ABDOMINAL CAVITY
... • The lesser sac has important clinical significance. As it is located posterior to the stomach, the posterior wall of the stomach is in contact with the sac. • Thus any posterior ulceration of the stomach will cause fluid to pass into this sac. • Also an injured pancreas or inflamed pancreas will c ...
... • The lesser sac has important clinical significance. As it is located posterior to the stomach, the posterior wall of the stomach is in contact with the sac. • Thus any posterior ulceration of the stomach will cause fluid to pass into this sac. • Also an injured pancreas or inflamed pancreas will c ...
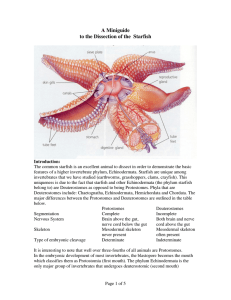
A Miniguide to the Dissection of the Starfish
... baglike cardiac stomach, which protrudes through the mouth while feeding. The everted stomach engulfs the prey and can insert itself into a slit in a shellfish only 0.1 mm wide. Digestion can begin outside the body until the cardiac stomach is retracted by five pairs of retractor muscles, one pair ...
... baglike cardiac stomach, which protrudes through the mouth while feeding. The everted stomach engulfs the prey and can insert itself into a slit in a shellfish only 0.1 mm wide. Digestion can begin outside the body until the cardiac stomach is retracted by five pairs of retractor muscles, one pair ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... (4) Which one of the following enzymes is used in detergents? (a) Pectinase (b) Xylanase (c) Laccase (d) Protease (5) Diagnostic enzymes that are released into the serum due to organ damage are known as (a) Primary enzymes (b) Secondary enzymes (c) Isozymes (d) Tertiary enzymes II. State whether the ...
... (4) Which one of the following enzymes is used in detergents? (a) Pectinase (b) Xylanase (c) Laccase (d) Protease (5) Diagnostic enzymes that are released into the serum due to organ damage are known as (a) Primary enzymes (b) Secondary enzymes (c) Isozymes (d) Tertiary enzymes II. State whether the ...
VOICE DISORDERS Chapter 11
... The cricothyroid joint permits rocking and gliding motion of the thyroid ...
... The cricothyroid joint permits rocking and gliding motion of the thyroid ...
Bryozoa - Formatted
... as Zoarium. The zoarium is covered all along its length by a non-living exoskeletal case known as zooecia (Sing. Zooecium). The zooids are cylindrical in shape, five times as long as broad with a wide crescentic mouth at the terminal end. The zooecium opens to the exterior by an orifice situated at ...
... as Zoarium. The zoarium is covered all along its length by a non-living exoskeletal case known as zooecia (Sing. Zooecium). The zooids are cylindrical in shape, five times as long as broad with a wide crescentic mouth at the terminal end. The zooecium opens to the exterior by an orifice situated at ...
Human Torso Model Activity
... 3. The heart is ___________________ to the lungs. The lungs are ________________ to the heart. (Fill with anterior, posterior, inferior, superior, medial, or lateral) 4. What body system does the brain belong to? Is the brain cranial or caudal to the cecum? *Turn the torso model over to the posterio ...
... 3. The heart is ___________________ to the lungs. The lungs are ________________ to the heart. (Fill with anterior, posterior, inferior, superior, medial, or lateral) 4. What body system does the brain belong to? Is the brain cranial or caudal to the cecum? *Turn the torso model over to the posterio ...
Muscles of the Head - Coach Frei Science
... Functions to flatten the cheek (when whistling or blowing a trumpet). Also compresses the cheek to hold food in between the teeth during chewing. ...
... Functions to flatten the cheek (when whistling or blowing a trumpet). Also compresses the cheek to hold food in between the teeth during chewing. ...
ON THE INTERNAL ANATOMY OF THE FAMILIES OF OPISTHOMI.
