LAB 5 – CORONAL 1 (Jan 29)
... The two lateral ventricles in the forebrain, the main parts of which lie in the temporal lobes immediately below the corpus callosum and above the thalamus, are separated by the septum pellucidum Caudate Nucleus One of the basal ganglia in the corpus striatum : a crescent-shaped mass of grey matter ...
... The two lateral ventricles in the forebrain, the main parts of which lie in the temporal lobes immediately below the corpus callosum and above the thalamus, are separated by the septum pellucidum Caudate Nucleus One of the basal ganglia in the corpus striatum : a crescent-shaped mass of grey matter ...
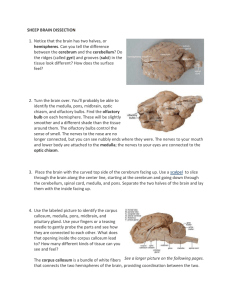
Sheep Brain Dissection Instructions
... pituitary gland. Use your fingers or a teasing needle to gently probe the parts and see how they are connected to each other. What does that opening inside the corpus callosum lead to? How many different kinds of tissue can you see and feel? The corpus callosum is a bundle of white fibers See a larg ...
... pituitary gland. Use your fingers or a teasing needle to gently probe the parts and see how they are connected to each other. What does that opening inside the corpus callosum lead to? How many different kinds of tissue can you see and feel? The corpus callosum is a bundle of white fibers See a larg ...
Popular Links
... stereotypic behaviors (e.g., flapping, rocking, spinning). When children display defensive behavior toward the stimuli (e.g., rub the spot where it touched them) or try to avoid the stimuli altogether (e.g., back away from the stimuli, tantrum, shout), they may be attempting to regulate the amount o ...
... stereotypic behaviors (e.g., flapping, rocking, spinning). When children display defensive behavior toward the stimuli (e.g., rub the spot where it touched them) or try to avoid the stimuli altogether (e.g., back away from the stimuli, tantrum, shout), they may be attempting to regulate the amount o ...
Is there a correlation between the use of cannabis and the
... THC effectively acts as a dopamine agonist, thus blocking the reuptake of dopamine and L-DOPA (which stimulates the synthesis of dopamine) ...
... THC effectively acts as a dopamine agonist, thus blocking the reuptake of dopamine and L-DOPA (which stimulates the synthesis of dopamine) ...
brain research methods 1-10
... Done when the participant in completely awake and engaged so changes in responses and behavior to certain stimuli may be observed. Involves using a device to stimulate the brain with a weak electrical current by activating or disrupting the normal activity of neurons in a specific brain area, there ...
... Done when the participant in completely awake and engaged so changes in responses and behavior to certain stimuli may be observed. Involves using a device to stimulate the brain with a weak electrical current by activating or disrupting the normal activity of neurons in a specific brain area, there ...
What is Nervous System?
... When we are conscious of what we learn. When we commit to memory. When we are conscious to the response we make to such stimuli. When the required responses are complex or new we may be aware of devoting effort to planning, monitoring & executing the information. In reflective thoughts or problem ...
... When we are conscious of what we learn. When we commit to memory. When we are conscious to the response we make to such stimuli. When the required responses are complex or new we may be aware of devoting effort to planning, monitoring & executing the information. In reflective thoughts or problem ...
Temporal Aspects of Visual Extinction
... can show recovery. • Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize and modify functions and adapt to internal and external changes – Important for learning – Important for rehabilitation – Younger brains tend to be more plastic ...
... can show recovery. • Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize and modify functions and adapt to internal and external changes – Important for learning – Important for rehabilitation – Younger brains tend to be more plastic ...
Chapter 1 - Center for Advanced Brain Imaging
... show recovery. Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize and modify functions and adapt to internal and external changes – Important for learning – Important for rehabilitation – Younger brains tend to be more plastic ...
... show recovery. Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize and modify functions and adapt to internal and external changes – Important for learning – Important for rehabilitation – Younger brains tend to be more plastic ...
The Nervous System - Watchung Hills Regional High School
... adjustment, self-hypnosis or meditation. Rare disease - affects less than 200,000 people US. The exact cause of TN is not fully understood. ...
... adjustment, self-hypnosis or meditation. Rare disease - affects less than 200,000 people US. The exact cause of TN is not fully understood. ...
Slide 1
... Thalamus – “gateway” to the cerbral cortex Afferent impulses from all senses converge and synapse in the thalamus Impulses of similar function are sorted out, “edited”, and relayed as a group to the appropriate area of the sensory cortex or association areas All inputs ascending to the cerebral cor ...
... Thalamus – “gateway” to the cerbral cortex Afferent impulses from all senses converge and synapse in the thalamus Impulses of similar function are sorted out, “edited”, and relayed as a group to the appropriate area of the sensory cortex or association areas All inputs ascending to the cerebral cor ...
Physiological bases of mental and physical work
... The second signaling system The development of the second signaling system was incredibly broadened and changed by quality of higher nervous activity of cerebral hemispheres. Words are signals of other signals. Man uses verbal signals for everything he perceives through the receptors. Words are a ...
... The second signaling system The development of the second signaling system was incredibly broadened and changed by quality of higher nervous activity of cerebral hemispheres. Words are signals of other signals. Man uses verbal signals for everything he perceives through the receptors. Words are a ...
ap psychology
... AIM: Explain how neurons are at the center of our existence. How does neural communication relate to behavior? ...
