carboxylic acids
... • Carboxylic acids have significantly higher boiling points than their corresponding alcohols or alkanes. ...
... • Carboxylic acids have significantly higher boiling points than their corresponding alcohols or alkanes. ...
Spectroscopy
... Spectroscopy Introduction Many substances absorb light at one wavelength and emit it at another. We make use of this in many ways, for example in glow-in-the-dark stickers. Compounds can also absorb and emit radiation that we cannot see, such as infrared, microwave and ultraviolet radiation. Finding ...
... Spectroscopy Introduction Many substances absorb light at one wavelength and emit it at another. We make use of this in many ways, for example in glow-in-the-dark stickers. Compounds can also absorb and emit radiation that we cannot see, such as infrared, microwave and ultraviolet radiation. Finding ...
Chapter 12: IR Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry
... lot of structural information, at this point you should only focus at trying to identify the M+ as this will indicate what is the mass of your compound. Be careful since next to M+ it is possible to observe M+ + 1 (due to the contribution of 13C) ...
... lot of structural information, at this point you should only focus at trying to identify the M+ as this will indicate what is the mass of your compound. Be careful since next to M+ it is possible to observe M+ + 1 (due to the contribution of 13C) ...
Chemistry for Changing Times 11th Edition Hill and Kolb
... Their names begin with a prefix denoting the number of carbon atoms followed by the suffix –yne. Ethyne (acetylene) is the simplest alkyne. ...
... Their names begin with a prefix denoting the number of carbon atoms followed by the suffix –yne. Ethyne (acetylene) is the simplest alkyne. ...
Study Guide – Solutions, Acids, and Bases Solutions: Describe the
... solution (completely let go of H+ ions) while weak acids only partially ionize/break apart. 27. How do you make a strong acid weak? OMIT 28. List the strong acids. HCl, HBr, HF 29. How do you know if a base is strong? Lets go off all of its OH- ions in solution 30. What is a titration? Uses a neutra ...
... solution (completely let go of H+ ions) while weak acids only partially ionize/break apart. 27. How do you make a strong acid weak? OMIT 28. List the strong acids. HCl, HBr, HF 29. How do you know if a base is strong? Lets go off all of its OH- ions in solution 30. What is a titration? Uses a neutra ...
PHYSICOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF ORGANIC MEDICINAL
... As in the case of the alcohols, the -OH function of phenols provides a dipole that significantly affects the physicochemical properties. The aromatic portion of phenols is relatively non-polar (lipophilic), thus phenols exhibit limited water solubility. Also, addition of lipophilic substituents to t ...
... As in the case of the alcohols, the -OH function of phenols provides a dipole that significantly affects the physicochemical properties. The aromatic portion of phenols is relatively non-polar (lipophilic), thus phenols exhibit limited water solubility. Also, addition of lipophilic substituents to t ...
BioN02 Introduction to organic chemistry Summer 2014
... CH3NH2 (a primary amine): methyl amine Secondary and tertiary amines are named by alphabetizing the R groups and then adding amine This is a 2o amine with two different R groups, ethyl and methyl. This is ethylmethylamine. ...
... CH3NH2 (a primary amine): methyl amine Secondary and tertiary amines are named by alphabetizing the R groups and then adding amine This is a 2o amine with two different R groups, ethyl and methyl. This is ethylmethylamine. ...
Wood Chemistry PSE 406/Chem E 470
... reactive species) to do the dirty work. A good example of this are the manganese peroxidases. In this system, the enzyme oxidizes Mn2+ to the powerful oxidant Mn3+ which can penetrate the cell wall to react with cell wall components. Many of the small radicals are produced through reaction of the en ...
... reactive species) to do the dirty work. A good example of this are the manganese peroxidases. In this system, the enzyme oxidizes Mn2+ to the powerful oxidant Mn3+ which can penetrate the cell wall to react with cell wall components. Many of the small radicals are produced through reaction of the en ...
Aldehyde and Ketone Identification
... It may take 15 minutes or gentle heating to achieve color change ...
... It may take 15 minutes or gentle heating to achieve color change ...
