Name School Class Date Laboratory Investigation on Cells Observing Plant Cells
... microscope slide. The piece of onion should be no bigger than 1cm . Cover this with one drop of iodine solution and place the cover slip over this. Observe the cells using the x10 objective lens. ...
... microscope slide. The piece of onion should be no bigger than 1cm . Cover this with one drop of iodine solution and place the cover slip over this. Observe the cells using the x10 objective lens. ...
Cell Organelles
... • This is a storage organelle. Plant cells generally have one large one that takes up most of the space within the cell and is used for storage of all sorts of molecules. ...
... • This is a storage organelle. Plant cells generally have one large one that takes up most of the space within the cell and is used for storage of all sorts of molecules. ...
Cells Test What do I need to know???? Know the parts of a plant
... What is the difference between a multicellular organism and a unicellular organism? ...
... What is the difference between a multicellular organism and a unicellular organism? ...
Cell structure and Function Practice Quiz
... Pick the choice that you think best answers the question If you get the answer correct you can move on to the next question If you get the answer wrong you will be returned to the question to try again ...
... Pick the choice that you think best answers the question If you get the answer correct you can move on to the next question If you get the answer wrong you will be returned to the question to try again ...
TEACHER NOTES AND ANSWERS Section 5.1
... 2. cell growth, normal functions, replications of organelles 3. synthesis 4. copies DNA 5. gap 2 6. additional growth and carrying out of normal functions 7. mitosis 8. cell division 9. prophase 10. metaphase 11. anaphase 12. telophase 13. cytokinesis 14. mitosis 15. interphase Cells divide at diffe ...
... 2. cell growth, normal functions, replications of organelles 3. synthesis 4. copies DNA 5. gap 2 6. additional growth and carrying out of normal functions 7. mitosis 8. cell division 9. prophase 10. metaphase 11. anaphase 12. telophase 13. cytokinesis 14. mitosis 15. interphase Cells divide at diffe ...
Cell death and authophagy in plant life
... Uppsala BioCenter, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences & Linnean Center for Plant Biology, Uppsala / Sweden ...
... Uppsala BioCenter, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences & Linnean Center for Plant Biology, Uppsala / Sweden ...
Unit 2 Part 1: The Cell Test Review 1. What is the function of a cell`s
... 12. What organelle in plant cells makes it possible for plants to carry out photosynthesis? 13. What does the structure of the endoplasmic reticulum look like? 14. How does the cell membrane function like a security gate? 15. What gets energy by absorbing materials and does not have chloroplast? 16. ...
... 12. What organelle in plant cells makes it possible for plants to carry out photosynthesis? 13. What does the structure of the endoplasmic reticulum look like? 14. How does the cell membrane function like a security gate? 15. What gets energy by absorbing materials and does not have chloroplast? 16. ...
Cells key word bingo
... A thin layer that surrounds the cell and controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell – CELL MEMBRANE A tough box like structure around a plant cell – CELL WALL The Parts of a plant cell that carry out photosynthesis – CHLOROPLASTS A jelly like substance that is found inside cells – CY ...
... A thin layer that surrounds the cell and controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell – CELL MEMBRANE A tough box like structure around a plant cell – CELL WALL The Parts of a plant cell that carry out photosynthesis – CHLOROPLASTS A jelly like substance that is found inside cells – CY ...
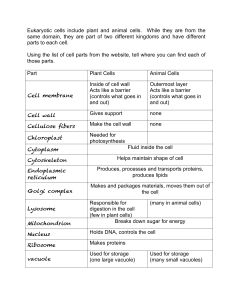
Cell membrane Cell wall Cellulose fibers Chloroplast Cytoplasm
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
Study Guide
... Summary Common Cell Traits All cells have an outer covering called a cell membrane. Cells can be classified as prokaryotic (cells that lack a distinct nucleus) or eukaryotic (cells with a distinct membrane-bound nucleus). Cell Organization Each cell in your body has a specific function. Most ...
... Summary Common Cell Traits All cells have an outer covering called a cell membrane. Cells can be classified as prokaryotic (cells that lack a distinct nucleus) or eukaryotic (cells with a distinct membrane-bound nucleus). Cell Organization Each cell in your body has a specific function. Most ...
Cell theory + structure
... Describe the contributions of the following scientists: Robert Hooke – Anton van Leeuwenhoek – Matthias Schleiden – Theodor Schwann – Rudolph Virchow – All cells come from pre-existing cells The Cell Theory State the three components of the cell theory: 1. ___________________________________________ ...
... Describe the contributions of the following scientists: Robert Hooke – Anton van Leeuwenhoek – Matthias Schleiden – Theodor Schwann – Rudolph Virchow – All cells come from pre-existing cells The Cell Theory State the three components of the cell theory: 1. ___________________________________________ ...
