Thermodynamics - WordPress.com
... Energy (Joule) • Energy can be transferred or transformed • kinetic • potential (chemical, electrical, gravitational, elastic) • radiant (sound, light and other electromagnetic waves) • internal (heat/thermal energy) ...
... Energy (Joule) • Energy can be transferred or transformed • kinetic • potential (chemical, electrical, gravitational, elastic) • radiant (sound, light and other electromagnetic waves) • internal (heat/thermal energy) ...
W - Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics
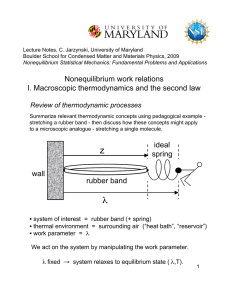
... but keep in mind that the meaning of the quantities involved depends on how we define our system of interest. ...
... but keep in mind that the meaning of the quantities involved depends on how we define our system of interest. ...
Temperature & Heat
... • A measure of hotness or coldness of an object • Based on average molecular kinetic energy Heat • Based on total internal energy of molecules • Doubling amount at same temperature doubles heat ...
... • A measure of hotness or coldness of an object • Based on average molecular kinetic energy Heat • Based on total internal energy of molecules • Doubling amount at same temperature doubles heat ...
Chapter 3 Chemical Reactions / Energy
... temperature (∆T) of a given mass (m) of a substance with a specific heat capacity (C) ...
... temperature (∆T) of a given mass (m) of a substance with a specific heat capacity (C) ...
THE IMP ACT OF METEORS` By John D. Boon Energy changes that
... (such as Meteor Crater) show little evidence of heat. Oliver'" in his book on meteors, calls attention to this fact and wonders why it is true. Nearly all articles that have been written concerning the impact of meteors assume that great heat must have been produced, and yet, in the crater mentioned ...
... (such as Meteor Crater) show little evidence of heat. Oliver'" in his book on meteors, calls attention to this fact and wonders why it is true. Nearly all articles that have been written concerning the impact of meteors assume that great heat must have been produced, and yet, in the crater mentioned ...
Internal Energy
... then added to the gas at constant volume until the original temperature is reached. What is the total work done on the gas? ...
... then added to the gas at constant volume until the original temperature is reached. What is the total work done on the gas? ...
AMS Weather Studies
... Emission of IR radiation to space is greater than absorption of solar radiation ...
... Emission of IR radiation to space is greater than absorption of solar radiation ...
Chapter 18
... Convection: Convection happens when a fluid comes in contact with an object whose temperature is higher than that of the fluid. Heat is transferred through the flow of the fluid. Radiation: Heat can be exchanged via electromagnetic waves, called thermal radiation. It does not need a medium. ...
... Convection: Convection happens when a fluid comes in contact with an object whose temperature is higher than that of the fluid. Heat is transferred through the flow of the fluid. Radiation: Heat can be exchanged via electromagnetic waves, called thermal radiation. It does not need a medium. ...
Activity 1 Solutions: Introduction to Physics 104
... TV remote, glow coil, infrared camera, radiometer 2) How do we experience this type of electromagnetic radiation? If you closed your eyes, how could you tell if an incandescent light bulb was lit? We experience infrared radiation as heat (thermal energy). You could feel the heat from a nearby incand ...
... TV remote, glow coil, infrared camera, radiometer 2) How do we experience this type of electromagnetic radiation? If you closed your eyes, how could you tell if an incandescent light bulb was lit? We experience infrared radiation as heat (thermal energy). You could feel the heat from a nearby incand ...
heat engine
... Refrigerators, air conditioners, and heat pumps are devices that make heat flow from cold to hot. This is called the refrigeration process. ...
... Refrigerators, air conditioners, and heat pumps are devices that make heat flow from cold to hot. This is called the refrigeration process. ...
6 Departure from thermal equilibrium
... a heavy virtual state with mass M . Neutrinos serve as a particularly important example, as they only interact through the weak interactions, involving the exchange of massive W or Z bosons. At temperatures T M the quantum mechanical amplitude for such a process is proportional to 1/M 2 , and Γ, w ...
... a heavy virtual state with mass M . Neutrinos serve as a particularly important example, as they only interact through the weak interactions, involving the exchange of massive W or Z bosons. At temperatures T M the quantum mechanical amplitude for such a process is proportional to 1/M 2 , and Γ, w ...
