Homework 1-6 Classifying Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes File
... Instructions: Use the clues to decide whether the organism is a Prokaryote or Eukaryote. 1. ___________ - This organism is made of many cells. Each cell has a nucleus, mitochondria and many chloroplasts. It can grow to over 100 ft tall and produces many woody cones for reproduction. 2. ___________- ...
... Instructions: Use the clues to decide whether the organism is a Prokaryote or Eukaryote. 1. ___________ - This organism is made of many cells. Each cell has a nucleus, mitochondria and many chloroplasts. It can grow to over 100 ft tall and produces many woody cones for reproduction. 2. ___________- ...
Study Guide for Cell Structure, Function, and Division
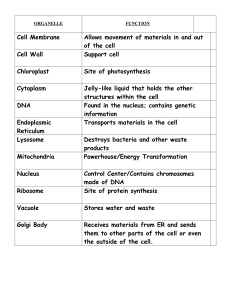
... Study Guide for Cell Structure, Function, and Division 1. What is the functions of all the following organelles: (also know how to identify them on a diagram) a. Ribosomes b. Rough ER c. Smooth ER d. Cell membrane e. Nucleus f. Golgi Body g. Lysosome h. Vacuoles i. Mitochondria 2. List two ways plan ...
... Study Guide for Cell Structure, Function, and Division 1. What is the functions of all the following organelles: (also know how to identify them on a diagram) a. Ribosomes b. Rough ER c. Smooth ER d. Cell membrane e. Nucleus f. Golgi Body g. Lysosome h. Vacuoles i. Mitochondria 2. List two ways plan ...
Unit: Cell Theory and Structure (Ch. 7 “I can…” state discuss
... Unit: Cell Theory and Structure (Ch. 7) ...
... Unit: Cell Theory and Structure (Ch. 7) ...
Week 9 CELL WALLS are found in plant cells. They are made up of
... A collection of cells that perform the same function and that work together is called a TISSUE. Examples of tissues include nervous tissues, muscle tissue, and blood tissue. ...
... A collection of cells that perform the same function and that work together is called a TISSUE. Examples of tissues include nervous tissues, muscle tissue, and blood tissue. ...
Cell Specialization
... • Tissue: A group of similar cells that perform a particular function • Organ: similar tissues of body which carry out 1+ similar functions • Organ system: work together to perform a specific function. ...
... • Tissue: A group of similar cells that perform a particular function • Organ: similar tissues of body which carry out 1+ similar functions • Organ system: work together to perform a specific function. ...
Cell Organelle Packet
... 4. Ribosomes and endoplasmic reticulum 5. Golgi apparatus and vesicles 6. Nucleolus and ribosomes 7. Mitochondria and sperm tail flagella 8. Smooth ER and cell membranes ...
... 4. Ribosomes and endoplasmic reticulum 5. Golgi apparatus and vesicles 6. Nucleolus and ribosomes 7. Mitochondria and sperm tail flagella 8. Smooth ER and cell membranes ...
programmed cell death
... BAX undergoes extensive conformational changes during the mitochondrial translocation process. The protein changes from a soluble cytoplasmic protein in healthy cells to one that appears to have at least 3 helices inserted in the mitochondrial membrane in apoptotic cells. Youle and Strasser (2008) T ...
... BAX undergoes extensive conformational changes during the mitochondrial translocation process. The protein changes from a soluble cytoplasmic protein in healthy cells to one that appears to have at least 3 helices inserted in the mitochondrial membrane in apoptotic cells. Youle and Strasser (2008) T ...
“Put that in the Form of a Question, Please!”
... These are organelles that are used for storage ...
... These are organelles that are used for storage ...
CELL PARTS
... --Converts light energy to carbohydrates --Has stacks of thylakoids --Has its own DNA ...
... --Converts light energy to carbohydrates --Has stacks of thylakoids --Has its own DNA ...
Chloroplasts
... In the beginning, there were Cells… • Bacteria are thought to be the earliest forms of life on the planet. • Simple life flourished in tidal pools near the sea. • Water was warm and full of nutrients. ...
