Oral cavity and pharynx
... the birth, sucklings have filled the oral cavity with the tongue. The tongue touches the hard and the soft palate and the mucosa of cheeks and it does not have an apex. This tight ...
... the birth, sucklings have filled the oral cavity with the tongue. The tongue touches the hard and the soft palate and the mucosa of cheeks and it does not have an apex. This tight ...
04-Diaphragm2009-03-14 13:192.3 MB
... Superior surface: Pericardiacophrenic & Musculophrenic arteries (internal thoracic) ...
... Superior surface: Pericardiacophrenic & Musculophrenic arteries (internal thoracic) ...
40_Biochemical functions of liver
... tract. • 3. The synthesis of proteins (proteins of plasma of blood among them), their deposition, transamination and desamination of aminoacids, the formation of urea, the synthesis of creatinine. • 4. The synthesis of glycogene from monosaccharides. • 5. The oxidation of fatty acids, the formation ...
... tract. • 3. The synthesis of proteins (proteins of plasma of blood among them), their deposition, transamination and desamination of aminoacids, the formation of urea, the synthesis of creatinine. • 4. The synthesis of glycogene from monosaccharides. • 5. The oxidation of fatty acids, the formation ...
Personal Anatomy Notes – The Thoracic Cage
... o Sliding Hernia: The lower esophageal sphincter slides into the thoracic cavity, allowing the contents of the stomach to come up into the esophagus leading to acid reflux. Worst one of the two. o Rolling Hernia (Paraesophageal): The hernia occurs and protrudes but the sphincter stays in place so th ...
... o Sliding Hernia: The lower esophageal sphincter slides into the thoracic cavity, allowing the contents of the stomach to come up into the esophagus leading to acid reflux. Worst one of the two. o Rolling Hernia (Paraesophageal): The hernia occurs and protrudes but the sphincter stays in place so th ...
kumc 40 abdominal aorta and ivc student
... Splenic artery branches: Short gastric arteries (6). Splenic arteries (6). Left gastroepiploic artery: ...
... Splenic artery branches: Short gastric arteries (6). Splenic arteries (6). Left gastroepiploic artery: ...
Folate
... #Since 10-30% of older people may malabsorb food-bound B12, it is advisable for those older than 50 years to meet their RDA mainly by taking foods fortified with B12 or a B12-containing supplement. ...
... #Since 10-30% of older people may malabsorb food-bound B12, it is advisable for those older than 50 years to meet their RDA mainly by taking foods fortified with B12 or a B12-containing supplement. ...
Biochemistry Lect 4 – N.42 – Lipid metabolism
... degrade dietary lipids in the small intestine is hormonally controlled . 2-Cells in the mucosa of lower duodenum and jejunum produce peptide hormone, cholecystokinin (CCK), in response to the presence of lipids and partially digested proteins entering these regions of the upper small intestine. CCK ...
... degrade dietary lipids in the small intestine is hormonally controlled . 2-Cells in the mucosa of lower duodenum and jejunum produce peptide hormone, cholecystokinin (CCK), in response to the presence of lipids and partially digested proteins entering these regions of the upper small intestine. CCK ...
Hepatology: Anatomy, Physiology and Dev
... -The liver has diaphragmatic and visceral surfaces which contact the diaphragm and abdominal viscera, respectively. Note the right triangular, left triangular, and coronary ligaments that attach to the diaphragm. Note also the bare area not covered by peritoneum. Anteriorly, there is a fold of per ...
... -The liver has diaphragmatic and visceral surfaces which contact the diaphragm and abdominal viscera, respectively. Note the right triangular, left triangular, and coronary ligaments that attach to the diaphragm. Note also the bare area not covered by peritoneum. Anteriorly, there is a fold of per ...
Anatomy of the Respiratory System
... The superior turbinate, which is the smallest turbinate, is above the middle turbinate. The posterior (or back) ethmoid cells drain into the superior meatus. The space between the superior turbinate, the septum and the sphenoid sinus front wall is known as the sphenoethmoid recess. The sphenoid drai ...
... The superior turbinate, which is the smallest turbinate, is above the middle turbinate. The posterior (or back) ethmoid cells drain into the superior meatus. The space between the superior turbinate, the septum and the sphenoid sinus front wall is known as the sphenoethmoid recess. The sphenoid drai ...
Chapter 1 Study Questions with Answers
... The exchange system divides foods into groups and assigns each food within a group a portion size comparable in calories and nutrients. A diet is planned by determining the number of servings from each exchange group that should be in each snack or meal. The individual decides whether he or she will ...
... The exchange system divides foods into groups and assigns each food within a group a portion size comparable in calories and nutrients. A diet is planned by determining the number of servings from each exchange group that should be in each snack or meal. The individual decides whether he or she will ...
Syllabus 2011-2012
... one another. 6. Discuss the interdependency of body systems as an influence on the proper functioning of the body. 7. Become aware of how to treat the human body to keep it healthy and promote a longer and richer life. Attendance: Class attendance for lectures is required, and is highly recommended. ...
... one another. 6. Discuss the interdependency of body systems as an influence on the proper functioning of the body. 7. Become aware of how to treat the human body to keep it healthy and promote a longer and richer life. Attendance: Class attendance for lectures is required, and is highly recommended. ...
