* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PHARYNX and LARYNX
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
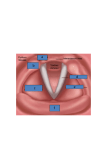
PHARYNX and LARYNX Muscles of Pharynx Meet posteriorly at pharyngeal raphe. Overlap constrictor muscles above. Lateral gaps occur between constrictor muscles anteriorly. Used in swallowing. Superior Pharyngeal Constrictor Gap above constrictor: Closed by pharyngobasilar fascia. Traversed by auditory tube. Forms tonsilar bed Middle Pharyngeal Constrictor Gap above middle constrictor: Traversed by: Stylopharyngeus muscle. Glossopharyngeal nerve. Innervation and Blood Supply of Pharynx Innervation: Vagus nerve via pharyngeal plexus: Except stylopharyngeus. Recurrent laryngeal nerves to lower part of inferior constrictor. Blood supply: Ascending pharyngeal artery. Laryngeal Skeleton: Thyroid Thyrohyoid membrane. Cricothyroid membrane. Laminae: Superior thyroid notch. Meet at: 90 degrees in male. 120 degrees in female. Superior and inferior horns. Laryngeal Skeleton: Cricoid Lies at level of cervical vertebra 6. Laryngeal Skeleton: Arytenoid Paired. Sit on superior surface of cricoid. Support corniculate cartilage. Processes: Muscular. Vocal: Attachment for vocal ligament. Laryngeal Skeleton: Epiglottis Attached to thyroid cartilage: Via thyro-epiglottic ligament. Mucosa on surface extends onto tongue and walls of oropharynx: Median glosso-epiglottic fold. Lateral pharyngo-epiglottic folds. Valleculae: Valleys on either side of glosso-epiglottic fold. Common sites for lodgement. Laryngeal Skeleton Other cartilages: Corniculate. Cuneiform. Laryngeal Cavity and Folds Characterized by superior and inferior pairs of folds. Vestibule: Lies between vestibular folds. Vestibular Folds: False vocal cords. Rima vestibuli: Space between vestibular folds. Laryngeal Cavity and Folds Ventricular folds: True vocal cords. Vocal ligaments. Rima glottidis: Space between vocal folds. Narrowest part of laryngeal cavity. Opens and closes to regulate passage of air. Laryngeal Cavity and Folds Infraglottic cavity: Lies between ventricular folds and lower border of cricoid cartilage. Continuous inferiorly with trachea. Innervation of Larynx Vagus nerve: External laryngeal branch: To cricothyroid muscle. Inferior laryngeal branch: All remaining muscles of the larynx. Sensory to mucosa of larynx below vocal folds. Internal laryngeal branch: Sensory to mucosa above vocal folds. Sensory to piriform recess and valleculae. Can be anesthetized in floor of piriform recess. Blood Supply of Larynx Superior laryngeal artery: From superior thyroid artery. Inferior laryngeal artery: Branch of inferior thyroid artery. Piriform Recess Part of laryngopharynx lateral to larynx: Lateral boundary: Thyrohyoid membrane and thyroid cartilage. Medial boundary: Aryepiglottic fold; arytenoid and cricoid cartilages. Site of lodgement.