Medical Physics - University of Waterloo
... The Physics of Radiotherapy X-rays from Linear Accelerators, Metcalfe, P., Kron, T., Hoban, P., Medical Physics Publishing, Madison, Wisconsin, USA, (1997). Modern Technology of Radiation Oncology: A Compendium for Medical Physicists and Radiation Oncologists, Van Dyk, J., editor, Medical Physic ...
... The Physics of Radiotherapy X-rays from Linear Accelerators, Metcalfe, P., Kron, T., Hoban, P., Medical Physics Publishing, Madison, Wisconsin, USA, (1997). Modern Technology of Radiation Oncology: A Compendium for Medical Physicists and Radiation Oncologists, Van Dyk, J., editor, Medical Physic ...
X-ray generation, interaction and detection
... like light and radio frequency waves; • Like all other waves, X-rays are also Photons; this aspect is predominant • Energy of X-Rays is usually measured in eV and mostly its multiple: keV • For medical imaging, energy of photons ranges from ~10 keV to less than 150 keV. (visible light ~2eV) ...
... like light and radio frequency waves; • Like all other waves, X-rays are also Photons; this aspect is predominant • Energy of X-Rays is usually measured in eV and mostly its multiple: keV • For medical imaging, energy of photons ranges from ~10 keV to less than 150 keV. (visible light ~2eV) ...
Dose reduction in maxillofacial imaging using low dose
... Effective dose was estimated according to ICRP60 report (EICRP ). An additional estimation of the effective dose was accomplished including the doses of the salivary glands (ESAL ). A Wilcoxon Signed Ranks Test was used for statistical analysis. Results: In the non-shielding technique the absorbed d ...
... Effective dose was estimated according to ICRP60 report (EICRP ). An additional estimation of the effective dose was accomplished including the doses of the salivary glands (ESAL ). A Wilcoxon Signed Ranks Test was used for statistical analysis. Results: In the non-shielding technique the absorbed d ...
National Diagnostic Reference Levels Factsheet
... doses of common protocols as recorded from data submitted to the National Diagnostic Reference Level Service. A local facility reference level (FRL) is defined as the median value of the spread of doses for common protocols surveyed at the local radiology facility. The development of DRLs will be de ...
... doses of common protocols as recorded from data submitted to the National Diagnostic Reference Level Service. A local facility reference level (FRL) is defined as the median value of the spread of doses for common protocols surveyed at the local radiology facility. The development of DRLs will be de ...
NSS-MIC-todd-Poster
... same mean subject dose of 4 cGy. The rationale for the present work is the large slope of the dose versus depth curve (solid red in Fig. 1 for monochromatic protons) at the distal edge of the Bragg peak, producing large image sensitivity to density variations. Experimental results from PSI show that ...
... same mean subject dose of 4 cGy. The rationale for the present work is the large slope of the dose versus depth curve (solid red in Fig. 1 for monochromatic protons) at the distal edge of the Bragg peak, producing large image sensitivity to density variations. Experimental results from PSI show that ...
Dose assessment in Nuclear Medicine Therapy
... The mean absorbed dose required to yield a surviving fraction equal to that arising from the probability distribution of dose values (absorbed dose or BED) given by the normalized DVH. Sgouros G et al Semin nucl Med 2008 ...
... The mean absorbed dose required to yield a surviving fraction equal to that arising from the probability distribution of dose values (absorbed dose or BED) given by the normalized DVH. Sgouros G et al Semin nucl Med 2008 ...
Basics of nuclear physics
... Eqivalent dose = Q. Absorbed dose Q is quality factor. For alpha particles, it equals 20, for neutrons from 5 to 20 (depending on energy), and for beta particles, X and gamma photons- 1 ...
... Eqivalent dose = Q. Absorbed dose Q is quality factor. For alpha particles, it equals 20, for neutrons from 5 to 20 (depending on energy), and for beta particles, X and gamma photons- 1 ...
Interpretation of measured dose data in X
... Patient dose determination is an essential part of the process of optimizing between adequate image quality and radiation detriment in diagnostic radiology. The radiation dose from an X-ray examination is needed to estimate the radiation-induced risk of cancer to the patient. Risk estimates are norm ...
