Esters - chymist.com
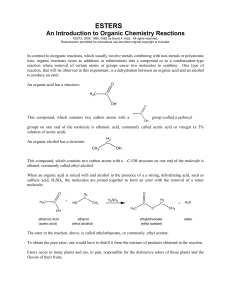
... In contrast to inorganic reactions, which usually involve metals combining with non-metals or polyatomic ions, organic reactions occur as additions or substitutions into a compound or as a condensation-type reaction where removal of certain atoms or groups cause two molecules to combine. One type of ...
... In contrast to inorganic reactions, which usually involve metals combining with non-metals or polyatomic ions, organic reactions occur as additions or substitutions into a compound or as a condensation-type reaction where removal of certain atoms or groups cause two molecules to combine. One type of ...
Practice Problem - HCC Southeast Commons
... • There are two nonsuperimposable ways that 4 different groups (or atoms) can be attached to one carbon atom – If two groups are the same, then there is only one way ...
... • There are two nonsuperimposable ways that 4 different groups (or atoms) can be attached to one carbon atom – If two groups are the same, then there is only one way ...
MacWorks - Horace Mann Webmail
... pentanoic acid (valeric) Acid #2 propanoic acid Acid #3 formic acid Acid #6 Concentrated Sulfuric Acid which will be on teacher’s bench. ...
... pentanoic acid (valeric) Acid #2 propanoic acid Acid #3 formic acid Acid #6 Concentrated Sulfuric Acid which will be on teacher’s bench. ...
PowerPoint for Part 1 - Dr. Samples` Chemistry Classes
... Properties of Alkanes • When an alkane (or any hydrocarbon) combusts, the two ideal products are carbon dioxide and water, although carbon monoxide and other unwanted products are made as well. • Of course, combustion reactions are exothermic, so a great deal of useful heat is given off as well. • ...
... Properties of Alkanes • When an alkane (or any hydrocarbon) combusts, the two ideal products are carbon dioxide and water, although carbon monoxide and other unwanted products are made as well. • Of course, combustion reactions are exothermic, so a great deal of useful heat is given off as well. • ...
Alcohols, phenols and ethers
... • Find longest, continuous C-chain to which the OH group (hydroxyl) is bound. Number the chain in a way that gives the OH group the lowest numbering. • Name and number other substituents present. • The name for the corresponding alkane chain (e.g. for a 6-C chain, hexane) loses the “e” and picks up ...
... • Find longest, continuous C-chain to which the OH group (hydroxyl) is bound. Number the chain in a way that gives the OH group the lowest numbering. • Name and number other substituents present. • The name for the corresponding alkane chain (e.g. for a 6-C chain, hexane) loses the “e” and picks up ...
Chemistry of Carbon - Churchill High School
... Long molecules built by linking repeating building blocks in a chain ...
... Long molecules built by linking repeating building blocks in a chain ...
Study Guide 1 - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... This activity demonstrates how much of the Organic Chemistry met in this Unit will be taught within the context of Kitchen Chemistry Flavour Most of our ‘tasting’ is done through our noses, so most flavour molecules are volatile (weak intermolecular forces) such as esters - many have sweet f ...
... This activity demonstrates how much of the Organic Chemistry met in this Unit will be taught within the context of Kitchen Chemistry Flavour Most of our ‘tasting’ is done through our noses, so most flavour molecules are volatile (weak intermolecular forces) such as esters - many have sweet f ...
LABORATORY 5 DETECTION OF FUNCTIONAL GROUPS IN
... Ferric chloride reacts with the hydroxyl groups of phenols and phenol derivatives and forms stable-colored complexes: violet, violet-bluish, blue, green and red. This reaction depends on the structure and presence of complex-created groups (aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic, hydroxyl, or sulfonic) locate ...
... Ferric chloride reacts with the hydroxyl groups of phenols and phenol derivatives and forms stable-colored complexes: violet, violet-bluish, blue, green and red. This reaction depends on the structure and presence of complex-created groups (aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic, hydroxyl, or sulfonic) locate ...
15_12_13rw
... 1. Hydrogen bonding is much weaker in thiols than in alcohols (S—H bond is less polar than O—H). 2. Low molecular weight thiols have foul odors. 3. Thiols are stronger acids than alcohols. 4. Thiols are more easily oxidized than alcohols; ...
