Atomic
... • Atoms want to be “stable” = full valence shell. • Share or transfer electrons. • To become stable, atoms will hold together by chemical bonds. • The strongest chemical bonds are covalent bonds and ionic bonds. ...
... • Atoms want to be “stable” = full valence shell. • Share or transfer electrons. • To become stable, atoms will hold together by chemical bonds. • The strongest chemical bonds are covalent bonds and ionic bonds. ...
Biochemistry H Silent Tea Party Name_______________ 1. What is
... Four main classes of large biological molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids) made up of many smaller molecules and atoms. 13. What are monomers? small chemical unit that can join together with other small units to form larger units called polymer 14. What are polymers? Large com ...
... Four main classes of large biological molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids) made up of many smaller molecules and atoms. 13. What are monomers? small chemical unit that can join together with other small units to form larger units called polymer 14. What are polymers? Large com ...
Data/hora: 18/04/2017 14:16:42 Provedor de dados: 189 País
... study, X-ray crystallography has been used to examine the structural details of the interaction between a wheat type 2 ns-LTP and a lipid, l-α--palmitoyl-phosphatidyl glycerol. This crystal structure was solved ab initio at 1.12 Å resolution by direct methods. The typical α--helical bundle fold of ...
... study, X-ray crystallography has been used to examine the structural details of the interaction between a wheat type 2 ns-LTP and a lipid, l-α--palmitoyl-phosphatidyl glycerol. This crystal structure was solved ab initio at 1.12 Å resolution by direct methods. The typical α--helical bundle fold of ...
1. Protein Interactions
... polymeric chains of amino acids. Each of the 20 standard amino acids have a oneletter symbol. A sequence of three symbols, as shown for RNA (right) is called a Amino acids have a central codon carbon atom attached to a hydrogen, a carboxyl group (COOH) and an amine ...
... polymeric chains of amino acids. Each of the 20 standard amino acids have a oneletter symbol. A sequence of three symbols, as shown for RNA (right) is called a Amino acids have a central codon carbon atom attached to a hydrogen, a carboxyl group (COOH) and an amine ...
Atomic and molecular models for macromolecular structure
... • Full quantum mechanics is not possible • Classical forces between atoms • Minimize energy to obtain structure ...
... • Full quantum mechanics is not possible • Classical forces between atoms • Minimize energy to obtain structure ...
CHM 101
... Supply the most appropriate word, phrase or numerical value for each of the following statements. ...
... Supply the most appropriate word, phrase or numerical value for each of the following statements. ...
Chemistry of Life
... Chemistry of Life Chemistry is the study of how matter interacts, thus we need to understand some of the basic rules and ideas about matter to ...
... Chemistry of Life Chemistry is the study of how matter interacts, thus we need to understand some of the basic rules and ideas about matter to ...
Biomolecules in water and water in biomolecules
... based on the statistical mechanics of liquids, or the 3D-RISM/RISM theory. The theory has demonstrated its amazing capability of “predicting” the process from the frist principle. [1] However, what we have investigated so far is an entirely equilibrium process both in protein conformation and solvat ...
... based on the statistical mechanics of liquids, or the 3D-RISM/RISM theory. The theory has demonstrated its amazing capability of “predicting” the process from the frist principle. [1] However, what we have investigated so far is an entirely equilibrium process both in protein conformation and solvat ...
Protein Structure and Folding
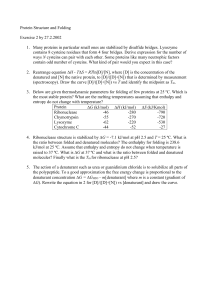
... contains 8 cysteine residues that form 4 four bridges. Derive expression for the number of ways N cysteins can pair with each other. Some proteins like many neutrophic factors contain odd number of cysteins. What kind of pair would you expect in this case? 2. Rearrange equation H - TS = RTln[D]/[N ...
... contains 8 cysteine residues that form 4 four bridges. Derive expression for the number of ways N cysteins can pair with each other. Some proteins like many neutrophic factors contain odd number of cysteins. What kind of pair would you expect in this case? 2. Rearrange equation H - TS = RTln[D]/[N ...
Dr. Fernando L. Barroso da Silva Protein complexation driven by
... are systems that show attraction in the weak-coupling regime where the expected behavior is repulsion (as predicted by the classical DVLO theory). The theoretical background for the physical interpretation of such systems goes back to Kirkwood’s structure sensitive electrostatic forces, where attrac ...
