3.2 3.3 3.4 Rock Types
... 1. What are the building blocks of rocks? 2. Minerals that form from magma form as the result of _______________________. 3. Why is color not a useful identification property? 4. What is a mineral’s streak? 5. What is the most common mineral group? ...
... 1. What are the building blocks of rocks? 2. Minerals that form from magma form as the result of _______________________. 3. Why is color not a useful identification property? 4. What is a mineral’s streak? 5. What is the most common mineral group? ...
WEEK 10: IGNEOUS ROCKS
... than 1mm and they will have a fine texture. Or, if they cooled really fast they might not have any crystals at all NON-CRYSTALLINE. If they were cooled super fast they’ll have a GLASSY texture. Some of these rocks may have gas pockets and have a vesicular texture. Be able to read the Scheme for Ig ...
... than 1mm and they will have a fine texture. Or, if they cooled really fast they might not have any crystals at all NON-CRYSTALLINE. If they were cooled super fast they’ll have a GLASSY texture. Some of these rocks may have gas pockets and have a vesicular texture. Be able to read the Scheme for Ig ...
along the crest of the arch, the higher members of the lower division
... division occur near Bridge of Earn, and extend beneath the estuary of the Tay and the Carse of Gowrie to near Dundee. Between Forgandenny and Bridge of Earn, the basement beds are found resting unconformably on the denuded Lower Old Red Sandstone volcanic rocks, where fragments of the latter occur i ...
... division occur near Bridge of Earn, and extend beneath the estuary of the Tay and the Carse of Gowrie to near Dundee. Between Forgandenny and Bridge of Earn, the basement beds are found resting unconformably on the denuded Lower Old Red Sandstone volcanic rocks, where fragments of the latter occur i ...
Rocks
... Sedimentary rocks are economically important in that they can be used as construction material. 3. Metamorphic rocks are formed by subjecting any rock type (including previously-formed metamorphic rock) to different temperature and pressure conditions than those in which the original rock was formed ...
... Sedimentary rocks are economically important in that they can be used as construction material. 3. Metamorphic rocks are formed by subjecting any rock type (including previously-formed metamorphic rock) to different temperature and pressure conditions than those in which the original rock was formed ...
Earth 50 2nd Midterm Exam November 14, 2005 Multiple Choice (2
... include coarse conglomerate interbedded with sandstone, fossiliferous limestone, and a lava flow interbedded between the limestone and sandstone. All these rocks are cross cut by a basaltic dike that has metamorphosed to rocks within a few meters of the dike, but not the sediments exposed only a 10 ...
... include coarse conglomerate interbedded with sandstone, fossiliferous limestone, and a lava flow interbedded between the limestone and sandstone. All these rocks are cross cut by a basaltic dike that has metamorphosed to rocks within a few meters of the dike, but not the sediments exposed only a 10 ...
Document
... 1. Compare and contrast uniformitarianism and catastrophism 2. Diagram the four basic internal structures of the earth. Describe the characteristics of each layer in terms of thickness, composition, and whether the layers are solid ,liquid or plastic. 3. What percent of the earth's mass does the cru ...
... 1. Compare and contrast uniformitarianism and catastrophism 2. Diagram the four basic internal structures of the earth. Describe the characteristics of each layer in terms of thickness, composition, and whether the layers are solid ,liquid or plastic. 3. What percent of the earth's mass does the cru ...
Unit 2 Review Guide
... 1. Define the following terms: earthquake, tsunami, tornado, volcano, hurricane, tropical depression, typhoon, Climate, weather, crust, plate tectonics, fold, fault, high-low-middle latitude belts, pangea 2. Where geographically is one most likely to find the following in the US and around the world ...
... 1. Define the following terms: earthquake, tsunami, tornado, volcano, hurricane, tropical depression, typhoon, Climate, weather, crust, plate tectonics, fold, fault, high-low-middle latitude belts, pangea 2. Where geographically is one most likely to find the following in the US and around the world ...
Chapter Questions
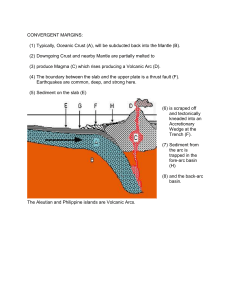
... volcanic settings like subduction zone volcanic arcs, continental hotpots, or continental rifting. Example: Granite. An accretionary wedge is a mass of sediment that derives from two sources: 1) sediment that is scraped off a subducting oceanic plate (might include pieces of ocean lithosphere as wel ...
... volcanic settings like subduction zone volcanic arcs, continental hotpots, or continental rifting. Example: Granite. An accretionary wedge is a mass of sediment that derives from two sources: 1) sediment that is scraped off a subducting oceanic plate (might include pieces of ocean lithosphere as wel ...
Tectonics of the Precambrian
... – High CO2 release – released at spreading centers when new crust forms and subducting crust has sediment on it including calcite which releases CO2 when it melts ...
... – High CO2 release – released at spreading centers when new crust forms and subducting crust has sediment on it including calcite which releases CO2 when it melts ...
Rock Cycle
... C. Forms much of the Earth’s crust. 2.Igneous rock can also form beneath Earth’s surface. A. Magma hardens beneath Earth’s surface. B. This is called intrusive rocks. C. Forms inside of many mountain ranges. The Latin word ignis means fire ...