What Part of the Cell am I?
... Since I contain many enzymes, I can digest an injured cell. And I can make a large molecule into a smaller one as well. What am I? ...
... Since I contain many enzymes, I can digest an injured cell. And I can make a large molecule into a smaller one as well. What am I? ...
Differences between the animal and plant cell: The plant cell has a
... The plant cell has a rigid cell wall for support and protection (1). If animal cells had cell walls, animals would not be able to move. ...
... The plant cell has a rigid cell wall for support and protection (1). If animal cells had cell walls, animals would not be able to move. ...
Important organells in a Cell 2
... Nucleus: contains the cell’s DNA. ‘Brain’ of the cell. Mitochondnon: Site of respiration. Provides the energy for the cell to function. Ribosomes: Site where proteins are made (including enzymes). Vacuole: Storage Cytoplasm: Watery fluid that all the cell organelles float in. _______________________ ...
... Nucleus: contains the cell’s DNA. ‘Brain’ of the cell. Mitochondnon: Site of respiration. Provides the energy for the cell to function. Ribosomes: Site where proteins are made (including enzymes). Vacuole: Storage Cytoplasm: Watery fluid that all the cell organelles float in. _______________________ ...
Biology cells/cell theory
... Cell membraneCell wallPlasmodesmaVacouleTonoplastCrystalPlastidsChloroplastLeucoplastChromoplastGolgi complexRibosomeEndoplasmic ReticulumMitochondrionMicrotubuleMicrofilamentLysosomeMicrobodyHyaloplasmNucleusNuclear envelopeNuclear porePlant cells vs animal cells: Animal Cell ...
... Cell membraneCell wallPlasmodesmaVacouleTonoplastCrystalPlastidsChloroplastLeucoplastChromoplastGolgi complexRibosomeEndoplasmic ReticulumMitochondrionMicrotubuleMicrofilamentLysosomeMicrobodyHyaloplasmNucleusNuclear envelopeNuclear porePlant cells vs animal cells: Animal Cell ...
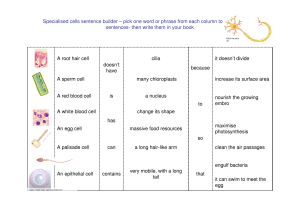
engulf bacteria to change its shape has A white blood cell nourish
... Specialised cells sentence builder – pick one word or phrase from each column to make 7 correct sentences- then write them in your book ...
... Specialised cells sentence builder – pick one word or phrase from each column to make 7 correct sentences- then write them in your book ...
PPT Version
... Cucurbitacin Q: a selective STAT3 activation inhibitor with potent antitumor activity. ...
... Cucurbitacin Q: a selective STAT3 activation inhibitor with potent antitumor activity. ...
cell organelle webquest
... Objective: Upon completion of this activity, you should be able to describe the cell and identify its parts (organelles). You should be able to distinguish between plant and animal cells. PART I Go to: www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP11604 Click “Next” to begin the activity. Answer ...
... Objective: Upon completion of this activity, you should be able to describe the cell and identify its parts (organelles). You should be able to distinguish between plant and animal cells. PART I Go to: www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP11604 Click “Next” to begin the activity. Answer ...
ADVANCED BIOLOGY Exam III (Chapter 3: Cell Structure and
... 3. Know the various types of organelles within both the animal and plant cells and their function(s). (Refer to Cell Function Wkshts) 4. What are the functions of all organelles within both the animal and plant cells. 5. Describe one similarity and one difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic c ...
... 3. Know the various types of organelles within both the animal and plant cells and their function(s). (Refer to Cell Function Wkshts) 4. What are the functions of all organelles within both the animal and plant cells. 5. Describe one similarity and one difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic c ...
Programmed cell death
Programmed cell-death (or PCD) is death of a cell in any form, mediated by an intracellular program. PCD is carried out in a regulated process, which usually confers advantage during an organism's life-cycle. For example, the differentiation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the fingers apoptose; the result is that the digits are separate. PCD serves fundamental functions during both plant and metazoa (multicellular animals) tissue development.Apoptosis and autophagy are both forms of programmed cell death, but necrosis is a non-physiological process that occurs as a result of infection or injury.Necrosis is the death of a cell caused by external factors such as trauma or infection and occurs in several different forms. Recently a form of programmed necrosis, called necroptosis, has been recognized as an alternate form of programmed cell death. It is hypothesized that necroptosis can serve as a cell-death backup to apoptosis when the apoptosis signaling is blocked by endogenous or exogenous factors such as viruses or mutations.