... In the beginning, there were Cells… • Bacteria are thought to be the earliest forms of life on the planet. • Simple life flourished in tidal pools near the sea. • Water was warm and full of nutrients. ...
1. All living things are made of cell
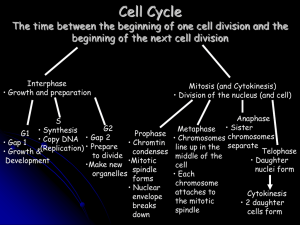
... 3. What process creates new cells for growth and repair through cell division that are identical to the parent cell? Mitosis ...
... 3. What process creates new cells for growth and repair through cell division that are identical to the parent cell? Mitosis ...
Cells
... Differences Between Plant & Animals Cells * Plants = cell walls *Plants = plastids *Plants = chloroplast ...
... Differences Between Plant & Animals Cells * Plants = cell walls *Plants = plastids *Plants = chloroplast ...
Biology Unit Study Check List Cell: • Organelles • Limit of size
... Plant Systems – meristematic cells, root system, vascular tissue (xylem and phloem), photosynthesis, gas exchange (stomata and guard cells) ...
... Plant Systems – meristematic cells, root system, vascular tissue (xylem and phloem), photosynthesis, gas exchange (stomata and guard cells) ...
Solutions - MIT OpenCourseWare
... microscope? Explain your answer. With a light microscope you could easily distinguish the prokaryotic bacteria from the other cell types. The prokaryotic bacteria would not have a nucleus, the other cell types would. The yeast cell wall would distinguish yeast cells from human and insect cells. Dist ...
... microscope? Explain your answer. With a light microscope you could easily distinguish the prokaryotic bacteria from the other cell types. The prokaryotic bacteria would not have a nucleus, the other cell types would. The yeast cell wall would distinguish yeast cells from human and insect cells. Dist ...
Chapter 1 Eukaryotic Cells Section 1
... Cell membrane – protective barrier that encloses a cell Cytoskeleton – web of proteins in the cytoplasm that keep the membrane from collapsing Nucleus – largest organelle in a eukaryotic cell, contains DNA that directs all cell activity Ribosomes – organelles that make protein Endoplasmic reticulum ...
... Cell membrane – protective barrier that encloses a cell Cytoskeleton – web of proteins in the cytoplasm that keep the membrane from collapsing Nucleus – largest organelle in a eukaryotic cell, contains DNA that directs all cell activity Ribosomes – organelles that make protein Endoplasmic reticulum ...
Cell Structure and Function Study Guide
... What are the three parts of the cell theory? How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? Be able to put them in to order from least to most complex and explain each one. CELL PARTS: Be able to name, give a function, and identify in a picture the f ...
... What are the three parts of the cell theory? How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? Be able to put them in to order from least to most complex and explain each one. CELL PARTS: Be able to name, give a function, and identify in a picture the f ...
Cell Structure Cloze - Science
... building blocks called _________________. These cells have many different basic structures in common called _________________. For example, cells are surrounded by a cell _________________ which controls the materials that move in and out of a cell. Another structure that most cells have in common i ...
... building blocks called _________________. These cells have many different basic structures in common called _________________. For example, cells are surrounded by a cell _________________ which controls the materials that move in and out of a cell. Another structure that most cells have in common i ...
Programmed cell death
Programmed cell-death (or PCD) is death of a cell in any form, mediated by an intracellular program. PCD is carried out in a regulated process, which usually confers advantage during an organism's life-cycle. For example, the differentiation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the fingers apoptose; the result is that the digits are separate. PCD serves fundamental functions during both plant and metazoa (multicellular animals) tissue development.Apoptosis and autophagy are both forms of programmed cell death, but necrosis is a non-physiological process that occurs as a result of infection or injury.Necrosis is the death of a cell caused by external factors such as trauma or infection and occurs in several different forms. Recently a form of programmed necrosis, called necroptosis, has been recognized as an alternate form of programmed cell death. It is hypothesized that necroptosis can serve as a cell-death backup to apoptosis when the apoptosis signaling is blocked by endogenous or exogenous factors such as viruses or mutations.