Slide 1
... from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended pedagogical purposes and the needs of other instructors who rely on these materials ...
... from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended pedagogical purposes and the needs of other instructors who rely on these materials ...
February 2010 Vol 21 No 2 - Cape Cod Astronomical Society
... The Great Orion Nebula was spectacular in the 16”. Not as much “depth” as one can see in the 18” (which we kept inside because of the cold and the snow) but we had a spectacular and clear view of the trapezium and a seemingly darker than usual dark nebulosity to their right as we looked in the eyepi ...
... The Great Orion Nebula was spectacular in the 16”. Not as much “depth” as one can see in the 18” (which we kept inside because of the cold and the snow) but we had a spectacular and clear view of the trapezium and a seemingly darker than usual dark nebulosity to their right as we looked in the eyepi ...
printer-friendly version of benchmark
... comparison. In such circumstances, it may be natural to assume that the smaller number represents a closer distance and the larger number represents a further distance. For example, when comparing distances of 4 light years, 10 A.U. and 150 million kilometers, students believe these are already arra ...
... comparison. In such circumstances, it may be natural to assume that the smaller number represents a closer distance and the larger number represents a further distance. For example, when comparing distances of 4 light years, 10 A.U. and 150 million kilometers, students believe these are already arra ...
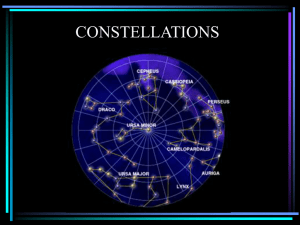
Constellations Overview
... Therefore, by ensuring the planting took place at the correct time the risk of a failed harvest was kept to a minimum. Since different constellations are visible at different times of the year, farmers were able to use them to tell what month it was. As a result, accurate calendar prediction was an ...
... Therefore, by ensuring the planting took place at the correct time the risk of a failed harvest was kept to a minimum. Since different constellations are visible at different times of the year, farmers were able to use them to tell what month it was. As a result, accurate calendar prediction was an ...
Venus Transit and the Astronomical Unit
... Being more distant and smaller, Mercury (left) appears much smaller than Venus (right) during transit. ...
... Being more distant and smaller, Mercury (left) appears much smaller than Venus (right) during transit. ...
Chapter 2 - Colorado Mesa University
... A. The supernova remnant still exists now, and we will watch it disperse over the next 10,000 Earth years. B. In reality, the supernova remnant has already dispersed, but we will watch it disperse over the next 10,000 Earth years. C. The image of the supernova dispersing will not reach us for anothe ...
... A. The supernova remnant still exists now, and we will watch it disperse over the next 10,000 Earth years. B. In reality, the supernova remnant has already dispersed, but we will watch it disperse over the next 10,000 Earth years. C. The image of the supernova dispersing will not reach us for anothe ...
Jan 2017 - Bays Mountain Park
... which mechanism is more important, says Tom Woods, a solar scientist at the University of Colorado at Boulder and principal investigator of MinXSS: “It’s helping address this very long-term problem that's been around for 50 years: how is the Corona heated to be so hot.” The $1 million original missi ...
... which mechanism is more important, says Tom Woods, a solar scientist at the University of Colorado at Boulder and principal investigator of MinXSS: “It’s helping address this very long-term problem that's been around for 50 years: how is the Corona heated to be so hot.” The $1 million original missi ...
3.5-star-id
... • The Summer Triangle is formed by three bright stars, Deneb, Vega, and Altair in the constellations Cygnus, Lyra, and Aquila. • Slicing through this triangle is the asterism, the Northern Cross, actually part of Cygnus the Swan. • Tonight you will find the summer triangle above the eastern sky and ...
... • The Summer Triangle is formed by three bright stars, Deneb, Vega, and Altair in the constellations Cygnus, Lyra, and Aquila. • Slicing through this triangle is the asterism, the Northern Cross, actually part of Cygnus the Swan. • Tonight you will find the summer triangle above the eastern sky and ...
Sky Watcher - Boise Astronomical Society
... The following information is for the beginning and younger astronomers. Even though man has studied the heavens for thousands of years, we still know very little about the Universe we live in. And as we continue to learn more, we are consistently amazed, and sometimes confused, by what we learn. Her ...