Chemistry 209 - Experiment 3, Spring 2003
... Hexane Solubility Test. Only non-polar compounds will dissolve in this very non-polar alkane solvent. Reactivity with 3 M HCl(aq). This acid reacts with basic organic compounds such as amines. Signs of reaction include heat evolution and dissolution. (If a compound does not dissolve in water but doe ...
... Hexane Solubility Test. Only non-polar compounds will dissolve in this very non-polar alkane solvent. Reactivity with 3 M HCl(aq). This acid reacts with basic organic compounds such as amines. Signs of reaction include heat evolution and dissolution. (If a compound does not dissolve in water but doe ...
video slide
... Enantiomers differ in spatial arrangement around an asymmetric carbon, resulting in molecules that are mirror images, like left and right hands. The two isomers are designated the L and D isomers from the Latin for left and right (levo and dextro). Enantiomers cannot be superimposed ...
... Enantiomers differ in spatial arrangement around an asymmetric carbon, resulting in molecules that are mirror images, like left and right hands. The two isomers are designated the L and D isomers from the Latin for left and right (levo and dextro). Enantiomers cannot be superimposed ...
Identification of Unknown Organic Compounds
... conversion of the purple ion MnO4- to a brown precipitate of MnO2 following the oxidation of an unsaturated compound. ...
... conversion of the purple ion MnO4- to a brown precipitate of MnO2 following the oxidation of an unsaturated compound. ...
Chemistry for the Health Sciences II
... 1. Identify and name compounds containing the different functional groups of oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur; 2. Demonstrate an understanding of the relationship between alcohols, aldehydes and ketones as organic chemicals and the biochemical molecules, carbohydrates; 3. Identify and name carboxylic aci ...
... 1. Identify and name compounds containing the different functional groups of oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur; 2. Demonstrate an understanding of the relationship between alcohols, aldehydes and ketones as organic chemicals and the biochemical molecules, carbohydrates; 3. Identify and name carboxylic aci ...
Unit 1: METABOLIC PROCESSES - Emery
... The building blocks (monomers) of macromolecules are amino acids, nucleotides, simple sugars, and fatty acids ...
... The building blocks (monomers) of macromolecules are amino acids, nucleotides, simple sugars, and fatty acids ...
Germ-a-CLENZ: All-purpose Antimicrobial Spray
... Thymol is a plant substance found in oil of thyme, extracted from Thymus vulgaris (common thyme) Class of naturally occurring plant compounds called biocides: Contain strong antimicrobial properties, especially when used in conjunction with carvacrol (also a plant biocide) Additional properties incl ...
... Thymol is a plant substance found in oil of thyme, extracted from Thymus vulgaris (common thyme) Class of naturally occurring plant compounds called biocides: Contain strong antimicrobial properties, especially when used in conjunction with carvacrol (also a plant biocide) Additional properties incl ...
Critical Thinking Question (cont`d.)
... What is Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning (POGIL)? POGIL is a classroom and laboratory technique that seeks to simultaneously teach content and key process skills such as the ability to think analytically and work effectively as part of a collaborative team. POGIL is based on research indica ...
... What is Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning (POGIL)? POGIL is a classroom and laboratory technique that seeks to simultaneously teach content and key process skills such as the ability to think analytically and work effectively as part of a collaborative team. POGIL is based on research indica ...
f3234 mod 1 revision guide rings acids and amines
... In a phenol the OH group is directly attached to the benzene ring. In a phenol the lone pair of electrons on the oxygen is delocalised with the electron charge cloud of the arene ring. The delocalised bonding changes the reactivity of the OH group and the arene ring. ...
... In a phenol the OH group is directly attached to the benzene ring. In a phenol the lone pair of electrons on the oxygen is delocalised with the electron charge cloud of the arene ring. The delocalised bonding changes the reactivity of the OH group and the arene ring. ...
Organic Compounds
... Models are often used by chemists to visualize molecular structures. Structural differences between functional groups provide reasons for differences in chemical reactivity. In preparation for this laboratory exercise, review the sections in your text book pertaining to molecular structure of compou ...
