Local group
... which live 'forever', • massive stars inject into ISM a mass pDMtotal of heavy elements (p depends on the IMF and the yield of SN- normalized to total mass of stars). • Assumptions: galaxies gas is well mixed, no infall or outflow, high mass stars return metals to ISM faster than time to form new st ...
... which live 'forever', • massive stars inject into ISM a mass pDMtotal of heavy elements (p depends on the IMF and the yield of SN- normalized to total mass of stars). • Assumptions: galaxies gas is well mixed, no infall or outflow, high mass stars return metals to ISM faster than time to form new st ...
ExoOrg_NAI
... that pre-dated Solar System formation, along with material processed in the Solar Nebula.6 Aspects of such processing are illustrated in Figure 1.0. Detailed study of interstellar ices has advanced greatly in recent years7 with enhanced theoretical models and laboratory analogs, as well as with remo ...
... that pre-dated Solar System formation, along with material processed in the Solar Nebula.6 Aspects of such processing are illustrated in Figure 1.0. Detailed study of interstellar ices has advanced greatly in recent years7 with enhanced theoretical models and laboratory analogs, as well as with remo ...
Lecture19
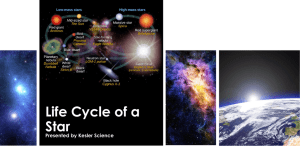
... All stars spend most of their time as main-sequence stars and then change dramatically near the ends of their lives. This figure illustrates the life stages of a high-mass star and a low-mass star and shows how long a star spends in each stage of life. Notice that the lifetime of a low-mass star is ...
... All stars spend most of their time as main-sequence stars and then change dramatically near the ends of their lives. This figure illustrates the life stages of a high-mass star and a low-mass star and shows how long a star spends in each stage of life. Notice that the lifetime of a low-mass star is ...
Booklet 5 – Stellar Processes and Evolution
... the outer regions and so a cloud of gas shrouds the core. If the cloud is particularly large it may produce multiple stars. This process of cloud collapse signifies the start of star formation. Under continuing collapse, the gas in the cloud begins to warm up and gradually brightens. Eventually the ...
... the outer regions and so a cloud of gas shrouds the core. If the cloud is particularly large it may produce multiple stars. This process of cloud collapse signifies the start of star formation. Under continuing collapse, the gas in the cloud begins to warm up and gradually brightens. Eventually the ...
Correct answers shown in boldface. Be sure to write your name and
... c. makes the emission lines of the galaxies in the cluster shift wavelength significantly due to relativity d. is almost all concentrated in its giant central galaxies e. is mostly in the form of very hot gas and dark matter 32. Why did astronomers in the 19th century believe that the solar system w ...
... c. makes the emission lines of the galaxies in the cluster shift wavelength significantly due to relativity d. is almost all concentrated in its giant central galaxies e. is mostly in the form of very hot gas and dark matter 32. Why did astronomers in the 19th century believe that the solar system w ...
ASTRO2010 SCIENCE WHITE PAPER
... Spitzer IRS indicate that mid-IR molecular emission is common in protoplanetary disks; roughly 90% of the ∼60 classical T Tau stars observed so far with Spitzer IRS show water and/or other simple molecules (Carr & Najita 2008, Salyk et al. 2008; J. Carr, personal communication). This will be rich te ...
... Spitzer IRS indicate that mid-IR molecular emission is common in protoplanetary disks; roughly 90% of the ∼60 classical T Tau stars observed so far with Spitzer IRS show water and/or other simple molecules (Carr & Najita 2008, Salyk et al. 2008; J. Carr, personal communication). This will be rich te ...
Astronomy 112: The Physics of Stars Class 18 Notes: Neutron Stars
... Thus when the core collapses to make a neutron star, the magnetic field that is trapped in the core is enhanced by a factor of (Ri /Rf )2 . The initial radius we said last time is about 104 km and the final one is 10 km, so the field intensity is boosted by a factor of 106 and the magnetic field ene ...
... Thus when the core collapses to make a neutron star, the magnetic field that is trapped in the core is enhanced by a factor of (Ri /Rf )2 . The initial radius we said last time is about 104 km and the final one is 10 km, so the field intensity is boosted by a factor of 106 and the magnetic field ene ...
Pluto_Friends
... The new moons are roughly 12x smaller and 600x fainter than Charon, and 4000x fainter than Pluto ...
... The new moons are roughly 12x smaller and 600x fainter than Charon, and 4000x fainter than Pluto ...