... widens out behind and particularly at the bend; it consists of the long anterior limb, the bend and the short posterior limb, ending in the pylorus. The pylorio portion is not demarcated externally from the cardiac portion. The pyloric constrictio:a is raised inside into an annular ridge in the form ...
... widens out behind and particularly at the bend; it consists of the long anterior limb, the bend and the short posterior limb, ending in the pylorus. The pylorio portion is not demarcated externally from the cardiac portion. The pyloric constrictio:a is raised inside into an annular ridge in the form ...
ANATOMICAL FEATURES OF THE ENDOCRINE GLANDS
... About 25g in weight and is enclosed by pretracheal fascia has two symmetrical lobes united by isthmus. Isthmus joins anterior surface of the lobes at their lower part, lies in front 2nd, 3rd and 4th tracheal rings. Pretracheal fascia is here fixed between them (It moves gland up and down during swal ...
... About 25g in weight and is enclosed by pretracheal fascia has two symmetrical lobes united by isthmus. Isthmus joins anterior surface of the lobes at their lower part, lies in front 2nd, 3rd and 4th tracheal rings. Pretracheal fascia is here fixed between them (It moves gland up and down during swal ...
flatworms powerpoint
... Lives in the intestine of its host and passes eggs through the feces Highly adapted to constant internal environments Lacks sensory organs, coordination for mobility and a digestive system (more room for reproductive structures!) Have a modified epidermis “tegument” which protects against the digest ...
... Lives in the intestine of its host and passes eggs through the feces Highly adapted to constant internal environments Lacks sensory organs, coordination for mobility and a digestive system (more room for reproductive structures!) Have a modified epidermis “tegument” which protects against the digest ...
6. The Pharynx - UCLA Linguistics
... bone, also has little function in speech. To some extent it can be considered as an elevator of the hyoid bone, but its most important role for speech is simply as the back wall of the vocal tract. The inferior pharyngeal constrictor also performs this function, but plays a more important role const ...
... bone, also has little function in speech. To some extent it can be considered as an elevator of the hyoid bone, but its most important role for speech is simply as the back wall of the vocal tract. The inferior pharyngeal constrictor also performs this function, but plays a more important role const ...
Biology 20 Final Review Package
... 3. Why are you able to swallow water while standing on your head? 4. How do the teeth and tongue function in digestion? 5. What prevents food from entering the trachea? 6. What is the purpose of saliva? 7. What prevents self-digestion of the stomach? 8. What is the combined effect of sphincter muscl ...
... 3. Why are you able to swallow water while standing on your head? 4. How do the teeth and tongue function in digestion? 5. What prevents food from entering the trachea? 6. What is the purpose of saliva? 7. What prevents self-digestion of the stomach? 8. What is the combined effect of sphincter muscl ...
Macromolecules Review 1. What is the function of starch and
... 3. Why are you able to swallow water while standing on your head? 4. How do the teeth and tongue function in digestion? 5. What prevents food from entering the trachea? 6. What is the purpose of saliva? 7. What prevents self-digestion of the stomach? 8. What is the combined effect of sphincter muscl ...
... 3. Why are you able to swallow water while standing on your head? 4. How do the teeth and tongue function in digestion? 5. What prevents food from entering the trachea? 6. What is the purpose of saliva? 7. What prevents self-digestion of the stomach? 8. What is the combined effect of sphincter muscl ...
Mary Enzyme with clay14
... ¡ Products: What the substrate becomes AFTER it interacts with an enzyme ...
... ¡ Products: What the substrate becomes AFTER it interacts with an enzyme ...
BDS Ist YEAR EXAMINATION 2008-09
... The mucosa of pecten part of anal canal is smooth and characterized by: a) Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium b) Presence of sweat and sebaceous glands c) Presence of hair follicles d) Presence of numerous somatic nerve endings Many types of neuroendocrine cell are scattered among the wall o ...
... The mucosa of pecten part of anal canal is smooth and characterized by: a) Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium b) Presence of sweat and sebaceous glands c) Presence of hair follicles d) Presence of numerous somatic nerve endings Many types of neuroendocrine cell are scattered among the wall o ...