... Patient dose determination is an essential part of the process of optimizing between adequate image quality and radiation detriment in diagnostic radiology. The radiation dose from an X-ray examination is needed to estimate the radiation-induced risk of cancer to the patient. Risk estimates are norm ...
CT Accreditation Program: Image Quality and Dose
... Volume CTDIW (CTDIvol) CTDIvol = CTDIW • N • T / I where I = the table increment per axial scan, or the table increment per rotation of the x-ray tube in a helical scan. In helical CT, the term pitch (P) is defined as the ratio of the table increment per tube rotation to the nominal (total) width of ...
... Volume CTDIW (CTDIvol) CTDIvol = CTDIW • N • T / I where I = the table increment per axial scan, or the table increment per rotation of the x-ray tube in a helical scan. In helical CT, the term pitch (P) is defined as the ratio of the table increment per tube rotation to the nominal (total) width of ...
CT Dose Summit 2011
... Number : Know Your History and Current Events • Know the (medical and societal) culture we work within and why we have the policies, regulations, and beliefs we do • Keep up with current media to understand what our patients and referring physicians know, don’t know, are afraid of, and expect from u ...
... Number : Know Your History and Current Events • Know the (medical and societal) culture we work within and why we have the policies, regulations, and beliefs we do • Keep up with current media to understand what our patients and referring physicians know, don’t know, are afraid of, and expect from u ...
CT Dose Summit 2011
... Number : Know Your History and Current Events • Know the (medical and societal) culture we work within and why we have the policies, regulations, and beliefs we do • Keep up with current media to understand what our patients and referring physicians know, don’t know, are afraid of, and expect from u ...
... Number : Know Your History and Current Events • Know the (medical and societal) culture we work within and why we have the policies, regulations, and beliefs we do • Keep up with current media to understand what our patients and referring physicians know, don’t know, are afraid of, and expect from u ...
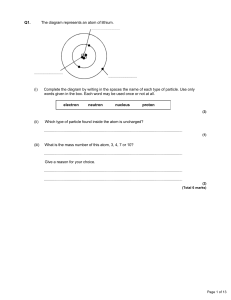
Radiation Questions March 4th
... Complete the diagram by writing in the spaces the name of each type of particle. Use only words given in the box. Each word may be used once or not at all. electron ...
... Complete the diagram by writing in the spaces the name of each type of particle. Use only words given in the box. Each word may be used once or not at all. electron ...
How to Create a World Class Dose Reduction Program
... Establishing a healthy dose reduction program at most facilities is about a one year project, with some larger or more complex facilities taking up to two years. With respect to assigning responsibilities, if there is an in-house diagnostic medical physicist (not a therapy medical physicist, as ther ...
... Establishing a healthy dose reduction program at most facilities is about a one year project, with some larger or more complex facilities taking up to two years. With respect to assigning responsibilities, if there is an in-house diagnostic medical physicist (not a therapy medical physicist, as ther ...
DAP and effective dose
... From: L. Struelens, Optimisation of Patient Doses linked to Image Quality in Vascular Radiology, 2005 ...
... From: L. Struelens, Optimisation of Patient Doses linked to Image Quality in Vascular Radiology, 2005 ...
3 JCI dosimetry for CT
... where ET is the effective dose to an organ or tissue type T (Sv) DT,R is the absorbed dose to an organ or tissue T delivered by radiation type R (Gy) WR is the radiation weighting factor for radiation type R WT is the tissue weighting factor for an organ or tissue type T ...
... where ET is the effective dose to an organ or tissue type T (Sv) DT,R is the absorbed dose to an organ or tissue T delivered by radiation type R (Gy) WR is the radiation weighting factor for radiation type R WT is the tissue weighting factor for an organ or tissue type T ...
Dose Reduction and Artifacts in CT
... Dose Alert Levels are typically much higher than Notification Levels and take into account all series within the exam Triggering a Dose Alert requires that the operator confirm the protocol and settings are correct by entering in his or her name. Optionally, sites may require that the operator provi ...
... Dose Alert Levels are typically much higher than Notification Levels and take into account all series within the exam Triggering a Dose Alert requires that the operator confirm the protocol and settings are correct by entering in his or her name. Optionally, sites may require that the operator provi ...
