Slide 1
... In some areas lava flows accumulated to a thickness of several kilometers. ► Although this seems like a lot of lava, most of the magma remained underground forming the Duluth Gabbro (12kmX160km) What is most basaltic magma/lava associated with? ► Large amounts of mafic magma typically signals the ...
... In some areas lava flows accumulated to a thickness of several kilometers. ► Although this seems like a lot of lava, most of the magma remained underground forming the Duluth Gabbro (12kmX160km) What is most basaltic magma/lava associated with? ► Large amounts of mafic magma typically signals the ...
When did Making Mountains the Modern Way Begin?
... One of the characteristic high pressure and low temperature metamorphic rock products of modern mountain belts like the Himalayas, which began forming some 50 million years ago, is eclogite, which often a visually striking and beautiful rock containing large red garnet crystals surrounded by green o ...
... One of the characteristic high pressure and low temperature metamorphic rock products of modern mountain belts like the Himalayas, which began forming some 50 million years ago, is eclogite, which often a visually striking and beautiful rock containing large red garnet crystals surrounded by green o ...
Notes: Rocks
... bands due to recrystallization or flattening. Has a sheet-like or flaky look ex. gneiss , schist, slate no bands or sheets----blocky looking. Looks to contain 1 mineral type. ex. marble, quartzite ...
... bands due to recrystallization or flattening. Has a sheet-like or flaky look ex. gneiss , schist, slate no bands or sheets----blocky looking. Looks to contain 1 mineral type. ex. marble, quartzite ...
Mountain Building Chapter 10 Learning Standard: I will analyze the
... Most mountain building occurs at convergent plate boundaries Aleutian-type mountain building • Where two oceanic plates converge and one is subducted beneath the other ...
... Most mountain building occurs at convergent plate boundaries Aleutian-type mountain building • Where two oceanic plates converge and one is subducted beneath the other ...
1. From the passage, it is inferred that igneous rock
... remove dissolved material and break rock into pieces; tiny grains of sand, silt, and clay or some other ground particles, which are called sediments. Over time, this fragmented material accumulates and is fused together to form sedimentary rocks. In this way, igneous rock can often become sedimentar ...
... remove dissolved material and break rock into pieces; tiny grains of sand, silt, and clay or some other ground particles, which are called sediments. Over time, this fragmented material accumulates and is fused together to form sedimentary rocks. In this way, igneous rock can often become sedimentar ...
Understanding Our Environment
... - Magma forced up through cracks in oceanic crust form mid-oceanic ridges. ...
... - Magma forced up through cracks in oceanic crust form mid-oceanic ridges. ...
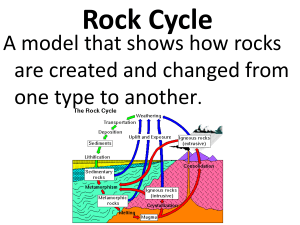
Rock Cycle
... 21. __________ is the process by which sediments get pressed together. 22. Sand grains, pebbles, mud, shells and leaves are all examples of ____________. 23. Any rock formed when another rock is changed by heat or _________ is a metamorphic rock. 24. The series of processes that slowly change Earth’ ...
... 21. __________ is the process by which sediments get pressed together. 22. Sand grains, pebbles, mud, shells and leaves are all examples of ____________. 23. Any rock formed when another rock is changed by heat or _________ is a metamorphic rock. 24. The series of processes that slowly change Earth’ ...
Earth System - Rock Cycle
... Rock Cycle Quiz 1. What are the three types of rocks that are part of the rock cycle? ...
... Rock Cycle Quiz 1. What are the three types of rocks that are part of the rock cycle? ...
The Outer Core - Geography1000
... The Inner and Outer Core • The Outer Core Molten and extending to a depth of about 3100 miles • The Inner Core • Solid and very dense mass having a radius of 900 miles • Both the inner and outer core are made of iron/nickel or iron/silicate. • Makes up 15% of the Earth’s volume and 32% of its mass ...
... The Inner and Outer Core • The Outer Core Molten and extending to a depth of about 3100 miles • The Inner Core • Solid and very dense mass having a radius of 900 miles • Both the inner and outer core are made of iron/nickel or iron/silicate. • Makes up 15% of the Earth’s volume and 32% of its mass ...
A short geologic history of the northeast United States
... a long Precambrian history which probably included repeated epochs of sedimentation, deformation, metamorphism, and intrusion. The major Grenville orogenic period, ending about 950 million years ago, concluded the Precambrian. The eastern limit of the Grenville rocks is not known; it may have lain w ...
... a long Precambrian history which probably included repeated epochs of sedimentation, deformation, metamorphism, and intrusion. The major Grenville orogenic period, ending about 950 million years ago, concluded the Precambrian. The eastern limit of the Grenville rocks is not known; it may have lain w ...
Rock Cycle
... Rocks that form when existing rocks are heated and squeezed deep inside the Earth. ...
... Rocks that form when existing rocks are heated and squeezed deep inside the Earth. ...
THE EARTH`S STRUCTURE
... geologists are unwilling to guess what the core is made of, but they think it must be very hot and dense. ...
... geologists are unwilling to guess what the core is made of, but they think it must be very hot and dense. ...
Earthquakes occur along faults.
... Along some parts of a fault, the rock on either side may slide along slowly and constantly. Along other parts of the fault, the rocks may stick, or lock together. The rocks bend as stress is put on them. Stress is the force exerted when an object presses on, pulls on, or pushes against another objec ...
