HotspotActivity_forSERC.v2
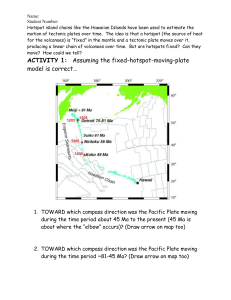
... Hotspot island chains like the Hawaiian Islands have been used to estimate the motion of tectonic plates over time. The idea is that a hotspot (the source of heat for the volcanoes) is “fixed” in the mantle and a tectonic plate moves over it, producing a linear chain of volcanoes over time. But are ...
... Hotspot island chains like the Hawaiian Islands have been used to estimate the motion of tectonic plates over time. The idea is that a hotspot (the source of heat for the volcanoes) is “fixed” in the mantle and a tectonic plate moves over it, producing a linear chain of volcanoes over time. But are ...
Directions: Select the best answer for each item. (8.P.1A.3) Some
... a. Normal Faults b. Reverse Faults c. Strike-Slip Faults d. Uplift Faults 18. (8.E.5B.2) The land formation modeled in this demonstration is __________. a. An Earthquake b. A Mountain c. A Ridge d. A Volcano 19. (8.E.5A.4) The type of boundary modeled in this demonstration is a _________. a. Converg ...
... a. Normal Faults b. Reverse Faults c. Strike-Slip Faults d. Uplift Faults 18. (8.E.5B.2) The land formation modeled in this demonstration is __________. a. An Earthquake b. A Mountain c. A Ridge d. A Volcano 19. (8.E.5A.4) The type of boundary modeled in this demonstration is a _________. a. Converg ...
Volcanos
... Anatomy of a Volcano • Conduit: tube structure through which lava travels to reach the surface • Vent: an opening in the conduit to allow lava to leave the conduit • Crater: a bowl shaped depression formed around the vent • Caldera: a larger depression that can form ...
... Anatomy of a Volcano • Conduit: tube structure through which lava travels to reach the surface • Vent: an opening in the conduit to allow lava to leave the conduit • Crater: a bowl shaped depression formed around the vent • Caldera: a larger depression that can form ...
9 - Mr. Neason`s Earth Science
... sea-floor spreading. Recall that Earth’s magnetic field is much like that of a bar magnet. Geophysicists learned that Earth’s magnetic field occasionally reverse polarity. That is, the north magnetic pole becomes the south magnetic pole and visa versa. When Earth’s magnetic field, it is said to be n ...
... sea-floor spreading. Recall that Earth’s magnetic field is much like that of a bar magnet. Geophysicists learned that Earth’s magnetic field occasionally reverse polarity. That is, the north magnetic pole becomes the south magnetic pole and visa versa. When Earth’s magnetic field, it is said to be n ...
Key concepts
... -know how to classify the layers of the earth by chemical composition AND by physical properties. Be able to name the layers using each classification scheme & describe their characteristics -know the difference between oceanic crust & continental crust -know how pressure and temperature change as y ...
... -know how to classify the layers of the earth by chemical composition AND by physical properties. Be able to name the layers using each classification scheme & describe their characteristics -know the difference between oceanic crust & continental crust -know how pressure and temperature change as y ...
Layers of the Earth
... to the top of the mantle, cools, then sinks, reheats, and rises again. These convection currents cause changes in the Earth’s surface ...
... to the top of the mantle, cools, then sinks, reheats, and rises again. These convection currents cause changes in the Earth’s surface ...
8-31 Core Mantle Crust.notebook
... The deepest hole ever drilled by man is the Kola Superdeep Borehole, in Russia. It reached a depth of 12,261 meters (about 40,226 feet or 7.62 miles). It was drilled for scientific research and gave up some unexpected discoveries, one of which was a huge deposit of hydrogen so massive that the ...
... The deepest hole ever drilled by man is the Kola Superdeep Borehole, in Russia. It reached a depth of 12,261 meters (about 40,226 feet or 7.62 miles). It was drilled for scientific research and gave up some unexpected discoveries, one of which was a huge deposit of hydrogen so massive that the ...
Layers of the Earth ppt
... to the top of the mantle, cools, then sinks, reheats, and rises again. These convection currents cause changes in the Earth’s surface ...
... to the top of the mantle, cools, then sinks, reheats, and rises again. These convection currents cause changes in the Earth’s surface ...
Explore and Discover… Volcanoes and Earthquakes
... Choose two of the rocks and compare their differences. Explain why they are different to each other. Comparisons between two of the four rocks on display should refer to the features stated below, eg gas bubbles, glassy appearance, crystals. Some students will be able to explain that the differences ...
... Choose two of the rocks and compare their differences. Explain why they are different to each other. Comparisons between two of the four rocks on display should refer to the features stated below, eg gas bubbles, glassy appearance, crystals. Some students will be able to explain that the differences ...
Types of Plate Boundaries Submitted by WWW.ASSIGNMENTPOINT
... apart (Figure 1). Today's active divergent boundaries are midoceanic ridges (sea floor spreading centers). Divergent boundaries can also develop on land, as did those that broke up Pangaea about 200 million years ago. Continental rifting can end before the crustal mass has been fully separated. Thes ...
