Handout 10 - Fat soluble vitamins
... a. Vitamin K can be derived as 50% from plants (as phylloquinone; K1) and 50% from bacteria (including intestinal bacteria; menaquinone; K2). b. Vitamin K is incorporated into mixed micelles and absorbed by diffusion into the enterocytes, where it is incorporated into chylomicrons. 1) The chylomicro ...
... a. Vitamin K can be derived as 50% from plants (as phylloquinone; K1) and 50% from bacteria (including intestinal bacteria; menaquinone; K2). b. Vitamin K is incorporated into mixed micelles and absorbed by diffusion into the enterocytes, where it is incorporated into chylomicrons. 1) The chylomicro ...
Replaced Common Hepatic Artery From Superior Mesenteric Artery
... and distant staging as well as assessment of local resectability. In addition, angiographic data sets can be rendered to create displays of the local venous and arterial anatomy that are familiar to surgeons(5-6). ...
... and distant staging as well as assessment of local resectability. In addition, angiographic data sets can be rendered to create displays of the local venous and arterial anatomy that are familiar to surgeons(5-6). ...
Squids - Charityoceanscience
... sea cephalopod. Their hemocyanin binds and transports oxygen more efficiently than in other cephalopods, aided by gills with especially large surface area along with other adaptations, like a low metabolic rate. This allows them to live within depths that few other organisms can bear, known as the “ ...
... sea cephalopod. Their hemocyanin binds and transports oxygen more efficiently than in other cephalopods, aided by gills with especially large surface area along with other adaptations, like a low metabolic rate. This allows them to live within depths that few other organisms can bear, known as the “ ...
Explanation of colon cancer pathophysiology through analyzing the
... In the present study, the conjugation reaction of bile acids was demonstrated to be strongly affected in colon cancer, resulting the increased levels of free bile acids and decreased levels of bile acids conjugates in serum. This alteration of bile acids homeostasis can result in the change of some ...
... In the present study, the conjugation reaction of bile acids was demonstrated to be strongly affected in colon cancer, resulting the increased levels of free bile acids and decreased levels of bile acids conjugates in serum. This alteration of bile acids homeostasis can result in the change of some ...
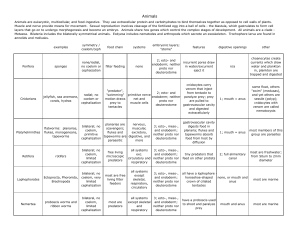
Animals
... Animals Animals are eukaryotic, multicellular, and food-ingestive. They use extracellular protein and carbohydrates to bind themselves together as opposed to cell walls of plants. Muscle and nerve provide means for movement. Sexual reproduction involves cleavage of the fertilized egg into a ball of ...
... Animals Animals are eukaryotic, multicellular, and food-ingestive. They use extracellular protein and carbohydrates to bind themselves together as opposed to cell walls of plants. Muscle and nerve provide means for movement. Sexual reproduction involves cleavage of the fertilized egg into a ball of ...
Lipoproteins
... increasing the surface area accessible to lipid-hydrolyzing enzymes. They also help to solubilize lipid breakdown products (e.g., mono- & diacylglycerols from triacylglycerol hydrolysis). ...
... increasing the surface area accessible to lipid-hydrolyzing enzymes. They also help to solubilize lipid breakdown products (e.g., mono- & diacylglycerols from triacylglycerol hydrolysis). ...
Alcoholic Liver Disease
... leading cause of liver disease in Western countries (>10 million in the US) major cause of morbidity and mortality often clinically silent generally problematic if >80g (4 drinks) per day for men, half that for women wide variation in susceptibility - gender, genetics, other liver diseases ...
... leading cause of liver disease in Western countries (>10 million in the US) major cause of morbidity and mortality often clinically silent generally problematic if >80g (4 drinks) per day for men, half that for women wide variation in susceptibility - gender, genetics, other liver diseases ...