... Along some parts of a fault, the rock on either side may slide along slowly and constantly. Along other parts of the fault, the rocks may stick, or lock together. The rocks bend as stress is put on them. Stress is the force exerted when an object presses on, pulls on, or pushes against another objec ...
Insights into a fossil plate interface of an erosional subduction zone
... Subduction zone seismicity and volcanism are triggered by processes occurring at the slab-wedge interface as a consequence of metamorphic reactions, mass-transfer and deformation. Although the shallow parts of subduction zones (<30-40 km) can be partly accessed by geophysical methods, the resolution ...
... Subduction zone seismicity and volcanism are triggered by processes occurring at the slab-wedge interface as a consequence of metamorphic reactions, mass-transfer and deformation. Although the shallow parts of subduction zones (<30-40 km) can be partly accessed by geophysical methods, the resolution ...
G: Glossary
... Precious metals: A general term for gold, silver, or any of the platinum-group metals, Shield: A large area of exposed basement rocks in a continental land mass surrounded by younger sedimentary rocks. The rocks of virtually all shield areas are Precambrian in age. Silicic: A general term used to de ...
... Precious metals: A general term for gold, silver, or any of the platinum-group metals, Shield: A large area of exposed basement rocks in a continental land mass surrounded by younger sedimentary rocks. The rocks of virtually all shield areas are Precambrian in age. Silicic: A general term used to de ...
Welcome to Mrs. Thompson`s 5th Grade Class
... Glassy Igneous Rocks Glassy Igneous Rocks cool so rapidly, that atoms don’t have enough time to get together, bond and form crystals. To cool this quickly the rocks MUST be extrusive. • Pumice (left) • Scoria (bottom left) • Obsidian (bottom right) • Note gasses in the lava can cause fine holes cal ...
... Glassy Igneous Rocks Glassy Igneous Rocks cool so rapidly, that atoms don’t have enough time to get together, bond and form crystals. To cool this quickly the rocks MUST be extrusive. • Pumice (left) • Scoria (bottom left) • Obsidian (bottom right) • Note gasses in the lava can cause fine holes cal ...
Proterozoic Rocks
... • Contains marble and siliciclastic sediments • Amphibolites to granulites • SE dipping foliations • ~1.2 gabbro-syenite-granite plutons ...
... • Contains marble and siliciclastic sediments • Amphibolites to granulites • SE dipping foliations • ~1.2 gabbro-syenite-granite plutons ...
2007 Q3 B folding faulting on landscape
... The Munster province of Ireland is made up of fold mountains. About 350 million years ago red sandstone rock was formed but it was covered with limestone. These two rocks were compressed together during the Amorican fold mountain time. The limestone was eroded from the fold anticlines and they are e ...
... The Munster province of Ireland is made up of fold mountains. About 350 million years ago red sandstone rock was formed but it was covered with limestone. These two rocks were compressed together during the Amorican fold mountain time. The limestone was eroded from the fold anticlines and they are e ...
Field Mapping of the Redrock Area, Burro Mountains, southwest
... depositional age, depositional setting, and source region, and they were subsequently metamorphosed by one or all of the magmatic events that occurred at 1.63 Ga, 1.46 Ga, and 1.25 Ga. The main goals of this project are to (1) use detrital zircons to evaluate the age and source regions for the proto ...
... depositional age, depositional setting, and source region, and they were subsequently metamorphosed by one or all of the magmatic events that occurred at 1.63 Ga, 1.46 Ga, and 1.25 Ga. The main goals of this project are to (1) use detrital zircons to evaluate the age and source regions for the proto ...
The Rock Cycle
... Created by the following geological processes: generation and movement of magma weathering erosion transportation deposition of sediment metamorphism of preexisting rocks. ...
... Created by the following geological processes: generation and movement of magma weathering erosion transportation deposition of sediment metamorphism of preexisting rocks. ...
Chapter 2 Regional Geologic Setting
... Nahlin fault, which more or less marks the western extent of the Cache Creek Terrane, is a steeply dipping to vertical fault (or series of faults). These have been intermittently active, probably since the Late Triassic into the Tertiary. The major Llewellyn fault trace forms the contact between reg ...
... Nahlin fault, which more or less marks the western extent of the Cache Creek Terrane, is a steeply dipping to vertical fault (or series of faults). These have been intermittently active, probably since the Late Triassic into the Tertiary. The major Llewellyn fault trace forms the contact between reg ...
Review
... 36. How does average temperature on Earth vary with latitude? 37. How do wind and air masses move in response to the coriolis effect in the northern hemisphere? 38. By what two broad criteria is climate defined? 39. How are marine environments broadly defined? Give some examples. Terms: actualism un ...
... 36. How does average temperature on Earth vary with latitude? 37. How do wind and air masses move in response to the coriolis effect in the northern hemisphere? 38. By what two broad criteria is climate defined? 39. How are marine environments broadly defined? Give some examples. Terms: actualism un ...
The Coastal Plain Province
... Largest of Virginia's physiographic provinces, the Piedmont extends from Virginia's "fall line" west to the Blue Ridge Mountains. Elevations range from around 100 feet in the east to more than 1,000 feet in the foothills of the Blue Ridge. Metamorphosed rocks characterize this region: schists, gneis ...
... Largest of Virginia's physiographic provinces, the Piedmont extends from Virginia's "fall line" west to the Blue Ridge Mountains. Elevations range from around 100 feet in the east to more than 1,000 feet in the foothills of the Blue Ridge. Metamorphosed rocks characterize this region: schists, gneis ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.