... AIM: Explain how neurons are at the center of our existence. How does neural communication relate to behavior? ...
Chapter 3: The nerve cell Multiple Choice Questions (1
... 1. If the synapse between neurons is inhibitory, the probability of the next neuron firing is a. increased b. decreased c. unchanged d. dependent upon the type of neuron 2. If the synapse between neurons is excitatory, the probability of the next neuron firing is a. increased b. decreased c. unchang ...
... 1. If the synapse between neurons is inhibitory, the probability of the next neuron firing is a. increased b. decreased c. unchanged d. dependent upon the type of neuron 2. If the synapse between neurons is excitatory, the probability of the next neuron firing is a. increased b. decreased c. unchang ...
The Nervous System
... from other parts of the brain and relays the information to a more complex part of the brain ...
... from other parts of the brain and relays the information to a more complex part of the brain ...
Gamma Band Oscillation
... events emerged locally… [and] were not directly related to the stimulus but were added on by the brain.” (Buzsáki, p. 240) Synchrony between various locations occurred only when neurons at those locations responded to related visual features of the object. Furthermore, the determining factor of the ...
... events emerged locally… [and] were not directly related to the stimulus but were added on by the brain.” (Buzsáki, p. 240) Synchrony between various locations occurred only when neurons at those locations responded to related visual features of the object. Furthermore, the determining factor of the ...
primary visual cortex
... by contrasting levels of illumination between the “on” and “off” regions of the receptive field. Diffuse light of a constant intensity shone on both the on and off regions does not effect the firing rate of simple cortical cells. Thus, simple cortical cells facilitate edge perception. ...
... by contrasting levels of illumination between the “on” and “off” regions of the receptive field. Diffuse light of a constant intensity shone on both the on and off regions does not effect the firing rate of simple cortical cells. Thus, simple cortical cells facilitate edge perception. ...
Psychology-Parts-of-the-Brain-and-Their
... The cerebrum is the largest portion of the brain, and contains tools which are responsible for most of the brain's function. It is divided into four sections: the temporal lobe, the occipital lobe, parietal lobe and frontal lobe. The cerebrum is divided into a right and left hemisphere which are con ...
... The cerebrum is the largest portion of the brain, and contains tools which are responsible for most of the brain's function. It is divided into four sections: the temporal lobe, the occipital lobe, parietal lobe and frontal lobe. The cerebrum is divided into a right and left hemisphere which are con ...
VISION John Gabrieli Melissa Troyer 9.00
... Copyright © 1973 by the American Psychological Association. Reproduced with permission. Pohl, W. "Dissociation of Spatial Discrimination Deficits Following Frontal and Parietal Lesions in Monkeys." Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology 82 (1973): 227–39. The use of APA information doe ...
... Copyright © 1973 by the American Psychological Association. Reproduced with permission. Pohl, W. "Dissociation of Spatial Discrimination Deficits Following Frontal and Parietal Lesions in Monkeys." Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology 82 (1973): 227–39. The use of APA information doe ...
The Brain and Cranial Nerves The Brain
... • Receives information from visceral receptors related to blood pressure, and other physiological factors important to body function • Monitors the body’s water concentration, hormone concentration, body temperature, and release of hormones from the pituitary gland. ...
... • Receives information from visceral receptors related to blood pressure, and other physiological factors important to body function • Monitors the body’s water concentration, hormone concentration, body temperature, and release of hormones from the pituitary gland. ...
Unit 2 - Monroe Community College
... ● but RH did process information - People could point out a picture of an object they had held in their left hand - people could point out pictures of things flashed to their left visual field ● RH is superior for assembling puzzles & copying drawings, even when the person is right handed ...
... ● but RH did process information - People could point out a picture of an object they had held in their left hand - people could point out pictures of things flashed to their left visual field ● RH is superior for assembling puzzles & copying drawings, even when the person is right handed ...
Higher brain functions
... information for less than a minute and retrieve it during this time (eg. repeating a list of items that has just been read to you, in their original order. In general, you can retain 5 to 9 items in short-term) • Long-term memory (LTM) includes both our memory of recent facts, which is often quite f ...
... information for less than a minute and retrieve it during this time (eg. repeating a list of items that has just been read to you, in their original order. In general, you can retain 5 to 9 items in short-term) • Long-term memory (LTM) includes both our memory of recent facts, which is often quite f ...
ANATOMY
... system connects the central nervous system to various body structures. Cranial nerves carry impulses to and from the brain, spinal nerves carry impulses to and from the spinal cord. ...
... system connects the central nervous system to various body structures. Cranial nerves carry impulses to and from the brain, spinal nerves carry impulses to and from the spinal cord. ...
Time perception

Time perception is a field of study within psychology and neuroscience that refers to the subjective experience of time, which is measured by someone's own perception of the duration of the indefinite and continuous unfolding of events. The perceived time interval between two successive events is referred to as perceived duration. Another person's perception of time cannot be directly experienced or understood, but it can be objectively studied and inferred through a number of scientific experiments. Time perception is a construction of the brain that is manipulable and distortable under certain circumstances. These temporal illusions help to expose the underlying neural mechanisms of time perception.Pioneering work, emphasizing species-specific differences, was conducted by Karl Ernst von Baer. Experimental work began under the influence of the psycho-physical notions of Gustav Theodor Fechner with studies of the relationship between perceived and measured time.