Chapter 3 Chemical Compounds
... electrical conductors (the flow of electricity is simply the flow of charged particles, like ions or electrons). Examples include H2(g), CO2(g), H2O( l ), C6H14( l ), and C12H22O11(s). ...
... electrical conductors (the flow of electricity is simply the flow of charged particles, like ions or electrons). Examples include H2(g), CO2(g), H2O( l ), C6H14( l ), and C12H22O11(s). ...
chemistry
... (ii) It failed to explain how and why atoms of elements combine with each other to form compound or molecules. (iii) It failed to explain the nature of forces that bind together different atoms in a molecule. (iv) It did not make any distinction between ultimate particle of an element that takes par ...
... (ii) It failed to explain how and why atoms of elements combine with each other to form compound or molecules. (iii) It failed to explain the nature of forces that bind together different atoms in a molecule. (iv) It did not make any distinction between ultimate particle of an element that takes par ...
6 Thermodynamics
... 15. The free energy change for a given reaction is −25 kJ. What is the equilibrium constant at 300 K? (A) e0 = 1.0 (B) e1 = 2.7 (C) e−10 = 4.4 × 10−5 (D) e10 = 2.3 × 104 ...
... 15. The free energy change for a given reaction is −25 kJ. What is the equilibrium constant at 300 K? (A) e0 = 1.0 (B) e1 = 2.7 (C) e−10 = 4.4 × 10−5 (D) e10 = 2.3 × 104 ...
Coarse-grained normal mode analysis in structural biology
... structure, typically an atomic-resolution structure such as in (a), colored according to secondary structure elements. As noted in the text, a lower-resolution structure, such as a cryo-EM map (c), can also be used as input for constructing an EN model. In order to process supramolecular assemblies, ...
... structure, typically an atomic-resolution structure such as in (a), colored according to secondary structure elements. As noted in the text, a lower-resolution structure, such as a cryo-EM map (c), can also be used as input for constructing an EN model. In order to process supramolecular assemblies, ...
Part 1
... 124 amino acids that cleaves single-stranded RNA molecules. It has four disulphide bonds in its native state that are essential for conformational folding and enzymatic activity. This was used by Christian Anfinsen to postulate the thermodynamic hypothesis of protein folding, according to which the ...
... 124 amino acids that cleaves single-stranded RNA molecules. It has four disulphide bonds in its native state that are essential for conformational folding and enzymatic activity. This was used by Christian Anfinsen to postulate the thermodynamic hypothesis of protein folding, according to which the ...
Table S17. P. gigantea hydrophobin models Existing model
... was relatively long with two short exons at the second and third positions. In C. subvermispora, most of the N terminal (5’) and C-terminal parts of the coding sequence of the protein (3’) were untranslated, although this did not significantly affect the size of the gene product. This protein has on ...
... was relatively long with two short exons at the second and third positions. In C. subvermispora, most of the N terminal (5’) and C-terminal parts of the coding sequence of the protein (3’) were untranslated, although this did not significantly affect the size of the gene product. This protein has on ...
No Slide Title
... How many H atoms are in 72.5 g of C3H8O ? 1 mol C3H8O = (3 x 12) + (8 x 1) + 16 = ______ g C3H8O 1 mol C3H8O molecules = ___________ mol H atoms 1 mol H = ___________ atoms H 1 mol C3H8O 8 mol H atoms 6.022 x 1023 H atoms 72.5 g C3H8O x ...
... How many H atoms are in 72.5 g of C3H8O ? 1 mol C3H8O = (3 x 12) + (8 x 1) + 16 = ______ g C3H8O 1 mol C3H8O molecules = ___________ mol H atoms 1 mol H = ___________ atoms H 1 mol C3H8O 8 mol H atoms 6.022 x 1023 H atoms 72.5 g C3H8O x ...
Building the sense of math in physics activities
... later) that in a dilute gas, D only depends on the average distance a molecule travels between collisions, λ, and it’s average speed v. If [λ] = L and [v] = L/T find an equation that expresses D in terms of λ and v. 2. Given that one of the following correctly represents the surface area of a sphere ...
... later) that in a dilute gas, D only depends on the average distance a molecule travels between collisions, λ, and it’s average speed v. If [λ] = L and [v] = L/T find an equation that expresses D in terms of λ and v. 2. Given that one of the following correctly represents the surface area of a sphere ...