... are systems that show attraction in the weak-coupling regime where the expected behavior is repulsion (as predicted by the classical DVLO theory). The theoretical background for the physical interpretation of such systems goes back to Kirkwood’s structure sensitive electrostatic forces, where attrac ...
Chemical Bonding File
... Hydrogen bond: Hydrogen bonding interactions play a major role in many chemical and biological processes.This bond is the attractive force between the hydrogen attached to an electronegative atom of one molecule and an electronegative atom of a different molecule. Usually the electronegative atom is ...
... Hydrogen bond: Hydrogen bonding interactions play a major role in many chemical and biological processes.This bond is the attractive force between the hydrogen attached to an electronegative atom of one molecule and an electronegative atom of a different molecule. Usually the electronegative atom is ...
Membrane Transport
... Transport Across the Membrane • The cell membrane is semipermeable • Small, nonpolar molecules can get through • Large, polar, or charged molecules need help from proteins to cross the membrane ...
... Transport Across the Membrane • The cell membrane is semipermeable • Small, nonpolar molecules can get through • Large, polar, or charged molecules need help from proteins to cross the membrane ...
HOW GOOD DO WE HAVE TO BE TO SOLVE THE PROTEIN FOLDING AND PROTEIN-LIGAND SCORING PROBLEMS?
... perspective. This talk will touch on several of these challenges and suggest ways in which to overcome them in the coming years. In particular, we will touch on the establishment of error bounds in computational prediction of the free energy of binding of a ligand for a protein target and the foldin ...
... perspective. This talk will touch on several of these challenges and suggest ways in which to overcome them in the coming years. In particular, we will touch on the establishment of error bounds in computational prediction of the free energy of binding of a ligand for a protein target and the foldin ...
Monte Carlo, Adaptive Integration and Protein
... Authors: Christopher A. Mirabzadeh, F. Marty Ytreberg Background and Objective: Our objective is to develop more efficient methods for calculating protein-protein binding affinities and using them to understand protein evolution. Specifically, we are developing the Adaptive Integration Method for us ...
... Authors: Christopher A. Mirabzadeh, F. Marty Ytreberg Background and Objective: Our objective is to develop more efficient methods for calculating protein-protein binding affinities and using them to understand protein evolution. Specifically, we are developing the Adaptive Integration Method for us ...
Chemistry in Biology Unit Test Review Name: Atoms, Elements and
... 4. What lipids can be found in cell membranes? What is important about their structure? ...
... 4. What lipids can be found in cell membranes? What is important about their structure? ...
The Nature of Solubility
... • Every water molecule has one oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms. • The chemical formula is H2O. • The hydrogen atoms are 105° apart from each other. ...
... • Every water molecule has one oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms. • The chemical formula is H2O. • The hydrogen atoms are 105° apart from each other. ...
November 19, 2012 3:00 PM Livermore Center 101 Isaac C. Sanchez
... separations. Using atomistic models, cavity size (free volume) distributions were determined by a combination of molecular dynamics (MD) and Monte Carlo methods for 6 thermally rearranged (TR) polyimides and their precursors. Diffusion, solubility, and permeation of gases in TR polymers and their pr ...
... separations. Using atomistic models, cavity size (free volume) distributions were determined by a combination of molecular dynamics (MD) and Monte Carlo methods for 6 thermally rearranged (TR) polyimides and their precursors. Diffusion, solubility, and permeation of gases in TR polymers and their pr ...
Day 1 - Questions 1) What is the smallest basic unit of matter? 2
... 1) What is the smallest basic unit of matter? ...
... 1) What is the smallest basic unit of matter? ...
Übung: Monte Carlo, Molecular Dynamics
... based on potentials of mean force. It is based on Cα-Cα distances. I do not distinguish between amino acids which are separated by one residue (i,i+2) and those separated by many residues. Why will this be a very bad approximation ? 8. I am working with a lattice model for a protein. Describe how I ...
... based on potentials of mean force. It is based on Cα-Cα distances. I do not distinguish between amino acids which are separated by one residue (i,i+2) and those separated by many residues. Why will this be a very bad approximation ? 8. I am working with a lattice model for a protein. Describe how I ...
Faraday Discussion Meeting September 2002
... Recently it has become possible to use nanotechnology tools such as the atomic force microscope and laser tweezers to manipulate individual molecules and explore the complex free energy landscape that describes protein conformation. The method of mechanically unfolding single proteins using the atom ...
... Recently it has become possible to use nanotechnology tools such as the atomic force microscope and laser tweezers to manipulate individual molecules and explore the complex free energy landscape that describes protein conformation. The method of mechanically unfolding single proteins using the atom ...