Solar_System - UF :: Astronomy
... Asteroids - rocks with sizes greater than 100m across Most asteroids remain in the Asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter but a few have orbits that cross ...
... Asteroids - rocks with sizes greater than 100m across Most asteroids remain in the Asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter but a few have orbits that cross ...
ch. 5 study guide
... o Know all of the following about the outer planets. (You will be asked to identify one which is not true about them.) They are the farthest from the Sun. They are all bigger than the inner planets. They all have rings. o The Sun is a medium-sized star in the universe. o Our galaxy is called the Mil ...
... o Know all of the following about the outer planets. (You will be asked to identify one which is not true about them.) They are the farthest from the Sun. They are all bigger than the inner planets. They all have rings. o The Sun is a medium-sized star in the universe. o Our galaxy is called the Mil ...
Document
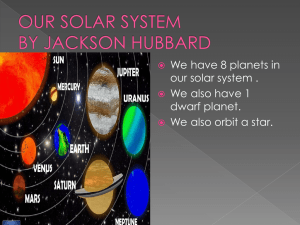
... Mars , Earth , Venus , and Mercury. Those are the inner planets that are surrounded by the asteroid belt ...
... Mars , Earth , Venus , and Mercury. Those are the inner planets that are surrounded by the asteroid belt ...
origin of solar system
... Proxima Centauri, the star nearest the sun, has a planetary system consisting of at least one planet. The new study analyzes and supplements earlier observations. These new measurements show that this planet, named Proxima Centauri b or simply Proxima b, has a mass close to that of Earth (1.3 times ...
... Proxima Centauri, the star nearest the sun, has a planetary system consisting of at least one planet. The new study analyzes and supplements earlier observations. These new measurements show that this planet, named Proxima Centauri b or simply Proxima b, has a mass close to that of Earth (1.3 times ...
Other Planetary Systems
... This Explains Why… …in many of the planetary systems detected so far, we find big, massive planets quite close to the parent stars (especially with the ‘wobble’ technique; using transits is better able to find smaller planets.) It will take many years, and improving technology, to allow the confirm ...
... This Explains Why… …in many of the planetary systems detected so far, we find big, massive planets quite close to the parent stars (especially with the ‘wobble’ technique; using transits is better able to find smaller planets.) It will take many years, and improving technology, to allow the confirm ...
Earth Science Chapter Two: What Makes Up the Solar System
... 9. What are the two basic features that make life possible on Earth? 10. What do Mars and Earth both have in common? 11. What planets make up the four outer planets? 12. Which objects in Earth’s solar system can also be called a gas giant? 13. What makes up Jupiter’s famous Great Red Spot? ...
... 9. What are the two basic features that make life possible on Earth? 10. What do Mars and Earth both have in common? 11. What planets make up the four outer planets? 12. Which objects in Earth’s solar system can also be called a gas giant? 13. What makes up Jupiter’s famous Great Red Spot? ...
new_qwk11
... A. When a star finishes burning all the hydrogen in its core, it ceases to be a main sequence star B. The “helium flash” (ignition of the helium core) takes place at the tip of the red giant branch C. A planetary nebula is formed when a star loses part of its outer envelope in a stellar wind and thi ...
... A. When a star finishes burning all the hydrogen in its core, it ceases to be a main sequence star B. The “helium flash” (ignition of the helium core) takes place at the tip of the red giant branch C. A planetary nebula is formed when a star loses part of its outer envelope in a stellar wind and thi ...
Formation of the Solar System • Questions
... • Ices as well as silicates available for solid bodies. • Larger protoplanets resulted. • These cores able to attract surrounding H & He gas in order to build giant planets. • Gravitational field of giant planets perturbed orbits of remaining planetesimals. • Most comets ejected into Oort Cloud ...
... • Ices as well as silicates available for solid bodies. • Larger protoplanets resulted. • These cores able to attract surrounding H & He gas in order to build giant planets. • Gravitational field of giant planets perturbed orbits of remaining planetesimals. • Most comets ejected into Oort Cloud ...
MHD_of_Accretion_Disks
... Weakly Ionized Plasmas are found in several astrophysical objects such as in circumstellar,and protoplanetary Disks . Because gas clouds have difficulty getting rid of excess angular momentum during a phase of dynamical collapse, there is reason to believe that all stars form with some sort of (acc ...
