Macrocyclic Leaflets
... three phosphonate anions, 1NH, five nitrate anions, and eight water molecules. Interestingly, 3 also forms a leaflet structure like 2, but has a complicated polymeric coordination network as the backbone, in which Cd(II) cations adopt octahedral geometry and form two unique Cd‚‚‚Cd metal contacts (3 ...
... three phosphonate anions, 1NH, five nitrate anions, and eight water molecules. Interestingly, 3 also forms a leaflet structure like 2, but has a complicated polymeric coordination network as the backbone, in which Cd(II) cations adopt octahedral geometry and form two unique Cd‚‚‚Cd metal contacts (3 ...
Carbon–carbon bond cleavage in the photoionization of ethanol and
... Ions were generated by the photoionization of a pulsed VUV laser beam, accelerated in a Wiley–Mclaren-type double electrostatic field to 1.9 keV, and then directed into an 80 cm long field-free flight tube. The ions were detected by a chevron microchannel plate 共MCP兲 detector. After amplification of ...
... Ions were generated by the photoionization of a pulsed VUV laser beam, accelerated in a Wiley–Mclaren-type double electrostatic field to 1.9 keV, and then directed into an 80 cm long field-free flight tube. The ions were detected by a chevron microchannel plate 共MCP兲 detector. After amplification of ...
Week 8 – Intermolecular Forces
... (B) H2O exhibits hydrogen bonding whereas H2S exhibits London (dispersion) forces (C) H2O exhibits hydrogen bonding whereas H2S exhibits dipole to dipole interactions (D) H2O is a liquid whereas H2S is a gas (E) H2S is more polarizable due to the greater amount of electrons 16. Of the following pure ...
... (B) H2O exhibits hydrogen bonding whereas H2S exhibits London (dispersion) forces (C) H2O exhibits hydrogen bonding whereas H2S exhibits dipole to dipole interactions (D) H2O is a liquid whereas H2S is a gas (E) H2S is more polarizable due to the greater amount of electrons 16. Of the following pure ...
Coordination properties of the diethyl (pyridin-3-ylmethyl)phosphonate ligand (3-pmpe)
... distance must be large, leading to observed only very weak antiferromagnetic coupling. ...
... distance must be large, leading to observed only very weak antiferromagnetic coupling. ...
Electron attachment to molecular clusters by collisional charge transfer
... A) were observed, but extensive signal averaging was required to detect any other positive ion species (for which typical signals are E A). Thus,here we present only observations of negative ions. As seen in Figure 2, the chlorine cluster system yields negative ions corresponding to electron attachm ...
... A) were observed, but extensive signal averaging was required to detect any other positive ion species (for which typical signals are E A). Thus,here we present only observations of negative ions. As seen in Figure 2, the chlorine cluster system yields negative ions corresponding to electron attachm ...
coinage metal complexes containing new scorpionate
... Moreover we have designed and synthesized the new triazole-based and water soluble bis(triazol-1yl)acetate, and the new nitro-substituted heteroscorpionate ligand, dihydridobis(3-nitro-1,2,4triazolyl)borate. New Cu(I) and Ag(I) complexes containing these scorpionates and phosphane coligands have bee ...
... Moreover we have designed and synthesized the new triazole-based and water soluble bis(triazol-1yl)acetate, and the new nitro-substituted heteroscorpionate ligand, dihydridobis(3-nitro-1,2,4triazolyl)borate. New Cu(I) and Ag(I) complexes containing these scorpionates and phosphane coligands have bee ...
Chapter 3
... Low melting points and density Generally poor conductors of heat and conductivity Combine with one another to form molecular compounds Metalloids Properties are intermediate between metals and nonmetals Some are raw material for semiconductor ...
... Low melting points and density Generally poor conductors of heat and conductivity Combine with one another to form molecular compounds Metalloids Properties are intermediate between metals and nonmetals Some are raw material for semiconductor ...
Coordination Compounds: Chemistry and Application
... from the difference between the charge of the metal ion and the anion. For example, [PtCl6]2- is a complex ion formed from one Pt4+ and six Cl-, which results in a net charge of 2-. In a case where the ligand does not carry a formal charge, such as NH3, an ammonia complex carries the charge of the m ...
... from the difference between the charge of the metal ion and the anion. For example, [PtCl6]2- is a complex ion formed from one Pt4+ and six Cl-, which results in a net charge of 2-. In a case where the ligand does not carry a formal charge, such as NH3, an ammonia complex carries the charge of the m ...
as a PDF
... lead systematically to core-shell particles. For example, Au(core)/Pd(shell) clusters were synthesized by reduction of the mixed ion aqueous17 or alcoholic solutions.18 Gold/palladium bimetallic particles having a palladium-rich shell were synthesized by Liu et al.19 Two-step alcoholic reduction giv ...