... C. Forms much of the Earth’s crust. 2.Igneous rock can also form beneath Earth’s surface. A. Magma hardens beneath Earth’s surface. B. This is called intrusive rocks. C. Forms inside of many mountain ranges. The Latin word ignis means fire ...
Field Studies Part 2 Highlands and Valley and Ridge b
... models include faulted plunging folds with large throw along the fault and rotational movement of blocks. ...
... models include faulted plunging folds with large throw along the fault and rotational movement of blocks. ...
Mountain Belts and Continental Crust
... and near-melting of mantle, eruption of basaltic crust, vertical subsidence (elevator tectonics) and partial melting moving rocks down Bowen's reaction series, leading to origin of continental crust. Size of area that needs to stay in isostatic equilibrium very small, maybe 5 or 10km. • Archean 3.8- ...
... and near-melting of mantle, eruption of basaltic crust, vertical subsidence (elevator tectonics) and partial melting moving rocks down Bowen's reaction series, leading to origin of continental crust. Size of area that needs to stay in isostatic equilibrium very small, maybe 5 or 10km. • Archean 3.8- ...
rocksmineralsjeopard[1] - fourthgradeteam2012-2013
... Rocks are changed from one type into another by a never ending process called ...
... Rocks are changed from one type into another by a never ending process called ...
Rocks PowerPoint
... Extrusive rocks- igneous rocks formed from lava (ex: basalt) Intrusive rocks- igneous rocks formed from magma (ex: granite) ...
... Extrusive rocks- igneous rocks formed from lava (ex: basalt) Intrusive rocks- igneous rocks formed from magma (ex: granite) ...
8th Grade Science Final - Union Beach School District
... 19. Primary waves, secondary waves, surface waves Primary waves- p-waves, move the fastest, push pull, 1st to arrive at the seismograph station, can travel through solid, liquid and gas Secondary waves – s-waves, slower, move side to side, second to arrive, can travel through solids Surface waves – ...
... 19. Primary waves, secondary waves, surface waves Primary waves- p-waves, move the fastest, push pull, 1st to arrive at the seismograph station, can travel through solid, liquid and gas Secondary waves – s-waves, slower, move side to side, second to arrive, can travel through solids Surface waves – ...
About 50 million years ago the Siletzia Island Chain was formed
... beneath the Pacific Ocean in the spreading zone between two plates generated a string of shield volcanoes, some as wide as 30 miles at the base. Some 38 million years ago, as the plate they rested on turned and began subducting beneath the North American Plate, they collided with our continent and w ...
... beneath the Pacific Ocean in the spreading zone between two plates generated a string of shield volcanoes, some as wide as 30 miles at the base. Some 38 million years ago, as the plate they rested on turned and began subducting beneath the North American Plate, they collided with our continent and w ...
Answers
... Metamorphic Rock Identification, the Texture can be foliated (top 4 rocks) or nonfoliated (bottom 4 rocks). Mineral alignment is found in the first three rocks, and the mineral pyroxene is found in schist and gneiss. Since the question states that the rock does not have banding it is not Gneiss and ...
... Metamorphic Rock Identification, the Texture can be foliated (top 4 rocks) or nonfoliated (bottom 4 rocks). Mineral alignment is found in the first three rocks, and the mineral pyroxene is found in schist and gneiss. Since the question states that the rock does not have banding it is not Gneiss and ...
Review Sheet for Exam 1
... How igneous rocks form and the two categories of igneous rocks Igneous textures & what they tell you about the rock that they make up Bowen’s Reaction Series (and the temperatures associated with the crystallization of mafic and felsic minerals) Processes that change the composition of magma ...
... How igneous rocks form and the two categories of igneous rocks Igneous textures & what they tell you about the rock that they make up Bowen’s Reaction Series (and the temperatures associated with the crystallization of mafic and felsic minerals) Processes that change the composition of magma ...
class outline - WordPress.com
... 2. I can compare and contrast the features of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks 3. I can sketch a diagram to summarize the rock cycle ...
... 2. I can compare and contrast the features of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks 3. I can sketch a diagram to summarize the rock cycle ...
Rocks and Minerals Prep
... When you can see through a mineral sample, but the image is blurry, it is called… translucent transparent ...
... When you can see through a mineral sample, but the image is blurry, it is called… translucent transparent ...
File
... • Occurs only at ocean-ocean convergent and ocean-continent convergent • Ocean crust recycles back into the mantle • Along the trench sediments are dragged down and metamorphosed • Resulting rock is high-temp blue schist • Chaotic mixture of ig and sed rocks from both crusts is a melange ...
... • Occurs only at ocean-ocean convergent and ocean-continent convergent • Ocean crust recycles back into the mantle • Along the trench sediments are dragged down and metamorphosed • Resulting rock is high-temp blue schist • Chaotic mixture of ig and sed rocks from both crusts is a melange ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.













![rocksmineralsjeopard[1] - fourthgradeteam2012-2013](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008523164_1-6ea33f4458138c9958be8b075d2e1c2a-300x300.png)