File - Mr Weng`s IB Chemistry
... • The mole is a fixed number of particles and refers to the amount, n, of substance. • Masses of atoms are compared on a scale relative to 12C and are expressed as relative atomic mass (Ar) and relative formula/molecular mass (Mr). • Molar mass (M) has the units g mol-1. • The empirical formula and ...
... • The mole is a fixed number of particles and refers to the amount, n, of substance. • Masses of atoms are compared on a scale relative to 12C and are expressed as relative atomic mass (Ar) and relative formula/molecular mass (Mr). • Molar mass (M) has the units g mol-1. • The empirical formula and ...
Chapter 3 Stoichiometry
... Stoichiometry: The study of quantities of materials consumed and produced in chemical reactions Atomic Masses: Are determined by comparing with 12C (carbon-12 scale). By definition, carbon-12 is assigned a mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units (amu) and the masses of all other atoms are given relativ ...
... Stoichiometry: The study of quantities of materials consumed and produced in chemical reactions Atomic Masses: Are determined by comparing with 12C (carbon-12 scale). By definition, carbon-12 is assigned a mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units (amu) and the masses of all other atoms are given relativ ...
Monte Carlo Simulations of HIV Capsid Protein
... Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling binding and conformational changes of small peptides,33 as well as in QM/MM calculations.34,35 Because the structures of free full-length CA dimers are unknown, however, these free-energy methods are not immediately applicable here, although they could be ...
... Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling binding and conformational changes of small peptides,33 as well as in QM/MM calculations.34,35 Because the structures of free full-length CA dimers are unknown, however, these free-energy methods are not immediately applicable here, although they could be ...
video slide
... aqueous status such as biological compounds. • This makes it especially attractive in clinical chemistry for drug confirmation, amino acid analysis and hormone separations. ...
... aqueous status such as biological compounds. • This makes it especially attractive in clinical chemistry for drug confirmation, amino acid analysis and hormone separations. ...
File
... • To balance an equation means to change the numbers of each molecule involved, so that the same number of atoms of each element appear on the reactants side and on the products side. • Chemical equations balance on an atomic level, not molecular. • You cannot change the formula of a substance, i.e. ...
... • To balance an equation means to change the numbers of each molecule involved, so that the same number of atoms of each element appear on the reactants side and on the products side. • Chemical equations balance on an atomic level, not molecular. • You cannot change the formula of a substance, i.e. ...
Protein structure prediction
... - hydrogen bonds H—O (fast to form/break) • Non-bonded interactions between atoms: - electrostatic (long-range) - van der Waals (short range) • Confirmation that minimizes the free energy (Anfinsen’s hypothesis) François Fages ...
... - hydrogen bonds H—O (fast to form/break) • Non-bonded interactions between atoms: - electrostatic (long-range) - van der Waals (short range) • Confirmation that minimizes the free energy (Anfinsen’s hypothesis) François Fages ...
(Figure 1.3) (Figure 1.6)
... (Figure 5.3) Surface potential of p140(375-480). (A) Electrostatic potential of the accessible surface of p140(375-480) is shown . Negative potential is colored in red and positive potential in blue. The residues contributing to the surface charge are indicated on the surface. (B) Surface accessible ...
... (Figure 5.3) Surface potential of p140(375-480). (A) Electrostatic potential of the accessible surface of p140(375-480) is shown . Negative potential is colored in red and positive potential in blue. The residues contributing to the surface charge are indicated on the surface. (B) Surface accessible ...
DR AMENA RAHIM BIOCHEMISTRY
... threonine, cysteine, asparagine, and glutamine.The polarity of serine and threonine is contributed by their hydroxyl groups; that of cysteine by its sulfhydryl group; and that of asparagine and glutamine by their amide groups. ...
... threonine, cysteine, asparagine, and glutamine.The polarity of serine and threonine is contributed by their hydroxyl groups; that of cysteine by its sulfhydryl group; and that of asparagine and glutamine by their amide groups. ...
Detailed Computational Study of Point Mutations of the TP53 Tumor-Suppressor Protein
... It is becoming progressively accepted that the progression of mammalian cells towards malignancy is an evolutionary process that involves an accumulation of mutations on both the molecular and chromosomal level. Inherent in models for malignant progression is the concept that an initial mutation in ...
... It is becoming progressively accepted that the progression of mammalian cells towards malignancy is an evolutionary process that involves an accumulation of mutations on both the molecular and chromosomal level. Inherent in models for malignant progression is the concept that an initial mutation in ...