Pharmaceuticals from Animal and Plant Products
... ingredient. Mixed bile acids is also used in prawn feed and in poultry and pig foods also. Natural taurine, (an amino acid, not a steroid) is used in infant milk formula to make it more like human milk, in health tonics ("smart drinks"), and for the prevention of side effects from excess alcohol con ...
... ingredient. Mixed bile acids is also used in prawn feed and in poultry and pig foods also. Natural taurine, (an amino acid, not a steroid) is used in infant milk formula to make it more like human milk, in health tonics ("smart drinks"), and for the prevention of side effects from excess alcohol con ...
Larynx, Trachea & Bronchi
... • Describe the Extent, structure and functions of the larynx. • Describe the Extent, structure and functions of the ...
... • Describe the Extent, structure and functions of the larynx. • Describe the Extent, structure and functions of the ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Developmental Aspects of the Digestive System Fetal Development ...
... Developmental Aspects of the Digestive System Fetal Development ...
Frog Dissection Lab Report
... 7. Layer two includes the gall bladder, the stomach, and the small intestine. 8. Examine the gall bladder. Under the liver, we see a small, greenish sac. This is the gall bladder. You might also see it by separating the right and middle lobes of the liver. 9. Examine the stomach. The stomach looks l ...
... 7. Layer two includes the gall bladder, the stomach, and the small intestine. 8. Examine the gall bladder. Under the liver, we see a small, greenish sac. This is the gall bladder. You might also see it by separating the right and middle lobes of the liver. 9. Examine the stomach. The stomach looks l ...
Right recurrent laryngeal nerve
... contains both sensory and motor fibers important for taste to oropharynx, and sensation and motor function to larynx and laryngopharynx. o important for airway protection o o ...
... contains both sensory and motor fibers important for taste to oropharynx, and sensation and motor function to larynx and laryngopharynx. o important for airway protection o o ...
Sheet 1
... How do you run a physical examination of the abdomen? the patient should be supine and the bed or examination table should be flat and the patient’s hands should be at their sides. The doctor then must stand opposite to the right side of the patient to have a better “internal” picture of the organs ...
... How do you run a physical examination of the abdomen? the patient should be supine and the bed or examination table should be flat and the patient’s hands should be at their sides. The doctor then must stand opposite to the right side of the patient to have a better “internal” picture of the organs ...
Embryology Lec6 Dr.Ban Tongue and Thyroid gland Development
... foramen cecum .Subsequently, the thyroid descends in front of the pharyngeal gut asa bilobeddiverticulum . During this migration, the thyroid remains connected to the tongue by a narrow canal, the thyroglossal duct. This duct later disappears. With further development, the thyroid gland descends in ...
... foramen cecum .Subsequently, the thyroid descends in front of the pharyngeal gut asa bilobeddiverticulum . During this migration, the thyroid remains connected to the tongue by a narrow canal, the thyroglossal duct. This duct later disappears. With further development, the thyroid gland descends in ...
Human digestive system

In the human digestive system, the process of digestion has many stages, the first of which starts in the mouth (oral cavity). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components which can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The secretion of saliva helps to produce a bolus which can be swallowed to pass down the oesophagus and into the stomach.Saliva also contains a catalytic enzyme called amylase which starts to act on food in the mouth. Another digestive enzyme called lingual lipase is secreted by some of the lingual papillae to enter the saliva. Digestion is helped by the mastication of food by the teeth and also by the muscular contractions of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach is essential for the continuation of digestion as is the production of mucus in the stomach.Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction of muscles that begins in the oesophagus and continues along the wall of the stomach and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. This initially results in the production of chyme which when fully broken down in the small intestine is absorbed as chyle into the lymphatic system. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine. Water and some minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood, in the colon of the large intestine. The waste products of digestion are defecated from the anus via the rectum.