7.3 * Families of Rocks
... As layers are compressed, they form different kinds of rock, depending on the nature of the particles in the sediment. Shale – a smooth sedimentary rock that is formed from layers of tiny particles of clay/silt Sandstone – a rougher rock, formed from layers of compressed sand Conglomerate – made fro ...
... As layers are compressed, they form different kinds of rock, depending on the nature of the particles in the sediment. Shale – a smooth sedimentary rock that is formed from layers of tiny particles of clay/silt Sandstone – a rougher rock, formed from layers of compressed sand Conglomerate – made fro ...
Mars * Earth Science - Milford-NASA
... Hot Spots: Are fixed places within the mantle or oceanic lithosphere where rocks melt to become magma. When a hot spot is situated in the oceanic lithosphere a shield volcanoes is built. Rock Cycle: There are three different ways rock can be created on earth and thus there are three main classificat ...
... Hot Spots: Are fixed places within the mantle or oceanic lithosphere where rocks melt to become magma. When a hot spot is situated in the oceanic lithosphere a shield volcanoes is built. Rock Cycle: There are three different ways rock can be created on earth and thus there are three main classificat ...
Objectives 6 E Review- TEST FRIDAY, JANUARY 4th Part A: Read
... If the answer is correct: Write why? If the answer is incorrect: Write why? And include the right answer ...
... If the answer is correct: Write why? If the answer is incorrect: Write why? And include the right answer ...
Biochemical Sedimentary Rock
... To understand Earth history, a geologist seeks to interpret the “Environment of Deposition” of a sedimentary rock…this reveals something about changes occurring on Earth’s surface ...
... To understand Earth history, a geologist seeks to interpret the “Environment of Deposition” of a sedimentary rock…this reveals something about changes occurring on Earth’s surface ...
Davidson and Yelverton, 2017
... Figure 3: Direct current from above discharged directly above crack (expected path of least resistance, confirmed in left image) near water (with Pyranine for ease of visualization). Current and water are attracted in the center image. Water is pulled to the original current pathway through the crac ...
... Figure 3: Direct current from above discharged directly above crack (expected path of least resistance, confirmed in left image) near water (with Pyranine for ease of visualization). Current and water are attracted in the center image. Water is pulled to the original current pathway through the crac ...
CHAPTER 18 Volcanism
... massive ranges that extends 2,500 kilometers across South Asia north of India. The Himalayas cover all or part of the countries of Tibet, Nepal, and Bhutan. A climber on the high slopes of Mt. Everest would probably be surprised to learn that the region was relatively flat about 40 million years ago ...
... massive ranges that extends 2,500 kilometers across South Asia north of India. The Himalayas cover all or part of the countries of Tibet, Nepal, and Bhutan. A climber on the high slopes of Mt. Everest would probably be surprised to learn that the region was relatively flat about 40 million years ago ...
Chapter 5: Mountain Belts and Continental Crust At this point in the
... just isn’t the case. The Airy model predicts that regions of thickened continental crust should be associated with higher elevations, which generally is the case. The really important prediction of the Airy model is that Earth’s mountain belts should possess crustal roots (i.e., thicker crust that p ...
... just isn’t the case. The Airy model predicts that regions of thickened continental crust should be associated with higher elevations, which generally is the case. The really important prediction of the Airy model is that Earth’s mountain belts should possess crustal roots (i.e., thicker crust that p ...
Nanaimo Group
... comprises much of Vancouver Island and some other areas - was accreted onto the edge of North America. The continent-continent collision would have created significant uplift and mountain building, and hence over the period of formation of the Nanaimo Group there would have been rapid erosion and hi ...
... comprises much of Vancouver Island and some other areas - was accreted onto the edge of North America. The continent-continent collision would have created significant uplift and mountain building, and hence over the period of formation of the Nanaimo Group there would have been rapid erosion and hi ...
Plate Tectonics Review
... A plume of hot magma rises from deep within the mantle pushing up the crust and causing pressure forcing the continent to break and separate. Lava flows and earthquakes would be seen. ...
... A plume of hot magma rises from deep within the mantle pushing up the crust and causing pressure forcing the continent to break and separate. Lava flows and earthquakes would be seen. ...
CRS_Ch03 - earthjay science
... C. Ocean rocks do not record reversals in Earth’s magnetic crust. D. Ocean plates converge at mid-ocean ridges. E. None of the above ANSWER: A, [p. 59] ...
... C. Ocean rocks do not record reversals in Earth’s magnetic crust. D. Ocean plates converge at mid-ocean ridges. E. None of the above ANSWER: A, [p. 59] ...
SECTION 1 HOW HAS THE EARTH EVOLVED?