... Models are often used by chemists to visualize molecular structures. Structural differences between functional groups provide reasons for differences in chemical reactivity. In preparation for this laboratory exercise, review the sections in your text book pertaining to molecular structure of compou ...
Experiment 10 — Qualitative Analysis
... Perhaps more important for our purposes, these tests will familiarize us with the chemical behavior of a variety of different compounds, they'll give us a chance to learn some new chemistry, and — gosh darn it — they're just plain old fashioned fun. In this lab you will use qualitative chemical test ...
... Perhaps more important for our purposes, these tests will familiarize us with the chemical behavior of a variety of different compounds, they'll give us a chance to learn some new chemistry, and — gosh darn it — they're just plain old fashioned fun. In this lab you will use qualitative chemical test ...
Marine Cyanobacteria Source of Lead Compounds of
... Apratoxin A (126) is another potent cytotoxic compound worthy of further biological investigation as anticancer agent due to it mechanism of action in attenuating the FGF (fibroblast growth factor) signaling pathway. FGF are a family of growth factors, with members involved in angiogenesis, wound he ...
... Apratoxin A (126) is another potent cytotoxic compound worthy of further biological investigation as anticancer agent due to it mechanism of action in attenuating the FGF (fibroblast growth factor) signaling pathway. FGF are a family of growth factors, with members involved in angiogenesis, wound he ...
Chapter 3 Carboxylic Acids
... C=O with -OH bonded to the same carbon. Carboxyl group is usually written -COOH. Aliphatic acids have an alkyl group bonded to COOH. Aromatic acids have an aryl group. Fatty acids are long-chain aliphatic acids. ...
... C=O with -OH bonded to the same carbon. Carboxyl group is usually written -COOH. Aliphatic acids have an alkyl group bonded to COOH. Aromatic acids have an aryl group. Fatty acids are long-chain aliphatic acids. ...
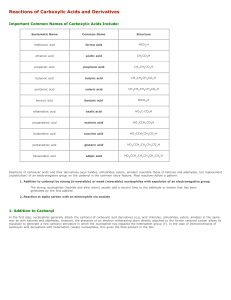
Reactions of Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives
... In the first step, nucleophiles generally attack the carbonyl of carboxylic acid derivatives (e.g. acid chlorides, anhydrides, esters, amides) in the same way as with ketones and aldehydes. However, the presence of an electron withdrawing atom directly attached to the former carbonyl carbon allows i ...
... In the first step, nucleophiles generally attack the carbonyl of carboxylic acid derivatives (e.g. acid chlorides, anhydrides, esters, amides) in the same way as with ketones and aldehydes. However, the presence of an electron withdrawing atom directly attached to the former carbonyl carbon allows i ...
Get Notes - Mindset Learn
... A laboratory assistant uses bromine water to distinguish between compounds D and E. She adds bromine water to a sample of each in two different test tubes. She observes that the one compound decolourises the bromine water immediately, whilst the other one only reacts after placing the test tube in d ...
... A laboratory assistant uses bromine water to distinguish between compounds D and E. She adds bromine water to a sample of each in two different test tubes. She observes that the one compound decolourises the bromine water immediately, whilst the other one only reacts after placing the test tube in d ...
File
... halide (usually primary) and sodium cyanide by an SN2 displacement, as shown in this synthesis of an acid: ...
... halide (usually primary) and sodium cyanide by an SN2 displacement, as shown in this synthesis of an acid: ...
Phenols

In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.Synonyms are arenols or aryl alcohols.Phenolic compounds are synthesized industrially; they also are produced by plants and microorganisms, with variation between and within species.Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12).Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides, although the term aryloxides is preferred according to the IUPAC Gold Book. Phenols can have two or more hydroxy groups bonded to the aromatic ring(s) in the same molecule. The simplest examples are the three benzenediols, each having two hydroxy groups on a benzene ring.Organisms that synthesize phenolic compounds do so in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research.ref name=Klepacka Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants. Others possess estrogenic or endocrine disrupting activity.