Pediatric Doses
... Z-axis Beam Modulation • Scanner determines changes in attenuation along z-axis from scout study • mA changed as patient moves through gantry ...
... Z-axis Beam Modulation • Scanner determines changes in attenuation along z-axis from scout study • mA changed as patient moves through gantry ...
Radiation Safety - Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and
... the product of air kerma and x-ray field area. PKA estimates potential stochastic effects (radiation induced cancer). Peak Skin Dose (PSD, Gy) is the maximum dose received by any local area of patient skin. No current method to measure PSD, it can be estimated if air kerma and x-ray geometry details ...
... the product of air kerma and x-ray field area. PKA estimates potential stochastic effects (radiation induced cancer). Peak Skin Dose (PSD, Gy) is the maximum dose received by any local area of patient skin. No current method to measure PSD, it can be estimated if air kerma and x-ray geometry details ...
Influence of CBCT exposure conditions on radiation dose
... tions. Along with all exposed TLDs, a set of unexposed control TLDs was also sent back to Landauer for reading. Landauer reported the results as dose equivalents in millirems. The values were then converted to modern SI units (gray and sievert). The data were entered into a spreadsheet and analyzed ...
... tions. Along with all exposed TLDs, a set of unexposed control TLDs was also sent back to Landauer for reading. Landauer reported the results as dose equivalents in millirems. The values were then converted to modern SI units (gray and sievert). The data were entered into a spreadsheet and analyzed ...
Glossary of Technical Terms - Institute for Energy and Environmental
... fissile material A material consisting of atoms whose nuclei can be split when irradiated with low energy (ideally, zero energy) neutrons. Well-known examples are plutonium-239 and uranium-235. fast reactor A reactor that is designed to use fast neutrons for sustaining the nuclear chain reaction. Fa ...
... fissile material A material consisting of atoms whose nuclei can be split when irradiated with low energy (ideally, zero energy) neutrons. Well-known examples are plutonium-239 and uranium-235. fast reactor A reactor that is designed to use fast neutrons for sustaining the nuclear chain reaction. Fa ...
CT Dose Summit 2011
... more commonly than adults – When children have cancer, they have sarcomas whereas adults have carcinomas. These cancers occur in different places and act differently. ...
... more commonly than adults – When children have cancer, they have sarcomas whereas adults have carcinomas. These cancers occur in different places and act differently. ...
Dosimetry/ Radiation Therapy Terms
... 84) Cone beam CT (CBCT) - based image guided systems have been integrated with medical linear accelerators to great success. With improvements in flat-panel technology, CBCT has been able to provide volumetric imaging, and allows for radiographic or fluoroscopic monitoring throughout the treatment p ...
... 84) Cone beam CT (CBCT) - based image guided systems have been integrated with medical linear accelerators to great success. With improvements in flat-panel technology, CBCT has been able to provide volumetric imaging, and allows for radiographic or fluoroscopic monitoring throughout the treatment p ...
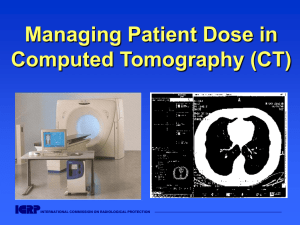
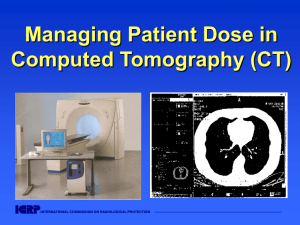
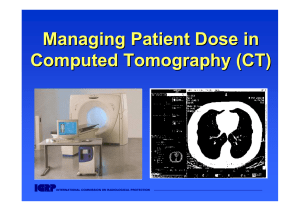
Managing Patient Dose in Computed Tomography (CT)
... This slide set is intended to be used with the complete text provided in ICRP ...
... This slide set is intended to be used with the complete text provided in ICRP ...
Pediatric CT: More than Just “Right-sizing” the Dose
... – Informal Poll of Image Gently Steering Committee ...
... – Informal Poll of Image Gently Steering Committee ...
Canadian Association of Radiologists Radiation Protection Working
... CT has an effective dose of 5-13 mSv [3,9e11]. Although the radiation from the examinations is different, their risks can be compared by using effective dose calculations; in this case, the CT examination has 2-3 times more risk than the nuclear medicine examination. By using the E, we can estimate ...
... CT has an effective dose of 5-13 mSv [3,9e11]. Although the radiation from the examinations is different, their risks can be compared by using effective dose calculations; in this case, the CT examination has 2-3 times more risk than the nuclear medicine examination. By using the E, we can estimate ...
CT2 - hullrad Radiation Physics
... CT scanner generate images in transaxial slices CT number represents average linear attenuation coefficient in the voxel Contrast in the displayed image is enhanced by windowing The scanner gantry carries the X-ray tube and generator and a curved bank of detectors The image is reconstructed by filte ...
... CT scanner generate images in transaxial slices CT number represents average linear attenuation coefficient in the voxel Contrast in the displayed image is enhanced by windowing The scanner gantry carries the X-ray tube and generator and a curved bank of detectors The image is reconstructed by filte ...
Making the difference with Live Image Guidance - InCenter
... where you need and expect them to be, makes working with the BV Pulsera easy and fast. With a touchscreen on the left monitor, patient administration and post-processing on acquired images is literally at your fingertips. ...
... where you need and expect them to be, makes working with the BV Pulsera easy and fast. With a touchscreen on the left monitor, patient administration and post-processing on acquired images is literally at your fingertips. ...
An Attempt to Establish National Dose Reference Levels for
... x-ray beam as the source of imaging light, protection against its damaging effects must be observed closely to ensure that the harmful effects to patients are minimum. Our study involved three Departments of Radiology in three major hospitals in the city of Malang, East Java, Indonesia. We took at l ...