... sediments came from, and what kind of rock could form from these sediments. Bring back some samples from the beach and present your findings to your class. • Take an imaginar y trip back in time to some period in the geological past and describe what it would be like to spend a day there. Be sure to ...
... sediments came from, and what kind of rock could form from these sediments. Bring back some samples from the beach and present your findings to your class. • Take an imaginar y trip back in time to some period in the geological past and describe what it would be like to spend a day there. Be sure to ...
Volcano-tectonic control of ore deposits, southwestern New Mexico
... Coney, and Rhodes, this Guidebook). The two regions are separated by a persistent structural high: the Pennsylvanian Florida Islands of Kottlowski (1960) and the Early Cretaceous structure christened the Burro Uplift (Elston, 1958a) . Significantly, all major known mineralized Laramide porphyries in ...
... Coney, and Rhodes, this Guidebook). The two regions are separated by a persistent structural high: the Pennsylvanian Florida Islands of Kottlowski (1960) and the Early Cretaceous structure christened the Burro Uplift (Elston, 1958a) . Significantly, all major known mineralized Laramide porphyries in ...
Lecture 9b: Upper Mantle Structure and Composition
... crust/mantle: Mohorovicic discontinuity (Moho)--compositional mantle/core: Gutenberg discontinuity--compositional inner/outer core: phase (liquid to solid) 400 km discontinuity: phase (olivine to spinel structure) 670 km discontinuity: phase (spinel structure to perovskite) ...
... crust/mantle: Mohorovicic discontinuity (Moho)--compositional mantle/core: Gutenberg discontinuity--compositional inner/outer core: phase (liquid to solid) 400 km discontinuity: phase (olivine to spinel structure) 670 km discontinuity: phase (spinel structure to perovskite) ...
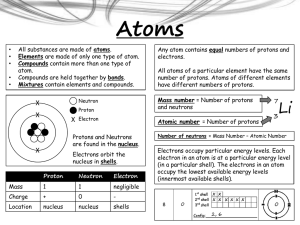
Ionic bonding
... In the nucleus of an atom there are protons and _________. Around the nucleus there are electrons in _________. What is the charge on a proton? Atoms are always neutral, explain why? How many protons, neutrons and electrons does Lithium have? What is the atomic number and mass number of Oxygen? What ...
... In the nucleus of an atom there are protons and _________. Around the nucleus there are electrons in _________. What is the charge on a proton? Atoms are always neutral, explain why? How many protons, neutrons and electrons does Lithium have? What is the atomic number and mass number of Oxygen? What ...
12.26MB - Stanford University
... Last update: March 23, 2005 The photographs shown here appear in the textbook and are provided to facilitate their display during course instruction. Permissions for publication of photographs must be requested from individual copyright holders. The source of each photograph is given below the figur ...
... Last update: March 23, 2005 The photographs shown here appear in the textbook and are provided to facilitate their display during course instruction. Permissions for publication of photographs must be requested from individual copyright holders. The source of each photograph is given below the figur ...
Earth`s Layers - Spaulding Middle School
... * The inner core of the Earth has temperatures and pressures so great that the metals are squeezed together and are not able to move. * The inner core is a solid. ...
... * The inner core of the Earth has temperatures and pressures so great that the metals are squeezed together and are not able to move. * The inner core is a solid. ...
Discovering Plate Boundaries
... see. At this point, do not try to explain the data; just observe! Part 3: Identify the plate boundaries Using your data from each scientist’s map, begin to collaborate on each known plate boundary type. Do this by obtaining a laminated plate boundary map from your teacher. At each labeled boundary ( ...
... see. At this point, do not try to explain the data; just observe! Part 3: Identify the plate boundaries Using your data from each scientist’s map, begin to collaborate on each known plate boundary type. Do this by obtaining a laminated plate boundary map from your teacher. At each labeled boundary ( ...
Earth`s Structure
... 1. Waves – The speed of waves traveling through the Earth depends on the density and nature of the material they are traveling through. For example, a wave travels faster in solid rock than it does in a liquid. By studying the speed of these waves and the paths they take, geologists uncover clues a ...
... 1. Waves – The speed of waves traveling through the Earth depends on the density and nature of the material they are traveling through. For example, a wave travels faster in solid rock than it does in a liquid. By studying the speed of these waves and the paths they take, geologists uncover clues a ...
(1 point
... this layer they ______________ _____, indicating the inner core is solid. g) At about ____________ , the inner core is the ____________________ part of Earth. h) The inner core, at the center of the Earth, also experiences the greatest amount of _____________________. i) The inner core makes up abou ...
... this layer they ______________ _____, indicating the inner core is solid. g) At about ____________ , the inner core is the ____________________ part of Earth. h) The inner core, at the center of the Earth, also experiences the greatest amount of _____________________. i) The inner core makes up abou ...