... 1. Hydrogen bonding is much weaker in thiols than in alcohols (S—H bond is less polar than O—H). 2. Low molecular weight thiols have foul odors. 3. Thiols are stronger acids than alcohols. 4. Thiols are more easily oxidized than alcohols; ...
Unit 2
... addition polymer and work out its repeat unit and the monomer from which it was formed. • The repeat unit of an addition polymer is always only two carbon atoms long. ...
... addition polymer and work out its repeat unit and the monomer from which it was formed. • The repeat unit of an addition polymer is always only two carbon atoms long. ...
Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
... As molecular weight increases for alcohols, they become more “alkanelike”. Long chain alcohols are less soluble in water and more soluble in nonpolar solvents, like benzene. ...
... As molecular weight increases for alcohols, they become more “alkanelike”. Long chain alcohols are less soluble in water and more soluble in nonpolar solvents, like benzene. ...
EXPERIMENT 9 (Organic Chemistry II) Pahlavan/Cherif
... Organic Chemistry is the study of compounds containing carbon. There are millions of organic compounds known because carbon atom has the unique ability to bond to other carbon atoms to from large molecules. In these compounds, carbon may be bonded to other carbons via single bonds, double bonds, and ...
... Organic Chemistry is the study of compounds containing carbon. There are millions of organic compounds known because carbon atom has the unique ability to bond to other carbon atoms to from large molecules. In these compounds, carbon may be bonded to other carbons via single bonds, double bonds, and ...
How to Name Alcohols
... The following is a list of Euphemisms in Science and their translations into plain English. ...
... The following is a list of Euphemisms in Science and their translations into plain English. ...
HIGHER CfE CHEMISTRY Nature`s Chemistry
... this experiment in the laboratory. b) Oxidation of propan-1-ol yields a compound X, formula C3H6O, which can be further oxidised to compound Y, formula C3H6O2. i) Name and draw the structure of compound X. ii) Name and draw the structure of compound Y. c) Name two other oxidising agents which could ...
... this experiment in the laboratory. b) Oxidation of propan-1-ol yields a compound X, formula C3H6O, which can be further oxidised to compound Y, formula C3H6O2. i) Name and draw the structure of compound X. ii) Name and draw the structure of compound Y. c) Name two other oxidising agents which could ...
Carboxylic Acids and Esters
... CARBOXYLIC ACIDS Carboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain the carboxyl group (COOH). The carboxyl group is always on a terminal carbon atom. Carboxylic acids are weak acids, since only a small fraction of acid molecules ionize when dissolved in water. They give up the hydrogen on the car ...
... CARBOXYLIC ACIDS Carboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain the carboxyl group (COOH). The carboxyl group is always on a terminal carbon atom. Carboxylic acids are weak acids, since only a small fraction of acid molecules ionize when dissolved in water. They give up the hydrogen on the car ...
Polyvalent Iodine in Synthesis (more than just Dess
... - [bis(trifluoroacetoxy)iodo]benzene - BTI - PhI(OCOCF3)2 - 50g ~$150 + Also can be used to make a TRAINLOAD of other [bis(acyloxy)iodo]arenes (WAY too many to partially list). + Attachment to make polymer-supported variations has also been detailed. + Most useful as an oxidant for alkenes, heteroat ...
... - [bis(trifluoroacetoxy)iodo]benzene - BTI - PhI(OCOCF3)2 - 50g ~$150 + Also can be used to make a TRAINLOAD of other [bis(acyloxy)iodo]arenes (WAY too many to partially list). + Attachment to make polymer-supported variations has also been detailed. + Most useful as an oxidant for alkenes, heteroat ...
alcohols ws 1 - Chesterhouse School
... (d) Lactic acid is chiral. Draw displayed formulae of the two optical isomers of lactic acid clearly showing their three-dimensional structures. Indicate with an asterisk (*) the chiral carbon atom in each. ...
... (d) Lactic acid is chiral. Draw displayed formulae of the two optical isomers of lactic acid clearly showing their three-dimensional structures. Indicate with an asterisk (*) the chiral carbon atom in each. ...