... The following information is for the beginning and younger astronomers. Even though man has studied the heavens for thousands of years, we still know very little about the Universe we live in. And as we continue to learn more, we are consistently amazed, and sometimes confused, by what we learn. Her ...
Word document - Moray`s Astronomy Club, SIGMA
... Martin Hendry – University of Glasgow The next 10 to 15 years should see some dramatic developments in how we observe the Universe. Martin will examine this exciting science that will open entirely new windows on our Universe. ...
... Martin Hendry – University of Glasgow The next 10 to 15 years should see some dramatic developments in how we observe the Universe. Martin will examine this exciting science that will open entirely new windows on our Universe. ...
DTU_9e_ch01
... Does the Moon have a dark side that we never see from Earth? Half of the Moon is always dark. Whenever we see less than a full Moon, we are seeing part of the Moon’s dark side. So, the dark side of the Moon is not the same as the far side of the Moon, which we never see from Earth. ...
... Does the Moon have a dark side that we never see from Earth? Half of the Moon is always dark. Whenever we see less than a full Moon, we are seeing part of the Moon’s dark side. So, the dark side of the Moon is not the same as the far side of the Moon, which we never see from Earth. ...
Introduction to space – Celestial sphere
... Declination tells us how far an object is north or south of the celestial equator, measured in degrees. Now imagine the Earth's Equator extended out to infinity, the corresponding point on the celestial sphere is the celestial equator. Just as the angle between the pole and the equator on Earth is ...
... Declination tells us how far an object is north or south of the celestial equator, measured in degrees. Now imagine the Earth's Equator extended out to infinity, the corresponding point on the celestial sphere is the celestial equator. Just as the angle between the pole and the equator on Earth is ...
IV. ASTRONOMY: THE SUN and the MOON
... a. The chemical composition can be determined by analysis of the absorption lines. b. This is how we know that stars consist of normal elements found on Earth. 4. The outer atmosphere of a star is transparent, and the “surface”(photosphere) is simply the region beyond which the gases are opaque. Thi ...
... a. The chemical composition can be determined by analysis of the absorption lines. b. This is how we know that stars consist of normal elements found on Earth. 4. The outer atmosphere of a star is transparent, and the “surface”(photosphere) is simply the region beyond which the gases are opaque. Thi ...
Toys Watch the Sky - The Sun is a close star
... centre of our Solar System. The Sun is located in an outer spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy, approximately 28,000 light-years from the galaxy's centre. (One light year is about 10 million million km.) In comparison with other stars, our Sun is very ordinary – it’s an average sized (1.4 million km ...
... centre of our Solar System. The Sun is located in an outer spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy, approximately 28,000 light-years from the galaxy's centre. (One light year is about 10 million million km.) In comparison with other stars, our Sun is very ordinary – it’s an average sized (1.4 million km ...
The Jerusalem Teddy Park Sundial
... seconds to reach the sundial. This is due to the fact that the Sun is at an average distance of about 150 million km from the Earth. The sundial is a device which is intended to display the time according to the relative position of the Sun in its apparent motion across the sky. The sundial represen ...
... seconds to reach the sundial. This is due to the fact that the Sun is at an average distance of about 150 million km from the Earth. The sundial is a device which is intended to display the time according to the relative position of the Sun in its apparent motion across the sky. The sundial represen ...
How Do We Know the Earth is Spherical?
... – If Earth were flat (but stars still a long ways away), everyone would see same sky. Star at zenith would always be at zenith. ...
... – If Earth were flat (but stars still a long ways away), everyone would see same sky. Star at zenith would always be at zenith. ...
THE SUN IS NOT AN AVERAGE STAR Sometimes biblical creation
... "We believe that the earth and the other planets are a natural by-product of the formation of the sun, and we have evidence that some of the essential ingredients for life were present on the earth from the time it formed. Similar conditions must have been met countless times in the history of the u ...
... "We believe that the earth and the other planets are a natural by-product of the formation of the sun, and we have evidence that some of the essential ingredients for life were present on the earth from the time it formed. Similar conditions must have been met countless times in the history of the u ...
section 16 powerpoint
... Granulation. The mottled structure of the photosphere caused by hot bubbles of gas at the Sun’s surface. Spicule. A spikey jet of hot gas from the solar chromosphere erupting into the solar corona. Prominence. Huge gaseous eruptions of arching clouds of ionized particles streaming between sunspots o ...