... apart (Figure 1). Today's active divergent boundaries are midoceanic ridges (sea floor spreading centers). Divergent boundaries can also develop on land, as did those that broke up Pangaea about 200 million years ago. Continental rifting can end before the crustal mass has been fully separated. Thes ...
Chapter 3 Notes - Todd S. Thuma Homepage
... C.Convergence zones – two major types 1. Subduction zones form trenches at plate boundaries a. Gravity-driven conveyor belt 1) Thinner, denser crust moves beneath less dense layer a) Pressure makes leading edge even denser b) Gravity pulls edge deeper causes earthquakes as it moves deeper c) ...
... C.Convergence zones – two major types 1. Subduction zones form trenches at plate boundaries a. Gravity-driven conveyor belt 1) Thinner, denser crust moves beneath less dense layer a) Pressure makes leading edge even denser b) Gravity pulls edge deeper causes earthquakes as it moves deeper c) ...
Volcano Notes
... alternate with lava. The magma that forms composite volcanoes commonly contains large amounts of silica, water, and gases. They are larger than cinder-cone volcanoes, and, because of their violently explosive nature, they are potentially dangerous to humans and the environment. ...
... alternate with lava. The magma that forms composite volcanoes commonly contains large amounts of silica, water, and gases. They are larger than cinder-cone volcanoes, and, because of their violently explosive nature, they are potentially dangerous to humans and the environment. ...
Discuss on Sea Floor Evidence Submitted by WWW
... symmetrical patterns of magnetic “bands,” anomalies parallel to midoceanic rifts (Figure ). The same patterns in relation to midoceanic rifts are present in different oceans. The magnetic anomalies coincide with the episodes of magnetic reversals that have been documented from studies on land, indic ...
... symmetrical patterns of magnetic “bands,” anomalies parallel to midoceanic rifts (Figure ). The same patterns in relation to midoceanic rifts are present in different oceans. The magnetic anomalies coincide with the episodes of magnetic reversals that have been documented from studies on land, indic ...
OCN100--Study Guide
... Describe the 4 steps in the "scientific method." How is a hypothesis different from a theory? Draw a diagram to illustrate how latitude and longitude are used to designate locations on Earth. Describe the characteristics and physical properties of each of the earth's layers: crust (continental and o ...
... Describe the 4 steps in the "scientific method." How is a hypothesis different from a theory? Draw a diagram to illustrate how latitude and longitude are used to designate locations on Earth. Describe the characteristics and physical properties of each of the earth's layers: crust (continental and o ...
Plate Tectonics
... is broken into plates. – Tectonic Plate- A large, solid piece of the earth’s crust that includes the continents and ocean floor. – These plates float or ride on the asthenosphere. ...
... is broken into plates. – Tectonic Plate- A large, solid piece of the earth’s crust that includes the continents and ocean floor. – These plates float or ride on the asthenosphere. ...
File
... effort into these problems, you will bring up your grade and be ready to ATTACK the PASS! Read the following passage about Earthquakes and answer the following questions. Earthquakes (1)Earthquakes are movements in the Earth’s crust that cause the ground to shake. (2) Earth’s crust consists of its s ...
... effort into these problems, you will bring up your grade and be ready to ATTACK the PASS! Read the following passage about Earthquakes and answer the following questions. Earthquakes (1)Earthquakes are movements in the Earth’s crust that cause the ground to shake. (2) Earth’s crust consists of its s ...
Forces in Earth’s Crust
... Stress: a force that acts on an area of rock to change its shape or volume 3 kinds of stress: tension, compression, and shearing Tension, compression, and shearing work over millions of years to change the shape and volume of rock. Tension: 2 plates move apart, pull on the rock, and stretch the rock ...
... Stress: a force that acts on an area of rock to change its shape or volume 3 kinds of stress: tension, compression, and shearing Tension, compression, and shearing work over millions of years to change the shape and volume of rock. Tension: 2 plates move apart, pull on the rock, and stretch the rock ...
Chapter 4 (Plate Tectonics)
... Types of convergent plate margins • “Subduction” zone – 1 plate plunges into mantle beneath another plate • 1 or 2 ocean plates involved • Ocean plates = higher density (heavier) due to composition (basalt) – Continents = granite (less dense) ...
... Types of convergent plate margins • “Subduction” zone – 1 plate plunges into mantle beneath another plate • 1 or 2 ocean plates involved • Ocean plates = higher density (heavier) due to composition (basalt) – Continents = granite (less dense) ...
Chapter 28 Notes
... The theory of plate tectonics explains the movement of continents and other geological events like earthquakes and volcanoes. The term tectonics means construction or building. The theory of plate tectonics, stated in 1965, refers to the movement of giant pieces of solid rock on Earth’s surfac ...
... The theory of plate tectonics explains the movement of continents and other geological events like earthquakes and volcanoes. The term tectonics means construction or building. The theory of plate tectonics, stated in 1965, refers to the movement of giant pieces of solid rock on Earth’s surfac ...
Name: Doe Date: May 13, 2015 Directions: 1. Read the following
... begins with the formation of (the, main, does) Earth, its layers and how the (layers, convection, solid) interact with each other. ...
... begins with the formation of (the, main, does) Earth, its layers and how the (layers, convection, solid) interact with each other. ...