CHEM 202_ Part 2
... Acid strength It is the extent of ionization of acid in water. The greater the amount of ionization, the stronger is the acid. The acidity of carboxylic compounds depends on its structure. ...
... Acid strength It is the extent of ionization of acid in water. The greater the amount of ionization, the stronger is the acid. The acidity of carboxylic compounds depends on its structure. ...
carboxylic acids and their derivatives
... Conjugation within the carbonyl group increases not only acidity of a compound but also basic properties of the double-bonded oxygen as compared with that of carbonyl compounds. This explains the fact that carboxylic acids exist normally in an associated form with strong intermolecular hydrogen bon ...
... Conjugation within the carbonyl group increases not only acidity of a compound but also basic properties of the double-bonded oxygen as compared with that of carbonyl compounds. This explains the fact that carboxylic acids exist normally in an associated form with strong intermolecular hydrogen bon ...
Quiz 2 - MSU Chemistry
... 2. 2-butanol shows the base peak (highest intensity) in its mass spectrum at m/z = 45. Draw the molecular ion of 2-butanol (M ) and the fragmentation mechanism that leads to this peak. Use these molecular masses in your calculations: C = 12; O = 16; H = 1. ...
... 2. 2-butanol shows the base peak (highest intensity) in its mass spectrum at m/z = 45. Draw the molecular ion of 2-butanol (M ) and the fragmentation mechanism that leads to this peak. Use these molecular masses in your calculations: C = 12; O = 16; H = 1. ...
2010 Fall Final key
... 16. A(n) peptide bond is an amide functional group that forms when the carboxylic acid group on one amino acid reacts with the amine group of another amino acid. 17. A(n) disulfide bond is a covalent bond between two sulfur atoms of two different amino acids in a protein molecule. 18. A(n) salt bri ...
... 16. A(n) peptide bond is an amide functional group that forms when the carboxylic acid group on one amino acid reacts with the amine group of another amino acid. 17. A(n) disulfide bond is a covalent bond between two sulfur atoms of two different amino acids in a protein molecule. 18. A(n) salt bri ...
DETERMINING THE CONCENTRATION OF A SOLUTION:
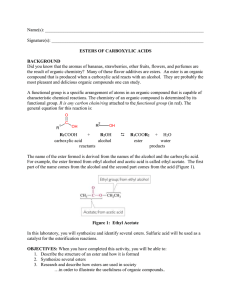
... Did you know that the aromas of bananas, strawberries, other fruits, flowers, and perfumes are the result of organic chemistry? Many of these flavor additives are esters. An ester is an organic compound that is produced when a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol. They are probably the most pleasa ...
... Did you know that the aromas of bananas, strawberries, other fruits, flowers, and perfumes are the result of organic chemistry? Many of these flavor additives are esters. An ester is an organic compound that is produced when a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol. They are probably the most pleasa ...
Chem 51A Chapter 3 2014
... How are ions transported across the cell membrane? Some ions are transported across the membrane with the help of ionophores. Ionophores are organic molecules that complex cations. They have a hydrophobic exterior that makes them soluble in the nonpolar interior of the cell membrane, and a central c ...
... How are ions transported across the cell membrane? Some ions are transported across the membrane with the help of ionophores. Ionophores are organic molecules that complex cations. They have a hydrophobic exterior that makes them soluble in the nonpolar interior of the cell membrane, and a central c ...
the Note
... Hydrocarbons – organic molecules that are made up of carbon and hydrogen atoms only. Homologous series – a family of organic molecules which are identified by the same functional group and obey the same general formula. Functional group – a bond, atom or group of atoms which identifies to which homo ...
... Hydrocarbons – organic molecules that are made up of carbon and hydrogen atoms only. Homologous series – a family of organic molecules which are identified by the same functional group and obey the same general formula. Functional group – a bond, atom or group of atoms which identifies to which homo ...
Ethers
... synonyms for oxolane and oxane, respectively. Many substances have more than one ether linkage. Two such compounds, often used as solvents, are the diethers 1,2-dimethoxyethane and 1,4-dioxane. Diglyme, also a commonly used solvent, is a triether. ...
... synonyms for oxolane and oxane, respectively. Many substances have more than one ether linkage. Two such compounds, often used as solvents, are the diethers 1,2-dimethoxyethane and 1,4-dioxane. Diglyme, also a commonly used solvent, is a triether. ...
Carbonyl Compounds_ Properties and Reactions
... Carbonyls show a limited/lack of hydrogen bonding between molecules, whereas the corresponding alcohol will show extensive intermolecular H bonding. Weaker polarity means aldehydes and ketones mix well with polar solvents such as water and will dissolve many organic compounds. ...
... Carbonyls show a limited/lack of hydrogen bonding between molecules, whereas the corresponding alcohol will show extensive intermolecular H bonding. Weaker polarity means aldehydes and ketones mix well with polar solvents such as water and will dissolve many organic compounds. ...
Chapter 19 Carboxylic Acids
... equilibrium lies far to the right; K is ~ 1011 as long as the molecular weight of the acid is not too high, sodium and potassium carboxylate salts are soluble in water ...
... equilibrium lies far to the right; K is ~ 1011 as long as the molecular weight of the acid is not too high, sodium and potassium carboxylate salts are soluble in water ...
Alcohols, acids and esters
... To introduce esters as products of the reactions of alcohols with carboxylic acids To observe properties of esters To demonstrate the procedure for making an ester on a laboratory scale To explain the purposes of practical techniques involved in the preparation of an ester ...
