
View flyer - Tufts University School of Engineering
... of trace acetylene (~1%) in ethylene feed streams destined for ethylene polymerization. An effective catalyst for this reaction converts all of the acetylene to ethylene without further conversion of ethylene to ethane such that there is a net increase in the amount of ethylene. Pd-Ag alloys, and mo ...
... of trace acetylene (~1%) in ethylene feed streams destined for ethylene polymerization. An effective catalyst for this reaction converts all of the acetylene to ethylene without further conversion of ethylene to ethane such that there is a net increase in the amount of ethylene. Pd-Ag alloys, and mo ...
Curriculum Vitae - Université Paris-Sud
... explained by assigning to the "quasi-atomic state" of the nascent metal specific thermodynamical properties distinct from those of the bulk metal that is stable under the same conditions.14 This concept implied that, as soon as formed, atoms and small clusters of a metal, even a noble metal, may exh ...
... explained by assigning to the "quasi-atomic state" of the nascent metal specific thermodynamical properties distinct from those of the bulk metal that is stable under the same conditions.14 This concept implied that, as soon as formed, atoms and small clusters of a metal, even a noble metal, may exh ...
Chemistry Unit Notes Organizing the Periodic Table All the elements
... Mg3(PO4)2 : 3 atoms of Mg 1*2 = 2 atoms of P 4*2 = 8 atoms of O Ca4(SO4)3: 4 atoms of Ca 1*3 = 3 atoms of S 4*3 = 12 atoms of O 4. A coefficient is a number written in front of a chemical formula. The coefficient indicates the number of molecules of that compound. A coefficient multiplies the number ...
... Mg3(PO4)2 : 3 atoms of Mg 1*2 = 2 atoms of P 4*2 = 8 atoms of O Ca4(SO4)3: 4 atoms of Ca 1*3 = 3 atoms of S 4*3 = 12 atoms of O 4. A coefficient is a number written in front of a chemical formula. The coefficient indicates the number of molecules of that compound. A coefficient multiplies the number ...
Lectures 29-31
... •The only way to determine this information is by experiment, but you should recognize that, in many hydrated salts, at least some of the water molecules serve as ligands. ...
... •The only way to determine this information is by experiment, but you should recognize that, in many hydrated salts, at least some of the water molecules serve as ligands. ...
Available - Ggu.ac.in
... of the splitting Δ that they produce (small Δ to large Δ): I− < Br− < S2− < SCN− < Cl− < NO3− < N3− < F− < OH− < C2O42− < H2O < NCS− < CH3CN < py < NH3 < en < 2,2'-bipyridine< phen < NO2− < PPh3 < CN− < CO It is useful to note that the ligands producing the most splitting are those that can engage i ...
... of the splitting Δ that they produce (small Δ to large Δ): I− < Br− < S2− < SCN− < Cl− < NO3− < N3− < F− < OH− < C2O42− < H2O < NCS− < CH3CN < py < NH3 < en < 2,2'-bipyridine< phen < NO2− < PPh3 < CN− < CO It is useful to note that the ligands producing the most splitting are those that can engage i ...
final1-final_report
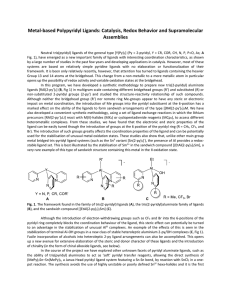
... Fig. 1), have emerged as a new important family of ligands with interesting coordination characteristics, as shown by a large number of studies in the past few years and developing applications in catalysis. However, most of these systems are based on relatively simple pyridine ligands with no elabo ...
... Fig. 1), have emerged as a new important family of ligands with interesting coordination characteristics, as shown by a large number of studies in the past few years and developing applications in catalysis. However, most of these systems are based on relatively simple pyridine ligands with no elabo ...
Chapter 2 PPT - AP - Westminster Public Schools
... A certain isotope X+ contains 54 electrons and 78 neutrons. What is the mass number of this isotope? ...
... A certain isotope X+ contains 54 electrons and 78 neutrons. What is the mass number of this isotope? ...
Name
... If so, how many? __2_ If not, explain why not. __the polar bonds are symmetrically arranged and cancel each other out.__ ...