... Weakly Ionized Plasmas are found in several astrophysical objects such as in circumstellar,and protoplanetary Disks . Because gas clouds have difficulty getting rid of excess angular momentum during a phase of dynamical collapse, there is reason to believe that all stars form with some sort of (acc ...
Beginnings - Big Picture
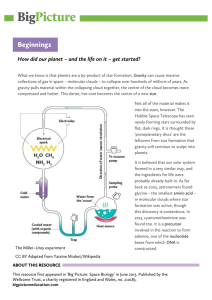
... How did our planet – and the life on it – get started? What we know is that planets are a by-product of star formation. Gravity can cause massive collections of gas in space – molecular clouds – to collapse over hundreds of millions of years. As gravity pulls material within the collapsing cloud tog ...
... How did our planet – and the life on it – get started? What we know is that planets are a by-product of star formation. Gravity can cause massive collections of gas in space – molecular clouds – to collapse over hundreds of millions of years. As gravity pulls material within the collapsing cloud tog ...
Solving the Mystery of Massive Star Birth
... As the cloud gets smaller, it gets clumpy. The clumps may eventually become so compact that they begin to heat up, growing hotter and hotter, until eventually they begin “burning” at their core. When the temperature at the core reaches a scorching 10 million degrees, the clump officially becomes a new ...
... As the cloud gets smaller, it gets clumpy. The clumps may eventually become so compact that they begin to heat up, growing hotter and hotter, until eventually they begin “burning” at their core. When the temperature at the core reaches a scorching 10 million degrees, the clump officially becomes a new ...
ppt
... Condensation nuclei (minute dust grains) attract other matter and begin to grow in size. The dust grains are present in the initial solar solar nebula This accretion phase continues, forming ever larger systems baseball size→basketball size→continent sized Planetesimals have enough gravity to now st ...
... Condensation nuclei (minute dust grains) attract other matter and begin to grow in size. The dust grains are present in the initial solar solar nebula This accretion phase continues, forming ever larger systems baseball size→basketball size→continent sized Planetesimals have enough gravity to now st ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... •Hydrogen fuses into helium •All stars (low and high mass) go through this •How long a star lives depends on its mass •Small stars use their fuel slow = longer lives ...
... •Hydrogen fuses into helium •All stars (low and high mass) go through this •How long a star lives depends on its mass •Small stars use their fuel slow = longer lives ...
ASTRONOMY 1001 FALL SEMESTER 2004
... Comets, ion and dust tails, structure, nucleus, origin, behavior in orbit Origin of solar system, patterns of motion, centrifugal force, conservation of angular momentum, interstellar clouds, gravitational contraction, accretion, planetesimals, protoplanets, collisions, solar wind 3) Sun: Structure, ...
... Comets, ion and dust tails, structure, nucleus, origin, behavior in orbit Origin of solar system, patterns of motion, centrifugal force, conservation of angular momentum, interstellar clouds, gravitational contraction, accretion, planetesimals, protoplanets, collisions, solar wind 3) Sun: Structure, ...
Astronomy Review fall 2013
... What is the approximate age of our Universe? 14.7 billion years old ...
... What is the approximate age of our Universe? 14.7 billion years old ...
Astro 10: Introductory Astronomy
... “Slow” Core Accretion goes faster when gravity gets strong enough, but… • Once the core grows past ~0.5-1 mile across, gravity becomes significant and accelerates the process. • Growth rate goes as radius to the 4th power (for constant density). • So, those cores which get to the self-gravity point ...
... “Slow” Core Accretion goes faster when gravity gets strong enough, but… • Once the core grows past ~0.5-1 mile across, gravity becomes significant and accelerates the process. • Growth rate goes as radius to the 4th power (for constant density). • So, those cores which get to the self-gravity point ...
File
... 9. What is the largest object in the solar system? The sun 10. Which way does Venus rotate? North and south (like rolling a ball) 11. What is the hottest planet in the solar system? Venus 12. What is Earth’s atmosphere made of? Water vapor and other gases 13. What features do the inner planets share ...
... 9. What is the largest object in the solar system? The sun 10. Which way does Venus rotate? North and south (like rolling a ball) 11. What is the hottest planet in the solar system? Venus 12. What is Earth’s atmosphere made of? Water vapor and other gases 13. What features do the inner planets share ...