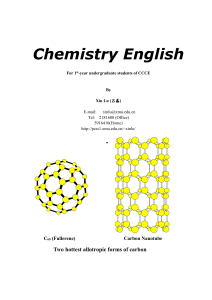
Chemistry English
... or 1s2 How to illustrate the 2p orbitals that contain 6 electrons? 3.12 Writing Electronic Configurations for Atoms The electronic configurations for an atom is written by listing the orbitals occupied by electrons in the atom along with the number of electrons in each orbitals. Three Rules which mu ...
... or 1s2 How to illustrate the 2p orbitals that contain 6 electrons? 3.12 Writing Electronic Configurations for Atoms The electronic configurations for an atom is written by listing the orbitals occupied by electrons in the atom along with the number of electrons in each orbitals. Three Rules which mu ...
chapter 3
... Examples include burning of gas, candles and glucose, flicking a bic lighter. A. C3H8 + O2 → ...
... Examples include burning of gas, candles and glucose, flicking a bic lighter. A. C3H8 + O2 → ...
Chemistry 11 Exam 1 Spring 2006 When answering questions be
... Solubility rules: Alkali metals, ammonium, nitrate, perchlorate (ClO4-), chlorate (ClO3-), nitrate, and acetate (C2H3O2-) salts are soluble. Chlorides, bromides (Br-), and iodides (I-) are soluble unless combined with Ag+, Pb+2, or Hg2+2. Sulfates are soluble unless combined with Pb+2, Ca+2, Sr+2, B ...
... Solubility rules: Alkali metals, ammonium, nitrate, perchlorate (ClO4-), chlorate (ClO3-), nitrate, and acetate (C2H3O2-) salts are soluble. Chlorides, bromides (Br-), and iodides (I-) are soluble unless combined with Ag+, Pb+2, or Hg2+2. Sulfates are soluble unless combined with Pb+2, Ca+2, Sr+2, B ...
File
... Dissolving Covalent Compounds • C12H22O11 (s) C12H22O11 (aq) • NO dissociation because NO ions • Sucrose dissolves in water because sugar is polar (-OH group), but dissociation does not occur. Sucrose molecules are simply separated from each other. No ions are formed ...
... Dissolving Covalent Compounds • C12H22O11 (s) C12H22O11 (aq) • NO dissociation because NO ions • Sucrose dissolves in water because sugar is polar (-OH group), but dissociation does not occur. Sucrose molecules are simply separated from each other. No ions are formed ...
Docking QM/MM
... solved to 2.4 Å resolution, and the average RMSD of theoretical models is ∼0.8 Å. In contrast 2UVX, the highest resolution structure at 2.0 Å, displays a mean RMSD of ∼0.2 Å. In between these, 1WCC and 1W7H are solved to a resolution of 2.2 Å, and the RMSDs of the theoretical structures are ∼0.3 Å o ...
... solved to 2.4 Å resolution, and the average RMSD of theoretical models is ∼0.8 Å. In contrast 2UVX, the highest resolution structure at 2.0 Å, displays a mean RMSD of ∼0.2 Å. In between these, 1WCC and 1W7H are solved to a resolution of 2.2 Å, and the RMSDs of the theoretical structures are ∼0.3 Å o ...
Protein Ubiquitination
... important role in protein folding. Chaperons safeguard the folding of nascent chains. ...
... important role in protein folding. Chaperons safeguard the folding of nascent chains. ...
Tertiary Protein Structure
... B. It is how the secondary elements folds over to form a tertiary structure. C. The scope of tertiary structure is thus long-range because we are talking about from one side of a protein to another. If something effects the protein here. It can cause a conformational change on the other side. It is ...
... B. It is how the secondary elements folds over to form a tertiary structure. C. The scope of tertiary structure is thus long-range because we are talking about from one side of a protein to another. If something effects the protein here. It can cause a conformational change on the other side. It is ...
CHEMISTRY – Summer Assignment Solutions 2013
... When sodium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid, the carbonic acid that is formed immediately breaks down into carbon dioxide and water. What mass of sodium carbonate would have been originally present if 5.0 L of carbon dioxide was produced? [hint - molar volume of a gas is 22.414 L/mol] Na2CO3 ...
... When sodium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid, the carbonic acid that is formed immediately breaks down into carbon dioxide and water. What mass of sodium carbonate would have been originally present if 5.0 L of carbon dioxide was produced? [hint - molar volume of a gas is 22.414 L/mol] Na2CO3 ...