Planet migration
... Proposed migration mechanism is interaction with the proto-planetary disk which results in three types of migration (Papaloizou et al. 2007): Type I: small mass planets, treated in linear regime (Ward 1997) Type II: larger mass planets open a gap (non-linear) (Lin & Papaloizou 1984) Type III: runawa ...
... Proposed migration mechanism is interaction with the proto-planetary disk which results in three types of migration (Papaloizou et al. 2007): Type I: small mass planets, treated in linear regime (Ward 1997) Type II: larger mass planets open a gap (non-linear) (Lin & Papaloizou 1984) Type III: runawa ...
Accretion as a Source of Energy
... For the nineteenth century physics, gravity was the only conceivable source of energy in celestial bodies, but gravity was inadequate to power the Sun for its known lifetime. In contrast, in the latter half of the twentieth century it is to gravity that we look to power the most luminous object Some ...
... For the nineteenth century physics, gravity was the only conceivable source of energy in celestial bodies, but gravity was inadequate to power the Sun for its known lifetime. In contrast, in the latter half of the twentieth century it is to gravity that we look to power the most luminous object Some ...
Disk Instability Models
... Heretical Explanation for Microlensing Planets • Most stars form in regions of high-mass star formation (e.g., Orion, Carina) where their protoplanetary disks can be photoevaporated away by nearby O stars. • Photoevaporation converts gas giant protoplanets into ice giants if the protoplanet orbit ...
... Heretical Explanation for Microlensing Planets • Most stars form in regions of high-mass star formation (e.g., Orion, Carina) where their protoplanetary disks can be photoevaporated away by nearby O stars. • Photoevaporation converts gas giant protoplanets into ice giants if the protoplanet orbit ...
X-ray Binaries and Cygnus X-1
... An X-ray binary is a system made up of a normal star and a compact object rotating about a common center of mass. The compact object pulls mass off of the outer atmospheres of the normal star and the particles spiral down toward the compact object, creating an accretion disk. Because of the internal ...
... An X-ray binary is a system made up of a normal star and a compact object rotating about a common center of mass. The compact object pulls mass off of the outer atmospheres of the normal star and the particles spiral down toward the compact object, creating an accretion disk. Because of the internal ...
Lecture Notes-PPT
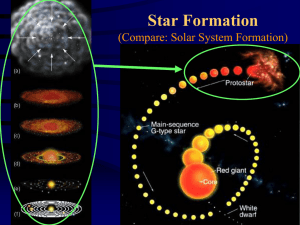
... Stars form inside relatively dense concentrations of interstellar gas known as molecular clouds. These regions are extremely cold, causing the gas to clump to high densities. Star formation begins when the denser parts of the cloud core collapse under gravity. These cores typically have masses aroun ...
... Stars form inside relatively dense concentrations of interstellar gas known as molecular clouds. These regions are extremely cold, causing the gas to clump to high densities. Star formation begins when the denser parts of the cloud core collapse under gravity. These cores typically have masses aroun ...
PHYS3380_102615_bw
... - dust cocoon absorbs almost all of the visible radiation - grows warm and reemits energy as IR radiation ...
... - dust cocoon absorbs almost all of the visible radiation - grows warm and reemits energy as IR radiation ...
a planet rotates on its own axis and revolves around
... with the inward force of gravity that the gas stopped collapsing ...
... with the inward force of gravity that the gas stopped collapsing ...
Instructor Notes
... The inner solar system consisted of 4 terrestrial (Earth‐like) planets; the outer solar system consisted of 4 Jovian (Jupiter‐like) planets and Pluto. An asteroid belt separated the inner and outer solar systems, and there were comets somewhere past the planets of the outer solar system ...
... The inner solar system consisted of 4 terrestrial (Earth‐like) planets; the outer solar system consisted of 4 Jovian (Jupiter‐like) planets and Pluto. An asteroid belt separated the inner and outer solar systems, and there were comets somewhere past the planets of the outer solar system ...
The planets in the solar system
... steadily accumulate mass to form ever-larger bodies. Local concentrations of mass known as planetesimals begin to form, and these accelerate the accretion process by drawing in additional material by their gravitational attraction. These concentrations become ever denser until they collapse inward u ...
... steadily accumulate mass to form ever-larger bodies. Local concentrations of mass known as planetesimals begin to form, and these accelerate the accretion process by drawing in additional material by their gravitational attraction. These concentrations become ever denser until they collapse inward u ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Unit 9
... 22. What are auroras? What causes them? Where do you normally see them? 23. How do sunspots form? 24. What is nuclear fusion? 25. How long is a sunspot cycle? 26. What is a coronal mass ejection? 27. Although the trigger for a solar flare is unknown, scientists know that… 28. The sun is composed mai ...
... 22. What are auroras? What causes them? Where do you normally see them? 23. How do sunspots form? 24. What is nuclear fusion? 25. How long is a sunspot cycle? 26. What is a coronal mass ejection? 27. Although the trigger for a solar flare is unknown, scientists know that… 28. The sun is composed mai ...
Extrasolar planets - Institut de Planétologie et d`Astrophysique de
... the planet escapes • Shock wave: if Ekinetic » Ebinding, the planet is destroyed Ekinetic = EpRp2/(4pD2) with E=1051 ergs Ebinding = -GMp2/Rp = -10-2 Ec → ??? ...
... the planet escapes • Shock wave: if Ekinetic » Ebinding, the planet is destroyed Ekinetic = EpRp2/(4pD2) with E=1051 ergs Ebinding = -GMp2/Rp = -10-2 Ec → ??? ...
Exoplanets
... Three Known Planets Planet Msini = 1.89 MJ a = 0.21 AU (61.0 days) Planet Msini = 0.56 MJ a = 0.13 AU (30.1 days) Planet Msini = 5.9 ME a = 0.021 AU (1.94 days) Star Mass = 0.32 M M4V ...
... Three Known Planets Planet Msini = 1.89 MJ a = 0.21 AU (61.0 days) Planet Msini = 0.56 MJ a = 0.13 AU (30.1 days) Planet Msini = 5.9 ME a = 0.021 AU (1.94 days) Star Mass = 0.32 M M4V ...
Document
... tokamak). The torus reconnects into self gravitating magnetic spheroids (spheromaks) that become planetary cores. The reconnection radiation and winds heat and compress the disk causing agglomeration out to the snow line. The cores grow by collecting material infalling toward the star. They are in u ...
... tokamak). The torus reconnects into self gravitating magnetic spheroids (spheromaks) that become planetary cores. The reconnection radiation and winds heat and compress the disk causing agglomeration out to the snow line. The cores grow by collecting material infalling toward the star. They are in u ...
t2 images part 1
... either by expelling their outer layers or as huge super nova explosions. So much heat and energy is produced by these events that all of the heavier elements are formed. Large stars burn through their fuel faster. ...
... either by expelling their outer layers or as huge super nova explosions. So much heat and energy is produced by these events that all of the heavier elements are formed. Large stars burn through their fuel faster. ...
Extrasolar planets
... First detection of any carbon-bearing molecule on a planet outside the Solar System! Swain et al., Nature, March 2008 Also confirmed previous discovery of water on this planet ...
... First detection of any carbon-bearing molecule on a planet outside the Solar System! Swain et al., Nature, March 2008 Also confirmed previous discovery of water on this planet ...














![Sun, Stars and Planets [Level 2] 2015](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007097773_1-15996a23762c2249db404131f50612f3-300x300.png)