Uses of Phosphoric Acid
... phosphoric(V) acid is a mineral (inorganic) acid having the chemical formula H3PO4. Orthophosphoric acid molecules can combine with themselves to form a variety of compounds which are also referred to as phosphoric acids, but in a more general way. The term phosphoric acid can also refer to a che ...
... phosphoric(V) acid is a mineral (inorganic) acid having the chemical formula H3PO4. Orthophosphoric acid molecules can combine with themselves to form a variety of compounds which are also referred to as phosphoric acids, but in a more general way. The term phosphoric acid can also refer to a che ...
Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation
... (acetaldehyde), and then to CH3COO¯ (the acetate anion). • This oxidation is catalyzed by alcohol dehydrogenase. • If more ethanol is ingested than can be metabolized, the concentration of acetaldehyde increases. Acetaldehyde, which is toxic, is responsible for the feelings associated with a hangove ...
... (acetaldehyde), and then to CH3COO¯ (the acetate anion). • This oxidation is catalyzed by alcohol dehydrogenase. • If more ethanol is ingested than can be metabolized, the concentration of acetaldehyde increases. Acetaldehyde, which is toxic, is responsible for the feelings associated with a hangove ...
CaCl2.2H2O assisted oxidation of alcohols with (NH4)2Cr2O7
... dichromate in the presence of CaCl2.2H2O (Table I, Scheme I). The reaction is simply performed by stirring a mixture of alcohol, (NH4)2Cr2O7 and CaCl2.2H2O in an oil-bath (60°C) for the appropriate time (Table I). Alcohols were oxidized efficiently and the corresponding carbonyl compounds were isola ...
... dichromate in the presence of CaCl2.2H2O (Table I, Scheme I). The reaction is simply performed by stirring a mixture of alcohol, (NH4)2Cr2O7 and CaCl2.2H2O in an oil-bath (60°C) for the appropriate time (Table I). Alcohols were oxidized efficiently and the corresponding carbonyl compounds were isola ...
review sheet plus practice problems
... Give the chain mechanism for free radical halogenation. What is the selectivity for brominations vs. fluorinations? Why are allylic radicals more stable than other types? Draw resonance for all allylic radicals. What is the definition of oxidation? Which compound is at a higher oxidation state? Is t ...
... Give the chain mechanism for free radical halogenation. What is the selectivity for brominations vs. fluorinations? Why are allylic radicals more stable than other types? Draw resonance for all allylic radicals. What is the definition of oxidation? Which compound is at a higher oxidation state? Is t ...
Chemistry of Carbon - The Bronx High School of Science
... C double bonded to O & single bonded to OH group compounds with COOH = acids ...
... C double bonded to O & single bonded to OH group compounds with COOH = acids ...
Acids and Bases
... 2.6 How the Structure of an acid Affects its pKa • The stronger the acid, the weaker is its conjugate base! • The stronger the acid, the more stable is its conjugate base! Factors that influence stability of the conjugate base include: • Resonance • Electronegativity • Atomic Size • Hybridization ...
... 2.6 How the Structure of an acid Affects its pKa • The stronger the acid, the weaker is its conjugate base! • The stronger the acid, the more stable is its conjugate base! Factors that influence stability of the conjugate base include: • Resonance • Electronegativity • Atomic Size • Hybridization ...
Chapter 22 Organic Chemistry
... Organic Chemistry Chapter 22–Assignment A: Drawing and Naming Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Millions of compounds have been identified in the chemistry laboratories of the world. About 95% are classified as organic compounds. This chapter gives you a brief survey of this important area of chemistry. The ...
... Organic Chemistry Chapter 22–Assignment A: Drawing and Naming Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Millions of compounds have been identified in the chemistry laboratories of the world. About 95% are classified as organic compounds. This chapter gives you a brief survey of this important area of chemistry. The ...
Phenols

In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.Synonyms are arenols or aryl alcohols.Phenolic compounds are synthesized industrially; they also are produced by plants and microorganisms, with variation between and within species.Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12).Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides, although the term aryloxides is preferred according to the IUPAC Gold Book. Phenols can have two or more hydroxy groups bonded to the aromatic ring(s) in the same molecule. The simplest examples are the three benzenediols, each having two hydroxy groups on a benzene ring.Organisms that synthesize phenolic compounds do so in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research.ref name=Klepacka Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants. Others possess estrogenic or endocrine disrupting activity.