... lead systematically to core-shell particles. For example, Au(core)/Pd(shell) clusters were synthesized by reduction of the mixed ion aqueous17 or alcoholic solutions.18 Gold/palladium bimetallic particles having a palladium-rich shell were synthesized by Liu et al.19 Two-step alcoholic reduction giv ...
Molecular Symmetry Chem 332.3 Fall 2005 Inorganic Chemistry II
... spectroscopic, magnetic and thermodynamic properties of inorganic compounds, organometallic chemistry and homogeneous catalysis. The laboratory work includes experiments on the preparation and characterization of transition metal compounds. Topics to be covered (Chapter references are to Housecraft ...
... spectroscopic, magnetic and thermodynamic properties of inorganic compounds, organometallic chemistry and homogeneous catalysis. The laboratory work includes experiments on the preparation and characterization of transition metal compounds. Topics to be covered (Chapter references are to Housecraft ...
Dynamics of electron solvation in I (CH3OH)n
... cluster anions, so no definitive assignment could be made. Recent experimental and theoretical investigations into methanol clusters have caused us to revisit the dynamics of I− (CH3 OH)n . Infrared (IR) predissociation studies on small (n ≤ 12) X− (CH3 OH)n clusters (X− = F− , Cl− , I− ) by Lisy, J ...
... cluster anions, so no definitive assignment could be made. Recent experimental and theoretical investigations into methanol clusters have caused us to revisit the dynamics of I− (CH3 OH)n . Infrared (IR) predissociation studies on small (n ≤ 12) X− (CH3 OH)n clusters (X− = F− , Cl− , I− ) by Lisy, J ...
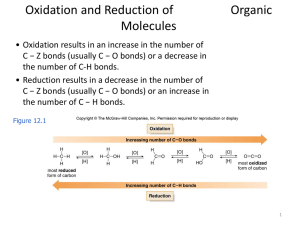
Oxidation and Reduction of Organic Molecules
... number of rings in the original compound. • For example, if a molecule with a formula C8H12 was converted to C8H14 upon hydrogenation, the original molecule contains one bond and two rings. • Carbonyl groups (C=O) in a molecule can also undergo hydrogenation to form alcohols since they contain a ...
... number of rings in the original compound. • For example, if a molecule with a formula C8H12 was converted to C8H14 upon hydrogenation, the original molecule contains one bond and two rings. • Carbonyl groups (C=O) in a molecule can also undergo hydrogenation to form alcohols since they contain a ...
Chapter 1: Fundamental Concepts
... • The oxidation state of the metal (charge!) D is greater for M3+ than for M2+ • The row of the metal in the periodic table (size!) for a given ligand and oxidation state of the metal, D increases going down in a group e.g. D is greater in Ru(NH3)63+ than in Fe(NH3)63+ Colors of metal complexes are ...
... • The oxidation state of the metal (charge!) D is greater for M3+ than for M2+ • The row of the metal in the periodic table (size!) for a given ligand and oxidation state of the metal, D increases going down in a group e.g. D is greater in Ru(NH3)63+ than in Fe(NH3)63+ Colors of metal complexes are ...
Transition Metal Complexes
... chains of linked ammonia molecules, with the nitrogens having five bonds and connecting a chloride to the metal. Alfred Werner proposed that the ammonia molecules could bond strongly and directly to the metal, with chlorides either directly bonded, or loosely bonded and ionic in solution. ...
... chains of linked ammonia molecules, with the nitrogens having five bonds and connecting a chloride to the metal. Alfred Werner proposed that the ammonia molecules could bond strongly and directly to the metal, with chlorides either directly bonded, or loosely bonded and ionic in solution. ...
The molar absorption coefficient, molar extinction
... The leading journals of the field define an "organometallic" compound as one in which there is a bonding interaction (ionic or covalent, localized or delocalized) between one or more carbon atoms of an organic group or molecule and a main group, transition, lanthanide, or actinide metal atom (o ...
... The leading journals of the field define an "organometallic" compound as one in which there is a bonding interaction (ionic or covalent, localized or delocalized) between one or more carbon atoms of an organic group or molecule and a main group, transition, lanthanide, or actinide metal atom (o ...
Slide 1
... • The amount of energy used to remove an electron is known as the ionization energy • Varies from element to elements • Energy increases from left to right(less reactive) • Energy decreases from top to bottom(easy to remove the electron, so it will be more reactive) • Ex: K is more reactive than Na ...
... • The amount of energy used to remove an electron is known as the ionization energy • Varies from element to elements • Energy increases from left to right(less reactive) • Energy decreases from top to bottom(easy to remove the electron, so it will be more reactive) • Ex: K is more reactive than Na ...