... x-ray beam as the source of imaging light, protection against its damaging effects must be observed closely to ensure that the harmful effects to patients are minimum. Our study involved three Departments of Radiology in three major hospitals in the city of Malang, East Java, Indonesia. We took at l ...
Radiation-Dose-Monitor 11062015.ai
... RDM is compatible with various types of imaging modalities from all manufacturers. It is designed for all medical professionals responsible for the dose cycle (Radiologists, Technologists, Director of Radiology, Medical Physicists, Etc. ). Thanks to its Web-based architecture, multiple control scree ...
... RDM is compatible with various types of imaging modalities from all manufacturers. It is designed for all medical professionals responsible for the dose cycle (Radiologists, Technologists, Director of Radiology, Medical Physicists, Etc. ). Thanks to its Web-based architecture, multiple control scree ...
Basic CT Physics - Society for Pediatric Radiology
... 1.) Current technology for cardiac CT imaging 2.) What influences radiation dose in cardiac imaging? 3.) What do these radiation units mean? 4.) How is radiation dose calculated in CT imaging? ...
... 1.) Current technology for cardiac CT imaging 2.) What influences radiation dose in cardiac imaging? 3.) What do these radiation units mean? 4.) How is radiation dose calculated in CT imaging? ...
CT2 - hullrad
... CT scanner generate images in transaxial slices CT number represents average linear attenuation coefficient in the voxel Contrast in the displayed image is enhanced by windowing The scanner gantry carries the X-ray tube and generator and a curved bank of detectors The image is reconstructed by filte ...
... CT scanner generate images in transaxial slices CT number represents average linear attenuation coefficient in the voxel Contrast in the displayed image is enhanced by windowing The scanner gantry carries the X-ray tube and generator and a curved bank of detectors The image is reconstructed by filte ...
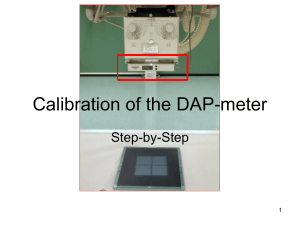
calibration factor
... • The real field size is measured with the accuracy of 1mm either from the film or the display • Please do notice that the image on the display can be in the wrong scale and must be adjusted with a proper measurement technique included in the computer program • It is also possible to place the scale ...
... • The real field size is measured with the accuracy of 1mm either from the film or the display • Please do notice that the image on the display can be in the wrong scale and must be adjusted with a proper measurement technique included in the computer program • It is also possible to place the scale ...
Document
... in cases where the damage is a double-strand breaks the repairs may not easy repaired which may lead to induction of solid cancers [2]. Measurements of these damage cause by photons are described in two main folds. Those damage cause by high dose rate during therapy and those cause by low dose rate ...
... in cases where the damage is a double-strand breaks the repairs may not easy repaired which may lead to induction of solid cancers [2]. Measurements of these damage cause by photons are described in two main folds. Those damage cause by high dose rate during therapy and those cause by low dose rate ...
Radiation safety and CT dose
... Source of Radiation Exposure David J. Brenner, Ph.D., D.Sc., and Eric J. Hall, D.Phil., D.Sc. ...
... Source of Radiation Exposure David J. Brenner, Ph.D., D.Sc., and Eric J. Hall, D.Phil., D.Sc. ...
Lecture Outline 16: Special Topics in Protection
... CT DOSE INDEX (CTDI) For a single slice, an ion chamber can be used to measure dose dose. That dose becomes what is called the CT dose index (CTDI) and can be used to perform calibration checks for quality control purposes. ...
... CT DOSE INDEX (CTDI) For a single slice, an ion chamber can be used to measure dose dose. That dose becomes what is called the CT dose index (CTDI) and can be used to perform calibration checks for quality control purposes. ...
Physics of CT
... a high contrast object occupies part of voxel (bone). scanner is unable to differentiate between a small amount of high-density material (e.g. bone) and a larger amount of other tissue densities (brain). The processor average out the two structures, it raises CT No of pixel & appears higher than it ...
... a high contrast object occupies part of voxel (bone). scanner is unable to differentiate between a small amount of high-density material (e.g. bone) and a larger amount of other tissue densities (brain). The processor average out the two structures, it raises CT No of pixel & appears higher than it ...
AAPM Licensure Update
... – Effective July 1, 2012 – Requires facilities that use CT to record the technical factors and dose of radiation on every CT study. • RDSR electronically sent to PACS when the study is complete if the ...
... – Effective July 1, 2012 – Requires facilities that use CT to record the technical factors and dose of radiation on every CT study. • RDSR electronically sent to PACS when the study is complete if the ...
organ and effective doses from a multidetector computed
... Committee 6-2 subgroup that in 2006 the per capita dose from medical exposure has increased almost 600%. The largest contributions and increases have come primarily from CT scanning and nuclear medicine. The 67 million CT scans account for 15% of the total medical radiation procedures and about 50% ...
... Committee 6-2 subgroup that in 2006 the per capita dose from medical exposure has increased almost 600%. The largest contributions and increases have come primarily from CT scanning and nuclear medicine. The 67 million CT scans account for 15% of the total medical radiation procedures and about 50% ...
What does your CT dose say about your facility?
... Dose Information As a way of showing its commitment to low dose imaging, Zwanger-Pesiri not only tells its patients how much dose they received, it also provides them with the printed information for their own personal medical files. ...
... Dose Information As a way of showing its commitment to low dose imaging, Zwanger-Pesiri not only tells its patients how much dose they received, it also provides them with the printed information for their own personal medical files. ...