.1 Introduction 2.2 Literature Review
... experiment may be regarded as a radiometric determination of the gold- point based on the theoretical value for σ, the result then being TAu = 133727± 0.40 K. This value is 0.31 K below the IPTS-68 value, derived by gas thermometry. Wray E.M [5] describes that tungsten bulb is used in a simple ammet ...
... experiment may be regarded as a radiometric determination of the gold- point based on the theoretical value for σ, the result then being TAu = 133727± 0.40 K. This value is 0.31 K below the IPTS-68 value, derived by gas thermometry. Wray E.M [5] describes that tungsten bulb is used in a simple ammet ...
Basic thermodynamics` definitions. Units and conversions.
... The objective of the course is to give the idea about the thermodynamic properties such as temperature, pressure, internal energy ,enthalpy, entropy etc. It also deals with the zeroth, first and second Law of Thermodynamics and its applications in environmental engineering field. Thermodynamics help ...
... The objective of the course is to give the idea about the thermodynamic properties such as temperature, pressure, internal energy ,enthalpy, entropy etc. It also deals with the zeroth, first and second Law of Thermodynamics and its applications in environmental engineering field. Thermodynamics help ...
Thermal radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation generated by the thermal motion of charged particles in matter. An object with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. When the temperature of the body is greater than absolute zero, interatomic collisions cause the kinetic energy of the atoms or molecules to change. This results in charge-acceleration and/or dipole oscillation which produces electromagnetic radiation, and the wide spectrum of radiation reflects the wide spectrum of energies and accelerations that occur even at a single temperature.Examples of thermal radiation include the visible light and infrared light emitted by an incandescent light bulb, the infrared radiation emitted by animals and detectable with an infrared camera, and the cosmic microwave background radiation. Thermal radiation is different from thermal convection and thermal conduction—a person near a raging bonfire feels radiant heating from the fire, even if the surrounding air is very cold.Sunlight is part of thermal radiation generated by the hot plasma of the Sun. The Earth also emits thermal radiation, but at a much lower intensity and different spectral distribution (infrared rather than visible) because it is cooler. The Earth's absorption of solar radiation, followed by its outgoing thermal radiation are the two most important processes that determine the temperature and climate of the Earth.If a radiation-emitting object meets the physical characteristics of a black body in thermodynamic equilibrium, the radiation is called blackbody radiation. Planck's law describes the spectrum of blackbody radiation, which depends only on the object's temperature. Wien's displacement law determines the most likely frequency of the emitted radiation, and the Stefan–Boltzmann law gives the radiant intensity.Thermal radiation is one of the fundamental mechanisms of heat transfer.