Coordination Compounds: Chemistry and Application
... from the difference between the charge of the metal ion and the anion. For example, [PtCl6]2- is a complex ion formed from one Pt4+ and six Cl-, which results in a net charge of 2-. In a case where the ligand does not carry a formal charge, such as NH3, an ammonia complex carries the charge of the m ...
... from the difference between the charge of the metal ion and the anion. For example, [PtCl6]2- is a complex ion formed from one Pt4+ and six Cl-, which results in a net charge of 2-. In a case where the ligand does not carry a formal charge, such as NH3, an ammonia complex carries the charge of the m ...
Alfred Werner: Father of Coordination Chemistry.
... PMe3 is placed along the unique (z) axis. What is the order of that axis? Symmetry operations/elements are lost as compared to W(CO)6. What are they? What is the point group assignment? How about multiply substituted complexes: ...
... PMe3 is placed along the unique (z) axis. What is the order of that axis? Symmetry operations/elements are lost as compared to W(CO)6. What are they? What is the point group assignment? How about multiply substituted complexes: ...
Lectures 29-31
... Mercury (Hg) is the only transition metal that is not a solid. The transition metals all have valence electrons in a d subshell. Like other metals, transition metals form cations not anions. We shall see that many transitions cations form beautifully coloured compounds (as shown on the previous page ...
... Mercury (Hg) is the only transition metal that is not a solid. The transition metals all have valence electrons in a d subshell. Like other metals, transition metals form cations not anions. We shall see that many transitions cations form beautifully coloured compounds (as shown on the previous page ...
Chapter 23 Metals and Metallurgy
... metal cation. • Electrons on the ligands repel electrons in the unhybridized d orbitals of the metal ion. • The result is the energies of the d orbitals are split. • The difference in energy depends on the complex formed and the kinds of ligands. ...
... metal cation. • Electrons on the ligands repel electrons in the unhybridized d orbitals of the metal ion. • The result is the energies of the d orbitals are split. • The difference in energy depends on the complex formed and the kinds of ligands. ...
Alkene complexes - Dewar/Chatt/Duncanson model
... Main group alkyls known from beginning ZnEt2 PbEt4 Quite stable (thermodynamically !) but it was found that synthesis of transition metal alkyls was difficult - i.e. didn't work Some exceptions Pope & Peachy (1901) PtCl4 + 3CH3MgI [(CH3)3PtI]4 "cubane" (C5H5)Fe(CO)2(CH3) The latter type had -acce ...
... Main group alkyls known from beginning ZnEt2 PbEt4 Quite stable (thermodynamically !) but it was found that synthesis of transition metal alkyls was difficult - i.e. didn't work Some exceptions Pope & Peachy (1901) PtCl4 + 3CH3MgI [(CH3)3PtI]4 "cubane" (C5H5)Fe(CO)2(CH3) The latter type had -acce ...
Oxidation reactions on neutral cobalt oxide clusters: experimental and theoretical studies
... adsorbed on the Co(II) and Co(III) sites by Pollard et al., employing the same method.37 A band centered at 2006 cm 1 is assigned to CO linearly adsorption on a Co(II) site; the adsorbed CO reacts with an oxygen atom bonded to a neighboring Co(III) to form CO2. In this process, Co(III) is reduced to ...
... adsorbed on the Co(II) and Co(III) sites by Pollard et al., employing the same method.37 A band centered at 2006 cm 1 is assigned to CO linearly adsorption on a Co(II) site; the adsorbed CO reacts with an oxygen atom bonded to a neighboring Co(III) to form CO2. In this process, Co(III) is reduced to ...
PPT File
... 17.4 The spectrochemical series and bonding in complex Are there ways to explain and eventually predict colors, spectrochemical series and magnetism? Crystal field theory : ionic description of the metal-ligand bonds Only considering the electrostatic interaction between ligand and metal atom: ...
... 17.4 The spectrochemical series and bonding in complex Are there ways to explain and eventually predict colors, spectrochemical series and magnetism? Crystal field theory : ionic description of the metal-ligand bonds Only considering the electrostatic interaction between ligand and metal atom: ...
Bonding, aromaticity and reactivity patterns in some all
... of the all-metal framework. The HOMO is also of π-type in nature with a pair of such electrons. This has opened a new vista of further work on the topic of all-metal aromaticity and since then this seminal theme of all-metal aromaticity5 has been explored by several researchers. Scientists have also ...
... of the all-metal framework. The HOMO is also of π-type in nature with a pair of such electrons. This has opened a new vista of further work on the topic of all-metal aromaticity and since then this seminal theme of all-metal aromaticity5 has been explored by several researchers. Scientists have also ...