... To introduce esters as products of the reactions of alcohols with carboxylic acids To observe properties of esters To demonstrate the procedure for making an ester on a laboratory scale To explain the purposes of practical techniques involved in the preparation of an ester ...
Functional Group Chemistry
... compound and determine what functional group(s) are present. To use any reaction as a test for a functional group, it is necessary for the product mixture to appear significantly different from the reactants. This may be due to formation of a precipitate or coloured product, or it may be due to cons ...
... compound and determine what functional group(s) are present. To use any reaction as a test for a functional group, it is necessary for the product mixture to appear significantly different from the reactants. This may be due to formation of a precipitate or coloured product, or it may be due to cons ...
BELLARMINE COLLEGE
... worth of the question (shown in parenthesis after the question). Write legibly. Marks will be deducted for unclear, messy and illegible work. You must show all calculations (including units) where appropriate. Also, remember to show answers to the correct number of significant figures. Answer in the ...
... worth of the question (shown in parenthesis after the question). Write legibly. Marks will be deducted for unclear, messy and illegible work. You must show all calculations (including units) where appropriate. Also, remember to show answers to the correct number of significant figures. Answer in the ...
Drawing Organic Structures Functional Groups Constitutional Isomers
... Nonaromatic • Either not cyclic, or not conjugated, or not planar • Examples: • Not cyclic: • Not conjugated: ...
... Nonaromatic • Either not cyclic, or not conjugated, or not planar • Examples: • Not cyclic: • Not conjugated: ...
Document
... Lower members of amines are _____________ with a smell of ___________; while the higher ones are liquids with a distinctive ____________ smell. Amines have ___________ boiling points than less polar compounds due to its ______________ bonding; but they have __________ boiling points than alcohol ...
... Lower members of amines are _____________ with a smell of ___________; while the higher ones are liquids with a distinctive ____________ smell. Amines have ___________ boiling points than less polar compounds due to its ______________ bonding; but they have __________ boiling points than alcohol ...
Online edition for students of organic chemistry lab
... Reading: Organic Chemistry by Francis Carey, 5th edition, pp. 87-90 (2.19); pp. 641-645 (15.10). Technique: Extraction. ...
... Reading: Organic Chemistry by Francis Carey, 5th edition, pp. 87-90 (2.19); pp. 641-645 (15.10). Technique: Extraction. ...
Long-Range Coupling
... Aromatics: Long-Range Coupling H’s on aromatic rings may couple with non-neighboring protons due to long-range coupling. You will see this in lab! Why? Nuclei “communicate” via bonding electrons - p electrons that are in resonance will allow non-neighboring H’s to “communicate” and couple/split. Thi ...
... Aromatics: Long-Range Coupling H’s on aromatic rings may couple with non-neighboring protons due to long-range coupling. You will see this in lab! Why? Nuclei “communicate” via bonding electrons - p electrons that are in resonance will allow non-neighboring H’s to “communicate” and couple/split. Thi ...
Chemistry
... 16. Chlorobenzene preferentially gives o- or p- derivatives on electrophilic substitution. Explain this with the concept of resonance 17. Why Sandmeyer’s reaction is considered to be an effective method in organic synthesis? ...
... 16. Chlorobenzene preferentially gives o- or p- derivatives on electrophilic substitution. Explain this with the concept of resonance 17. Why Sandmeyer’s reaction is considered to be an effective method in organic synthesis? ...
Functional Groups: Centers of Reactivity
... hydrogen and carbon. Alkanes are compounds of hydrogen and carbon which contain only single bonds. ...
... hydrogen and carbon. Alkanes are compounds of hydrogen and carbon which contain only single bonds. ...
Naming the Carboxylic Acids
... polarized molecules such as water, alcohols and other carboxylic acids. Carboxylic acids up to butanoic acid are completely soluble in water. As neat liquids, and even in fairly dilute solutions, carboxylic acids form hydrogenbonded dimers (6–8 kcal mol-1). ...
... polarized molecules such as water, alcohols and other carboxylic acids. Carboxylic acids up to butanoic acid are completely soluble in water. As neat liquids, and even in fairly dilute solutions, carboxylic acids form hydrogenbonded dimers (6–8 kcal mol-1). ...
Chapter 19 Summary - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Protonation of the carbonyl oxygen activates the carbonyl group toward nucleophilic addition. Addition of an alcohol gives a tetrahedral intermediate (shown in the box in the preceding equation), which has the capacity to revert to starting materials or to undergo dehydration to yield an ester. Sect ...
... Protonation of the carbonyl oxygen activates the carbonyl group toward nucleophilic addition. Addition of an alcohol gives a tetrahedral intermediate (shown in the box in the preceding equation), which has the capacity to revert to starting materials or to undergo dehydration to yield an ester. Sect ...
Phenols

In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.Synonyms are arenols or aryl alcohols.Phenolic compounds are synthesized industrially; they also are produced by plants and microorganisms, with variation between and within species.Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12).Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides, although the term aryloxides is preferred according to the IUPAC Gold Book. Phenols can have two or more hydroxy groups bonded to the aromatic ring(s) in the same molecule. The simplest examples are the three benzenediols, each having two hydroxy groups on a benzene ring.Organisms that synthesize phenolic compounds do so in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research.ref name=Klepacka Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants. Others possess estrogenic or endocrine disrupting activity.