Liver
... exercise. Everything that enters the body must pass through the liver to be processed. The liver functions as a filter to protect the body from harmful substances and is responsible for the production and use of most nutrients. Therefore, everything that is ingested has an effect on the liver—some p ...
... exercise. Everything that enters the body must pass through the liver to be processed. The liver functions as a filter to protect the body from harmful substances and is responsible for the production and use of most nutrients. Therefore, everything that is ingested has an effect on the liver—some p ...
Chapter 5 PPT
... • The skeletal system provides protection for organs, allows for movement, and gives the body its shape. ...
... • The skeletal system provides protection for organs, allows for movement, and gives the body its shape. ...
13. submandibular-M.N.V2010-10
... submandibular duct and the lingual nerve. Then runs along the under surface of tongue as deep lingual A. to reach its tip and anastomoses with artery of opposite side. It supply the anterior part of the tongue. ...
... submandibular duct and the lingual nerve. Then runs along the under surface of tongue as deep lingual A. to reach its tip and anastomoses with artery of opposite side. It supply the anterior part of the tongue. ...
OMFS Lecture
... salivary glands from which numerous ducts travel and open onto the top of each fold. Each gland does not have a single duct, but many which open directly into the oral cavity. ...
... salivary glands from which numerous ducts travel and open onto the top of each fold. Each gland does not have a single duct, but many which open directly into the oral cavity. ...
File
... Lacrimal sac which then goes into the Nasolacrimal duct which empties into the nasal cavity. When Lacrimal secretions increase substantially tears spill over the eyelids, fill the nasal cavities and cause “sniffles” o Occurs when eyes are irritated or emotionally upset Homeostatic Imbalance (p 274 ...
... Lacrimal sac which then goes into the Nasolacrimal duct which empties into the nasal cavity. When Lacrimal secretions increase substantially tears spill over the eyelids, fill the nasal cavities and cause “sniffles” o Occurs when eyes are irritated or emotionally upset Homeostatic Imbalance (p 274 ...
Parapharyngeal Space
... Superiorly with the nasopharynx Inferiorly with the hypopharynx The palatine tonsils lie laterally between the anterior and posterior pillars ...
... Superiorly with the nasopharynx Inferiorly with the hypopharynx The palatine tonsils lie laterally between the anterior and posterior pillars ...
SELECT THE ONE BEST ANSWER OR COMPLETION 1. The
... 20. With regard to the cochlea and conchlear duct, the A. scala tympani is most closely related to the oval window B. scala vestibuli contains the Organ of Corti C. scala vestibuli is most closely related to the oval window D. cochlear duct is filled with perilymph E. endolymphatic sac is filled wit ...
... 20. With regard to the cochlea and conchlear duct, the A. scala tympani is most closely related to the oval window B. scala vestibuli contains the Organ of Corti C. scala vestibuli is most closely related to the oval window D. cochlear duct is filled with perilymph E. endolymphatic sac is filled wit ...
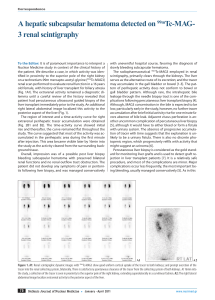
A hepatic subcapsular hematoma detected on 99mTc-MAG
... leakage through the needle biopsy tract is one of the complications following percutaneous liver transplant biopsy [4]. Although, MAG3 concentration in the bile is expected to be low, particularly early in the study, however, no further tracer accumulation after brief initial activity rise for one m ...
... leakage through the needle biopsy tract is one of the complications following percutaneous liver transplant biopsy [4]. Although, MAG3 concentration in the bile is expected to be low, particularly early in the study, however, no further tracer accumulation after brief initial activity rise for one m ...
Cranial Nerves
... superior oblique (eye movement) intrinsic smooth muscle of iris (constriction in response to brightness) and lens (controls shape for focusing) ...
... superior oblique (eye movement) intrinsic smooth muscle of iris (constriction in response to brightness) and lens (controls shape for focusing) ...
2010‐P8 Systemic Pathology The Liver and the Biliary Tract Hepatic Injury
... – Genomic instability with integrated HBV DNA – Integration pattern is clonal – HBV X‐protein disrupts cell cycle control – Certain HBV proteins inactivate p53 ...
... – Genomic instability with integrated HBV DNA – Integration pattern is clonal – HBV X‐protein disrupts cell cycle control – Certain HBV proteins inactivate p53 ...
Human digestive system

In the human digestive system, the process of digestion has many stages, the first of which starts in the mouth (oral cavity). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components which can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The secretion of saliva helps to produce a bolus which can be swallowed to pass down the oesophagus and into the stomach.Saliva also contains a catalytic enzyme called amylase which starts to act on food in the mouth. Another digestive enzyme called lingual lipase is secreted by some of the lingual papillae to enter the saliva. Digestion is helped by the mastication of food by the teeth and also by the muscular contractions of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach is essential for the continuation of digestion as is the production of mucus in the stomach.Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction of muscles that begins in the oesophagus and continues along the wall of the stomach and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. This initially results in the production of chyme which when fully broken down in the small intestine is absorbed as chyle into the lymphatic system. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine. Water and some minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood, in the colon of the large intestine. The waste products of digestion are defecated from the anus via the rectum.