Name: Date: Chapter 9 Changes to Earth`s Surface Study Guide
... 1. Match the following landforms with the method by which they form. moraine ___ glacial groove ___ sand dune ___ ...
... 1. Match the following landforms with the method by which they form. moraine ___ glacial groove ___ sand dune ___ ...
Physical Geology
... or chemically precipitated. Metamorphic Rocks - Igneous rocks, sediment, or sedimentary rocks altered by being subjected to temperature or pressure conditions above those at the Earth's surface. ...
... or chemically precipitated. Metamorphic Rocks - Igneous rocks, sediment, or sedimentary rocks altered by being subjected to temperature or pressure conditions above those at the Earth's surface. ...
11 EG SP Exam 1 Review
... (c) age measured only by carbon-14 dating. (d) age measured only by potassium-argon dating. The principle of original horizontality is based on the fact that (a) sediment usually accumulates in horizontal layers. (b) sedimentary rocks generally become younger from bottom to top. (c) sedimentary rock ...
... (c) age measured only by carbon-14 dating. (d) age measured only by potassium-argon dating. The principle of original horizontality is based on the fact that (a) sediment usually accumulates in horizontal layers. (b) sedimentary rocks generally become younger from bottom to top. (c) sedimentary rock ...
Name
... Which list of silicate minerals shows the order in which they would weather from least resistant to most resistant? The atmospheric gas that forms a weak acid when dissolved in water is _______. If granite and basalt were exposed in an area with a hot and humid climate: Which of the following is NOT ...
... Which list of silicate minerals shows the order in which they would weather from least resistant to most resistant? The atmospheric gas that forms a weak acid when dissolved in water is _______. If granite and basalt were exposed in an area with a hot and humid climate: Which of the following is NOT ...
Geology Test
... present location of part of the Hawaiian Island chain. These volcanic islands may have formed as the Pacific Plate moved over a mantle hot spot. This diagram provides evidence that the Pacific Crustal Plate was moving toward the ...
... present location of part of the Hawaiian Island chain. These volcanic islands may have formed as the Pacific Plate moved over a mantle hot spot. This diagram provides evidence that the Pacific Crustal Plate was moving toward the ...
IGNEOUS
... *Form when rocks weather, erode, deposit, compact and cement together. *Have thicker layers that are loosely compacted. *Often dull in luster and can break easily. *Can have fossils in them. *Clastic- made of rock fragments / sediment. *Organic- made of remains of plants and animals *Chemical- made ...
... *Form when rocks weather, erode, deposit, compact and cement together. *Have thicker layers that are loosely compacted. *Often dull in luster and can break easily. *Can have fossils in them. *Clastic- made of rock fragments / sediment. *Organic- made of remains of plants and animals *Chemical- made ...
Midterm Study Guide2013
... 6. What is a rock? 7. Which type of rock in the rock cycle can only be formed at depths of a few kilometers below Earth’s surface? 8. What two sources of energy drive the processes that form rocks in the rock cycle? 9. What is the difference between extrusive igneous rocks and intrusive igneous rock ...
... 6. What is a rock? 7. Which type of rock in the rock cycle can only be formed at depths of a few kilometers below Earth’s surface? 8. What two sources of energy drive the processes that form rocks in the rock cycle? 9. What is the difference between extrusive igneous rocks and intrusive igneous rock ...
Bell Activity #15
... layers are squeezed together and pushed upward. B. Fault-Block Mountains Fault-block mountains form when this tension causes large blocks of the Earth’s crust to drop down relative to other blocks. ...
... layers are squeezed together and pushed upward. B. Fault-Block Mountains Fault-block mountains form when this tension causes large blocks of the Earth’s crust to drop down relative to other blocks. ...
13. Deformation and Mountain Building
... the large buildup of andesitic volcanism in this area and emplacement of granitic plutons and batholith development (6) The accretionary wedge along the coast formed as a response to the continued collision composed of folded and faulted ophiolite sequences (7) To the east is sedimentary rocks that ...
... the large buildup of andesitic volcanism in this area and emplacement of granitic plutons and batholith development (6) The accretionary wedge along the coast formed as a response to the continued collision composed of folded and faulted ophiolite sequences (7) To the east is sedimentary rocks that ...
Sedimentary Rocks
... • Cover about 75% of Earth’s surface, BUT• Account for only about 5% of Earth’s crust (They make a very thin layer.) • Are the key to Earth’s history. ...
... • Cover about 75% of Earth’s surface, BUT• Account for only about 5% of Earth’s crust (They make a very thin layer.) • Are the key to Earth’s history. ...
Middle Paleozoic Mountain Building
... Similar sequence of Limestones (Heldeberg Grp.), sands, silts, and shales deeper water flysch (Hamilton Group) and Redbed Molasse Deposits (braided streams and alluvial fans) Siccar Point-famous angular unconformity from James Hutton. Old Red Sandstone sitting on top of Silurain Rocks. Formed from t ...
... Similar sequence of Limestones (Heldeberg Grp.), sands, silts, and shales deeper water flysch (Hamilton Group) and Redbed Molasse Deposits (braided streams and alluvial fans) Siccar Point-famous angular unconformity from James Hutton. Old Red Sandstone sitting on top of Silurain Rocks. Formed from t ...