Death of Stars • Models of Star behavior can give estimates of how
... to fuse now finds that the temperature has risen and can begin to fuse. But because it fuses in a thin shell, the P-T thermostat does not come into play here, and it releases a lot of energy quickly which heats the outer layers of the star and causes them to expand. • These outer layers then begin t ...
... to fuse now finds that the temperature has risen and can begin to fuse. But because it fuses in a thin shell, the P-T thermostat does not come into play here, and it releases a lot of energy quickly which heats the outer layers of the star and causes them to expand. • These outer layers then begin t ...
Observations, Modeling and Theory of Debris Disks
... in thermal emission or scattered light. These disks may persist over Gyrs through steady-state evolution and/or may also experience sporadic stirring and major collisional breakups, rendering them atypically bright for brief periods of time. Most interestingly, they provide direct evidence that the ...
... in thermal emission or scattered light. These disks may persist over Gyrs through steady-state evolution and/or may also experience sporadic stirring and major collisional breakups, rendering them atypically bright for brief periods of time. Most interestingly, they provide direct evidence that the ...
Systems of Multiple Planets
... Abstract. To date, 10 stars are known which harbor two or three planets. These systems reveal secular and mean motion resonances in some systems and consist of widely separated, eccentric orbits in others. Both of the triple planet systems, namely Upsilon And and 55 Cancri, exhibit evidence of reson ...
... Abstract. To date, 10 stars are known which harbor two or three planets. These systems reveal secular and mean motion resonances in some systems and consist of widely separated, eccentric orbits in others. Both of the triple planet systems, namely Upsilon And and 55 Cancri, exhibit evidence of reson ...
2017 Div. C (High School) Astronomy Help Session
... They are red giants – very late stages of stellar evolution for low mass stars, on the asymptotic giant branch, – will expel their outer envelopes as planetary nebulae and become white dwarfs within a few million years. Massive enough that they have undergone helium fusion in their cores but are les ...
... They are red giants – very late stages of stellar evolution for low mass stars, on the asymptotic giant branch, – will expel their outer envelopes as planetary nebulae and become white dwarfs within a few million years. Massive enough that they have undergone helium fusion in their cores but are les ...
PH607 – Galaxies
... MACHO: astronomical object that might explain the apparent presence of dark matter in galaxy halos. A MACHO is a small chunk of normal baryonic matter, which emits little or no radiation and drifts through interstellar space. Since MACHOs would not emit any light of their own, they would be very har ...
... MACHO: astronomical object that might explain the apparent presence of dark matter in galaxy halos. A MACHO is a small chunk of normal baryonic matter, which emits little or no radiation and drifts through interstellar space. Since MACHOs would not emit any light of their own, they would be very har ...
observing cards - NC Science Festival
... Stars in open clusters are bright, young, and often blue - the teenage sisters of stars. They’ve blown off the rest of their parental gas and dust and hang together. Eventually the stars drift apart, but for now, they travel in a pack through ...
... Stars in open clusters are bright, young, and often blue - the teenage sisters of stars. They’ve blown off the rest of their parental gas and dust and hang together. Eventually the stars drift apart, but for now, they travel in a pack through ...
GG_CERN_0707
... Apparently dark-matter dominated ~ 10km/s, 10 < ~ M/L <~ 100 Metal-poor, mean stellar metallicity < ~ –1.5 dex All contain old stars; extended star-formation histories typical, intermediate-age stars dominate Most common galaxy nearby Crucial tests for CDM and other models ...
... Apparently dark-matter dominated ~ 10km/s, 10 < ~ M/L <~ 100 Metal-poor, mean stellar metallicity < ~ –1.5 dex All contain old stars; extended star-formation histories typical, intermediate-age stars dominate Most common galaxy nearby Crucial tests for CDM and other models ...
D109-08x
... characterization of the knots over a broader color baseline than obtainable from the ground coupled with higher resolution imaging of their morphology are necessary to both better resolve the knots in the aggregate and to determine their mean stellar ages (which are likely quite young). At the momen ...
... characterization of the knots over a broader color baseline than obtainable from the ground coupled with higher resolution imaging of their morphology are necessary to both better resolve the knots in the aggregate and to determine their mean stellar ages (which are likely quite young). At the momen ...
Lives of the Stars Lecture 5: Star birth
... emerging from its birth cloud of dust and gas. The region shown is about 2/3 of a light year across. ...
... emerging from its birth cloud of dust and gas. The region shown is about 2/3 of a light year across. ...