Tongji Univesity School of Medicine 2012
... E. Urethral bulb part 22 The correct description of cochlea is that A. scala vestibuli ends round widow B. it is full of perilymph fluid in the cochlea C. it receives vibration only from ossicle chain in tympanic cavity D. apparatus of balance is located in the cochlea E. there is no communication b ...
... E. Urethral bulb part 22 The correct description of cochlea is that A. scala vestibuli ends round widow B. it is full of perilymph fluid in the cochlea C. it receives vibration only from ossicle chain in tympanic cavity D. apparatus of balance is located in the cochlea E. there is no communication b ...
Drug use in Gastrointestinal Diseases
... Structure and functions of the digestive system. GI tract Teeth Tongue Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine Rectum Anus Mucosa, gland ...
... Structure and functions of the digestive system. GI tract Teeth Tongue Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine Rectum Anus Mucosa, gland ...
D23-1 UNIT 23. DISSECTION: PHARYNX AND LARYNX
... medially and posteriorly to the two carotid arteries. It then divides into internal and external laryngeal branches. Trace the hypoglossal nerve from its emergence from the hypoglossal canal, noting that this nerve passes lateral and anterior to both of the carotid arteries. You will observe that th ...
... medially and posteriorly to the two carotid arteries. It then divides into internal and external laryngeal branches. Trace the hypoglossal nerve from its emergence from the hypoglossal canal, noting that this nerve passes lateral and anterior to both of the carotid arteries. You will observe that th ...
Fetal Pig I External and Ventral Body Cavity Anatomy Introduction to
... right side. The gall bladder stores bile produced by the liver and releases it through a duct, common bile duct, into the duodenum. d) spleen: finger-like dark red organ that lies over the greater curvature of the stomach. The speen functions as a lymphatic organ to cleanse the blood. ...
... right side. The gall bladder stores bile produced by the liver and releases it through a duct, common bile duct, into the duodenum. d) spleen: finger-like dark red organ that lies over the greater curvature of the stomach. The speen functions as a lymphatic organ to cleanse the blood. ...
FN303-WSV
... #Since 10-30% of older people may malabsorb food-bound B12, it is advisable for those older than 50 years to meet their RDA mainly by taking foods fortified with B12 or a B12-containing supplement. ...
... #Since 10-30% of older people may malabsorb food-bound B12, it is advisable for those older than 50 years to meet their RDA mainly by taking foods fortified with B12 or a B12-containing supplement. ...
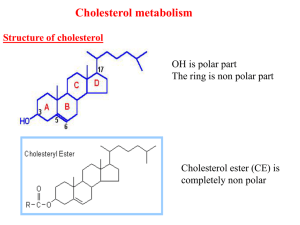
Lec4 Cholesterol met..
... 2- Drug inhibition: Statins such as atorvastatin (by Pfizer), lovastatin and simvastatin are drugs with a side chain structurally similar to HMG-CoA so competitively inhibit HMG-CoA reductase. They are used to decrease cholesterol levels in patients with hypercholesterolemia. 3- Diet: its activity a ...
... 2- Drug inhibition: Statins such as atorvastatin (by Pfizer), lovastatin and simvastatin are drugs with a side chain structurally similar to HMG-CoA so competitively inhibit HMG-CoA reductase. They are used to decrease cholesterol levels in patients with hypercholesterolemia. 3- Diet: its activity a ...
Colitis There are several different types of Colitis, all of which are
... Crohn’s disease (affects any part of the gastrointestinal tract) Ulcerative colitis (affects only the colon, also known as the large intestine) Ischemic colitis (lack of sufficient blood supply to the colon) Infectious enterocolitis CMV colitis (a viral infection of the colon) Q. How is Colitis trea ...
... Crohn’s disease (affects any part of the gastrointestinal tract) Ulcerative colitis (affects only the colon, also known as the large intestine) Ischemic colitis (lack of sufficient blood supply to the colon) Infectious enterocolitis CMV colitis (a viral infection of the colon) Q. How is Colitis trea ...
larynx
... A cute little way to remember innervation of larynx and pharynx: both end w/ x, x = X, X = vagus Muscles which move larynx as a whole: Infrahyoid muscles (omohyoid, sternohyoid, sternothyroid) – depressors Suprahyoid muscles (stylohyoid, digastric, mylohyoid, geniohyoid,) + stylopharyngeus elevate ...