Plant development is strongly influenced by temperature. Other
... Plant development is strongly influenced by temperature. Other factors affect plant development to smaller extent. Plant development is affected by rate of enzymatic reactions which depend on temperature surrounding plant. Temperature and time are integrated into thermal time which is defined as sum ...
... Plant development is strongly influenced by temperature. Other factors affect plant development to smaller extent. Plant development is affected by rate of enzymatic reactions which depend on temperature surrounding plant. Temperature and time are integrated into thermal time which is defined as sum ...
solutions
... • Zeroth: If two systems are both in thermal equilibrium with a third then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other. • First: The increase in internal energy of a closed system is equal to the heat supplied to the system minus work done by it. • Second: The entropy of any isolated system neve ...
... • Zeroth: If two systems are both in thermal equilibrium with a third then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other. • First: The increase in internal energy of a closed system is equal to the heat supplied to the system minus work done by it. • Second: The entropy of any isolated system neve ...
Thermodynamics - Issaquah Connect
... environment (the areas surrounding a system) in three ways: Through a temperature difference—thermal energy is transferred from the higher temperature to the lower temperature until equilibrium is reached. Doing work on the system (i.e. compressing a piston of gas) Allowing work to be done on ...
... environment (the areas surrounding a system) in three ways: Through a temperature difference—thermal energy is transferred from the higher temperature to the lower temperature until equilibrium is reached. Doing work on the system (i.e. compressing a piston of gas) Allowing work to be done on ...
název projektu
... If the two thermodynamic objects are in equillibrium and stay in it after heat transfer is enabled, they have the same ...
... If the two thermodynamic objects are in equillibrium and stay in it after heat transfer is enabled, they have the same ...
Thermodynamics - Centre for Theoretical Chemistry and Physics
... they are warmed up. But some substances do the opposite by shrinking in certain directions as they are heated and expanding when cooled. Now researchers in the UK have found an inorganic crystalline material composed of silver, cobalt, carbon and nitrogen that expands more than any other known mater ...
... they are warmed up. But some substances do the opposite by shrinking in certain directions as they are heated and expanding when cooled. Now researchers in the UK have found an inorganic crystalline material composed of silver, cobalt, carbon and nitrogen that expands more than any other known mater ...
12 Limits to the Second Law of Thermodynamics
... of justification, ergodicity and related notions (such as use of the thermal state) have been so successful in the description of physical and chemical phenomena. Quantum Heat Engine Enhanced by Coherence: Revisiting Chambadal-Novikov Efficiency, KONSTANTIN E. DORFMAN (Precision Measurement Group, S ...
... of justification, ergodicity and related notions (such as use of the thermal state) have been so successful in the description of physical and chemical phenomena. Quantum Heat Engine Enhanced by Coherence: Revisiting Chambadal-Novikov Efficiency, KONSTANTIN E. DORFMAN (Precision Measurement Group, S ...
Thermal radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation generated by the thermal motion of charged particles in matter. An object with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. When the temperature of the body is greater than absolute zero, interatomic collisions cause the kinetic energy of the atoms or molecules to change. This results in charge-acceleration and/or dipole oscillation which produces electromagnetic radiation, and the wide spectrum of radiation reflects the wide spectrum of energies and accelerations that occur even at a single temperature.Examples of thermal radiation include the visible light and infrared light emitted by an incandescent light bulb, the infrared radiation emitted by animals and detectable with an infrared camera, and the cosmic microwave background radiation. Thermal radiation is different from thermal convection and thermal conduction—a person near a raging bonfire feels radiant heating from the fire, even if the surrounding air is very cold.Sunlight is part of thermal radiation generated by the hot plasma of the Sun. The Earth also emits thermal radiation, but at a much lower intensity and different spectral distribution (infrared rather than visible) because it is cooler. The Earth's absorption of solar radiation, followed by its outgoing thermal radiation are the two most important processes that determine the temperature and climate of the Earth.If a radiation-emitting object meets the physical characteristics of a black body in thermodynamic equilibrium, the radiation is called blackbody radiation. Planck's law describes the spectrum of blackbody radiation, which depends only on the object's temperature. Wien's displacement law determines the most likely frequency of the emitted radiation, and the Stefan–Boltzmann law gives the radiant intensity.Thermal radiation is one of the fundamental mechanisms of heat transfer.