Sedimentary Rocks - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Plate tectonics theory Earth’s crust is outer, lighter portion of the lithosphere Lithosphere broken into 12 large and numerous small plates that slide & drift over the asthenosphere Plate movement may be caused by convection ...
... Plate tectonics theory Earth’s crust is outer, lighter portion of the lithosphere Lithosphere broken into 12 large and numerous small plates that slide & drift over the asthenosphere Plate movement may be caused by convection ...
geology of bc
... rocks into the Rocky Mountains. Approach of more micro-continents. Subduction related volcanism and intrusive bodies. The Intermontane terrane is mostly volcanic and sedimentary rocks that formed a long way away. ...
... rocks into the Rocky Mountains. Approach of more micro-continents. Subduction related volcanism and intrusive bodies. The Intermontane terrane is mostly volcanic and sedimentary rocks that formed a long way away. ...
Final Exam Study Guide Answer Key
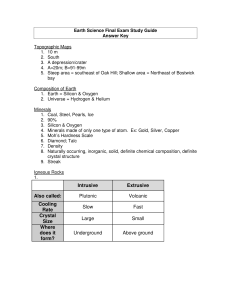
... 8. Naturally occurring, inorganic, solid, definite chemical composition, definite crystal structure 9. Streak Igneous Rocks ...
... 8. Naturally occurring, inorganic, solid, definite chemical composition, definite crystal structure 9. Streak Igneous Rocks ...
GeologyOfTheUS
... post-shield, and rejuvenated stages. During their younger phases, most Hawaiian volcanoes rise above sea level, forming islands. As the islands age, they erode and subside, becoming atolls and seamounts. ...
... post-shield, and rejuvenated stages. During their younger phases, most Hawaiian volcanoes rise above sea level, forming islands. As the islands age, they erode and subside, becoming atolls and seamounts. ...
METAMORPHIC ROCKS
... quartzite which may look the same whether it forms under low-grade to high-grade metamorphic conditions ...
... quartzite which may look the same whether it forms under low-grade to high-grade metamorphic conditions ...
Document
... At mid-oceanic ridges, basaltic magma forms by decompression melting of rising mantle rock. Some magma intrudes upward through dikes and erupts in the rift zone. Seawater is heated as it circulates through the hot crust and causes extensive hydrothermal alteration, metamorphosing large volumes ...
... At mid-oceanic ridges, basaltic magma forms by decompression melting of rising mantle rock. Some magma intrudes upward through dikes and erupts in the rift zone. Seawater is heated as it circulates through the hot crust and causes extensive hydrothermal alteration, metamorphosing large volumes ...
Igneous Rocks
... GEOLOGISTS RECOGNIZE THREE TYPES OF ROCKS 1) Igneous – rocks that cool from a molten state. 2) Sedimentary – rocks that form from the eroded and weathered particles of pre-existing rocks, a “re-cycled rock”. 3) Metamorphic – rocks that form by the alteration of pre-existing rocks through heat and pr ...
... GEOLOGISTS RECOGNIZE THREE TYPES OF ROCKS 1) Igneous – rocks that cool from a molten state. 2) Sedimentary – rocks that form from the eroded and weathered particles of pre-existing rocks, a “re-cycled rock”. 3) Metamorphic – rocks that form by the alteration of pre-existing rocks through heat and pr ...
Table of Contents - Mr. Tobin's Earth Science Class
... Bands always form perpendicular to pressure. Example: Gneiss - formed from granitic rock. 2. Nonfoliated: Minerals that form blocky crystal shapes. Examples: Quartzite - formed from quartz rich sandstone. Marble - formed from limestone. ...
... Bands always form perpendicular to pressure. Example: Gneiss - formed from granitic rock. 2. Nonfoliated: Minerals that form blocky crystal shapes. Examples: Quartzite - formed from quartz rich sandstone. Marble - formed from limestone. ...
Deformation - Bakersfield College
... • Strike is the intersection of a horizontal plane with the bed (a horizontal line measured as a compass direction) • Dip is the direction straight down the slope and is normal to the strike (measured from horizontal) ...
... • Strike is the intersection of a horizontal plane with the bed (a horizontal line measured as a compass direction) • Dip is the direction straight down the slope and is normal to the strike (measured from horizontal) ...
300_S2005_solid_earth
... important for determining earth’s history (put down in layers, contain fossils) lithification (= transformation of sediments into sedimentary rock) 2 sources of particles (solid – from weathered rock = detritus) (soluble material = chemical sedimentary) detrital – dominated by clay minerals and quar ...
... important for determining earth’s history (put down in layers, contain fossils) lithification (= transformation of sediments into sedimentary rock) 2 sources of particles (solid – from weathered rock = detritus) (soluble material = chemical sedimentary) detrital – dominated by clay minerals and quar ...
The Rock Cycle
... What are Rocks? Rocks are aggregates of 2 or more minerals. Petrology is the study of rocks. There are three classifications of rocks: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. ...
... What are Rocks? Rocks are aggregates of 2 or more minerals. Petrology is the study of rocks. There are three classifications of rocks: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.