Waves notes section 5 - Nuclear radiation
... present. Some of the factors affecting background radiation levels are: • Rocks which contain radioactive material, exposing us to ionising particles • Cosmic rays from the sun and outer space which emit lots of protons which cause ionisation in our atmosphere • Building materials containing radioac ...
... present. Some of the factors affecting background radiation levels are: • Rocks which contain radioactive material, exposing us to ionising particles • Cosmic rays from the sun and outer space which emit lots of protons which cause ionisation in our atmosphere • Building materials containing radioac ...
RADIATION PROTECTION IN DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY
... • Justification in CT is of particular importance for RP • CT examination is a “high dose” procedure • A series of clinical factors play a special part – Adequate clinical information, including the records of previous imaging investigations, must be available – In certain applications prior investi ...
... • Justification in CT is of particular importance for RP • CT examination is a “high dose” procedure • A series of clinical factors play a special part – Adequate clinical information, including the records of previous imaging investigations, must be available – In certain applications prior investi ...
Appraisal of Radiation Dose Received in Abdominal Computed
... number of slices, rotation time, displayed CTDIvol and displayed DLP). Ethics and research committees at all hospitals approved the study and informed consent was obtained from all patients prior to the procedure. The patient dose estimation from CT examination using the Monte Carlo technique requir ...
... number of slices, rotation time, displayed CTDIvol and displayed DLP). Ethics and research committees at all hospitals approved the study and informed consent was obtained from all patients prior to the procedure. The patient dose estimation from CT examination using the Monte Carlo technique requir ...
Reducing Unnecessary Medical Imaging Exposure
... • FDA > Medical Devices > Industry Assistance – “Guidance Documents” ...
... • FDA > Medical Devices > Industry Assistance – “Guidance Documents” ...
Why Quantitative I-131
... Indications: Quantitative estimate of 131I in metastases or thyroid remnants requiring complete dosimetry to protect critical organs. Patient Preparation: This exam should not be performed if the patient has had any ...
... Indications: Quantitative estimate of 131I in metastases or thyroid remnants requiring complete dosimetry to protect critical organs. Patient Preparation: This exam should not be performed if the patient has had any ...
1 Comparison of Effective Dose and Lifetime Risk of Cancer
... TLDs for lymph nodes, muscle, bone surface and skin was not performed as they are large organs/systems and it was deemed these would contribute very little to the overall E and lifetime biological risk calculations as only a small proportion of the tissue would be exposed during the imaging process ...
... TLDs for lymph nodes, muscle, bone surface and skin was not performed as they are large organs/systems and it was deemed these would contribute very little to the overall E and lifetime biological risk calculations as only a small proportion of the tissue would be exposed during the imaging process ...
Document
... • increased radiosensitivity of certain tissues, particularly in infancy • longer lifetime for radiation-related cancer to occur(慢 性效應) • The thyroid gland, breast tissue, and gonads are structures that have an increased sensitivity to radiation in growing children. ...
... • increased radiosensitivity of certain tissues, particularly in infancy • longer lifetime for radiation-related cancer to occur(慢 性效應) • The thyroid gland, breast tissue, and gonads are structures that have an increased sensitivity to radiation in growing children. ...
WG-28-2014-12-02-Min-rev - Dicom
... diagnostic studies and discussed how to move forward on the recommendations from this TG to make changes to the CT and XA RDSR. 3. Develop Patient Radiation Dose Structured Reportand potential requirments for Patient Dose SR Reviewed the progress on current template development and start work on TID ...
... diagnostic studies and discussed how to move forward on the recommendations from this TG to make changes to the CT and XA RDSR. 3. Develop Patient Radiation Dose Structured Reportand potential requirments for Patient Dose SR Reviewed the progress on current template development and start work on TID ...
Managing the imaging dose during Image-guided Radiotherapy Martin J Murphy PhD
... Summing doses • Because of the differing qualities of kV, planar, CT, and MV exposures the doses should only be compared and summed in units of “effective dose”, which represents the approximate stochastic risk associated with a given integral dose ...
... Summing doses • Because of the differing qualities of kV, planar, CT, and MV exposures the doses should only be compared and summed in units of “effective dose”, which represents the approximate stochastic risk associated with a given integral dose ...