... A cute little way to remember innervation of larynx and pharynx: both end w/ x, x = X, X = vagus Muscles which move larynx as a whole: Infrahyoid muscles (omohyoid, sternohyoid, sternothyroid) – depressors Suprahyoid muscles (stylohyoid, digastric, mylohyoid, geniohyoid,) + stylopharyngeus elevate ...
Malabsorption
... • Asses the integrity of the – Stomach • Cobalamin:R-binder protein complex (acidic milieu) ...
... • Asses the integrity of the – Stomach • Cobalamin:R-binder protein complex (acidic milieu) ...
The Whipple Operation – Illustrations
... Fig. 9. Illustration of the important surgical anatomy of the superior mesenteric vein (SMV). The SMV usually bifurcates into two main branches, one to the ileum and one to the jejunum. Adequate venous return from the small bowel requires that one or the other of these two main SMV-tributaries is i ...
... Fig. 9. Illustration of the important surgical anatomy of the superior mesenteric vein (SMV). The SMV usually bifurcates into two main branches, one to the ileum and one to the jejunum. Adequate venous return from the small bowel requires that one or the other of these two main SMV-tributaries is i ...
11 Axial Muscles - Orange Coast College
... Support and protect the abdominal and pelvic organs. Are not responsible for stabilizing or moving the pectoral or pelvic girdles or their attached limbs. ...
... Support and protect the abdominal and pelvic organs. Are not responsible for stabilizing or moving the pectoral or pelvic girdles or their attached limbs. ...
Transcripts/3_19 8
... after anesthetizing the inferior alveolar some sensation remains in the mandibular teeth. It is thought in these cases that some sensation may come from the nerve to the mylohyoid. b. For the superior teeth, (the teeth in the upper jaw bone or the maxillary teeth), are innervated by the superior alv ...
... after anesthetizing the inferior alveolar some sensation remains in the mandibular teeth. It is thought in these cases that some sensation may come from the nerve to the mylohyoid. b. For the superior teeth, (the teeth in the upper jaw bone or the maxillary teeth), are innervated by the superior alv ...
Transforming growth factor β1
... Vitamin D deficiency causes toll like receptor (TLR ) activation ...
... Vitamin D deficiency causes toll like receptor (TLR ) activation ...
lecture 17
... oral cavity; 2/3 of tongue • Lingual Frenulum: Underside of tongue; Joins inferior tongue & mandible; stabilizing tongue during movement 21 ...
... oral cavity; 2/3 of tongue • Lingual Frenulum: Underside of tongue; Joins inferior tongue & mandible; stabilizing tongue during movement 21 ...
Anatomy for the Gynecologic Oncologist
... spleen, stomach, small bowel, colon and liver? • What are their functions? • How do you manage these organs postoperatively if they are injured or removed? ...
... spleen, stomach, small bowel, colon and liver? • What are their functions? • How do you manage these organs postoperatively if they are injured or removed? ...
Human digestive system

In the human digestive system, the process of digestion has many stages, the first of which starts in the mouth (oral cavity). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components which can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The secretion of saliva helps to produce a bolus which can be swallowed to pass down the oesophagus and into the stomach.Saliva also contains a catalytic enzyme called amylase which starts to act on food in the mouth. Another digestive enzyme called lingual lipase is secreted by some of the lingual papillae to enter the saliva. Digestion is helped by the mastication of food by the teeth and also by the muscular contractions of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach is essential for the continuation of digestion as is the production of mucus in the stomach.Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction of muscles that begins in the oesophagus and continues along the wall of the stomach and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. This initially results in the production of chyme which when fully broken down in the small intestine is absorbed as chyle into the lymphatic system. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine. Water and some minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood, in the colon of the large intestine. The waste products of digestion are defecated from the anus via the rectum.