... Granulation. The mottled structure of the photosphere caused by hot bubbles of gas at the Sun’s surface. Spicule. A spikey jet of hot gas from the solar chromosphere erupting into the solar corona. Prominence. Huge gaseous eruptions of arching clouds of ionized particles streaming between sunspots o ...
September 2011 - Newbury Astronomical Society
... reduction) are of a reasonable quality. Binoculars with an aperture of less than 50mm are not best suited for astronomy as they cannot capture enough light. Most binoculars have the following features that are designed into the instrument to allow it to be adjusted to suit the user and the purpose o ...
... reduction) are of a reasonable quality. Binoculars with an aperture of less than 50mm are not best suited for astronomy as they cannot capture enough light. Most binoculars have the following features that are designed into the instrument to allow it to be adjusted to suit the user and the purpose o ...
The Black Drop effect - ROSS
... Just after the apparent internal contact between the discs of the Sun and Venus, the disc of the planet seems to remain attached to the rim of the solar disc for a couple of seconds, becoming deformed and assuming a black drop shape. This phenomenon is repeated right before the last internal contact ...
... Just after the apparent internal contact between the discs of the Sun and Venus, the disc of the planet seems to remain attached to the rim of the solar disc for a couple of seconds, becoming deformed and assuming a black drop shape. This phenomenon is repeated right before the last internal contact ...
Astronomy and the Great Pyramid
... either of those dates, which despite the flimsiness of his argument is not entirely ridiculous when compared to the modern estimate at about 2500 B.C. A long–standing problem relating not only to the Great Pyramid but also its smaller cousins is the question of how the builders managed to orient suc ...
... either of those dates, which despite the flimsiness of his argument is not entirely ridiculous when compared to the modern estimate at about 2500 B.C. A long–standing problem relating not only to the Great Pyramid but also its smaller cousins is the question of how the builders managed to orient suc ...
Slide 1 - Typepad
... When we are in the phase of the moon from First Quarter to Full moon, we can see how much light (even natural light) can obscure the fainter celestial objects Fred Lossing Observatory Operated in the area by the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada (RASC) 16” telescope with research grade optics pro ...
... When we are in the phase of the moon from First Quarter to Full moon, we can see how much light (even natural light) can obscure the fainter celestial objects Fred Lossing Observatory Operated in the area by the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada (RASC) 16” telescope with research grade optics pro ...
Archaeoastronomy

Archaeoastronomy (also spelled archeoastronomy) is the study of how people in the past ""have understood the phenomena in the sky, how they used these phenomena and what role the sky played in their cultures."" Clive Ruggles argues it is misleading to consider archaeoastronomy to be the study of ancient astronomy, as modern astronomy is a scientific discipline, while archaeoastronomy considers symbolically rich cultural interpretations of phenomena in the sky by other cultures. It is often twinned with ethnoastronomy, the anthropological study of skywatching in contemporary societies. Archaeoastronomy is also closely associated with historical astronomy, the use of historical records of heavenly events to answer astronomical problems and the history of astronomy, which uses written records to evaluate past astronomical practice.Archaeoastronomy uses a variety of methods to uncover evidence of past practices including archaeology, anthropology, astronomy, statistics and probability, and history. Because these methods are diverse and use data from such different sources, integrating them into a coherent argument has been a long-term difficulty for archaeoastronomers. Archaeoastronomy fills complementary niches in landscape archaeology and cognitive archaeology. Material evidence and its connection to the sky can reveal how a wider landscape can be integrated into beliefs about the cycles of nature, such as Mayan astronomy and its relationship with agriculture. Other examples which have brought together ideas of cognition and landscape include studies of the cosmic order embedded in the roads of settlements.Archaeoastronomy can be applied to all cultures and all time periods. The meanings of the sky vary from culture to culture; nevertheless there are scientific methods which can be applied across cultures when examining ancient beliefs. It is perhaps the need to balance the social and scientific aspects of archaeoastronomy which led Clive Ruggles to describe it as: ""...[A] field with academic work of high quality at one end but uncontrolled speculation bordering on lunacy at the other.""