... If so, how many? __2_ If not, explain why not. __the polar bonds are symmetrically arranged and cancel each other out.__ ...
Ken Raymond
... • Spontaneous Assembly of non-covalently linked molecular clusters of unique shape and composition. – Requires a driving force – Requires a dynamic system – This allows for all possible molecular structures to be explored to generate the formation of the thermodynamically favored product. ...
... • Spontaneous Assembly of non-covalently linked molecular clusters of unique shape and composition. – Requires a driving force – Requires a dynamic system – This allows for all possible molecular structures to be explored to generate the formation of the thermodynamically favored product. ...
Other Organic Compounds
... • F, Cl, Br, and I – are substituted for one or more hydrogen atoms in a hydrocarbon. • Add prefixes (fluoro for F, chloro for Cl, bromo for Br, and iodo I to the name of the alkane corresponding to the number of carbon atoms in the chain. If more than one halogen is present, add the halogen prefixe ...
... • F, Cl, Br, and I – are substituted for one or more hydrogen atoms in a hydrocarbon. • Add prefixes (fluoro for F, chloro for Cl, bromo for Br, and iodo I to the name of the alkane corresponding to the number of carbon atoms in the chain. If more than one halogen is present, add the halogen prefixe ...
Chapter 9. Coordination Chemistry 1
... ▪ [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] – only two isomers were synthesized - possible structures ...
... ▪ [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] – only two isomers were synthesized - possible structures ...
Isolation and characterization of {MnII [MnIII (salicylhydroximate)] 4
... suited for sequestration of the hard alkaline earths and alkali metals. Selectivity is introduced by varying the ring size and the number of oxygen donors. This results in a central pocket designed for specific ions.4~~Although ligands of the type 12-crown-4 have been known for many years, there are ...
... suited for sequestration of the hard alkaline earths and alkali metals. Selectivity is introduced by varying the ring size and the number of oxygen donors. This results in a central pocket designed for specific ions.4~~Although ligands of the type 12-crown-4 have been known for many years, there are ...
Chapter notes Class: IX Chapter Name: Atoms and molecules Top
... 29. The molecular mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of the substance. It is therefore the relative mass of molecule expressed in atomic mass units (u) 30.The formula unit mass of a substance is a sum of the atomic masses of all atoms in a formula unit ...
... 29. The molecular mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of the substance. It is therefore the relative mass of molecule expressed in atomic mass units (u) 30.The formula unit mass of a substance is a sum of the atomic masses of all atoms in a formula unit ...
Lectures 29-31
... •Where does the variety in colour come from? •Many co-ordination complexes have octahedral geometry. This means that two of the d orbitals on the transition metal point directly at ligands while the other three do not: ...
... •Where does the variety in colour come from? •Many co-ordination complexes have octahedral geometry. This means that two of the d orbitals on the transition metal point directly at ligands while the other three do not: ...
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Bonding: Ionic vs
... e- in lone pairs + 1/2(# of bonding e-] • IMPORTANT! The sum of all the FC for a species or ion MUST equal the net charge on the species! Example: Calculate the FC on each atom in CN-: FC can help when drawing Lewis Structures 1. FC on each atom should be as small as possible 2. (-) FC should appear ...
... e- in lone pairs + 1/2(# of bonding e-] • IMPORTANT! The sum of all the FC for a species or ion MUST equal the net charge on the species! Example: Calculate the FC on each atom in CN-: FC can help when drawing Lewis Structures 1. FC on each atom should be as small as possible 2. (-) FC should appear ...
SC-Database
... • An edited sub-set of SC-Database has been prepared and is included with SCDatabase and with Sol-Eq.(Solution Equilibria; principles and applications). And other packages. • Ionic strength corrections using Specific Interaction Theory have been added. ...
... • An edited sub-set of SC-Database has been prepared and is included with SCDatabase and with Sol-Eq.(Solution Equilibria; principles and applications). And other packages. • Ionic strength corrections using Specific Interaction Theory have been added. ...
Copper(I) and Silver(I) Ions in Unusual poly Donor
... As a consequence the lone pairs of these three donor atoms are hardly (N(2) [N(4)] and S(1) [S(3)] or not at all (S(2) [S(4)]) directed towards the M’ centre. Accordingly, it may be concluded that the NzSz ligand is primarily bonded via one imine N atom. The two strong M-N (M = Cur or Agr) interacti ...
... As a consequence the lone pairs of these three donor atoms are hardly (N(2) [N(4)] and S(1) [S(3)] or not at all (S(2) [S(4)]) directed towards the M’ centre. Accordingly, it may be concluded that the NzSz ligand is primarily bonded via one imine N atom. The two strong M-N (M = Cur or Agr) interacti ...
6. d and f-Block Elements and Coordination Chemistry
... The transition elements comprise those metals in Groups 3 to 12, i.e. the d-block elements, as well as the so-called “inner transition elements” which are the lanthanides and actinides, also know as the f-block elements. These are all metallic elements, so they are often called the transition metals ...
... The transition elements comprise those metals in Groups 3 to 12, i.e. the d-block elements, as well as the so-called “inner transition elements” which are the lanthanides and actinides, also know as the f-block elements. These are all metallic elements, so they are often called the transition metals ...
24.2 Nomenclature and Coordination Chemistry
... Lewis Acid : e- acceptor (metals are good e- acceptor) Lewis Base : e- donor (Ligands with lone pair electrons) Ligands, atoms or cluster of atoms with lone pair electrons available to donate Complexing Agent: H2O, NH3, Cl- CN- ...
... Lewis Acid : e- acceptor (metals are good e- acceptor) Lewis Base : e- donor (Ligands with lone pair electrons) Ligands, atoms or cluster of atoms with lone pair electrons available to donate Complexing Agent: H2O, NH3, Cl- CN- ...
When Gold Is Not Noble: Nanoscale Gold
... LHt. Through mapping of the potential energy surface along the C-O1 reaction coordinate (via total relaxation of the system with the variable C-O1 distance as a constraint) we determined a rather low energy barrier ∆Eb (LHt) ) 0.1 eV (occurring at db(CO1) ≈ 2.0 Å) for the LHT oxidation channel with ...
... LHt. Through mapping of the potential energy surface along the C-O1 reaction coordinate (via total relaxation of the system with the variable C-O1 distance as a constraint) we determined a rather low energy barrier ∆Eb (LHt) ) 0.1 eV (occurring at db(CO1) ≈ 2.0 Å) for the LHT oxidation channel with ...
Introduction to Nanoscience
... A nanodevice that often appears in science fiction is a nanocamera. This is used to view the inside of the body or in other confined spaces where an ordinary camera would not fit. Unfortunately, it is not possible to make such a camera using conventional far field optics. Light sources and light det ...
... A nanodevice that often appears in science fiction is a nanocamera. This is used to view the inside of the body or in other confined spaces where an ordinary camera would not fit. Unfortunately, it is not possible to make such a camera using conventional far field optics. Light sources and light det ...
1.1.4 Amount of Substance / The Mole
... determine molar and indirectly atomic mass at the Karlsuhe ...
... determine molar and indirectly atomic mass at the Karlsuhe ...
Crowns and Crypts
... Generally the complexes of alkali-crowns can survive indefinitely in non-aqueous solutions whereas those of alkali-crypts in aqueous solutions as well. The crypts show similar high selectivity towards the alkalies as that of crowns. For Crypt-222, for example, K+ is appropriate to fit in the cavity ...
... Generally the complexes of alkali-crowns can survive indefinitely in non-aqueous solutions whereas those of alkali-crypts in aqueous solutions as well. The crypts show similar high selectivity towards the alkalies as that of crowns. For Crypt-222, for example, K+ is appropriate to fit in the cavity ...
L11S08
... 1. Mining (getting the ore out of the ground) 2. Concentrating (preparing it for further treatment). Differences in the chemical and physical properties of the mineral of interest and the undesired material, called, gangue, are used to separate the components. Example: Iron maybe separated from ...
... 1. Mining (getting the ore out of the ground) 2. Concentrating (preparing it for further treatment). Differences in the chemical and physical properties of the mineral of interest and the undesired material, called, gangue, are used to separate the components. Example: Iron maybe separated from ...










![Isolation and characterization of {MnII [MnIII (salicylhydroximate)] 4](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016650300_1-b43c0f04bd9bb8b75975bb569ca22736-300x300.png)











