life and death of a high mass star 2
... AFTER THAT, THEY LOSE THEIR MASS AND HEAT AND BEGIN TO DIE. THIS PROCESS TAKES BILLIONS AND BILLIONS OF YEARS. ...
... AFTER THAT, THEY LOSE THEIR MASS AND HEAT AND BEGIN TO DIE. THIS PROCESS TAKES BILLIONS AND BILLIONS OF YEARS. ...
Scales of the Universe
... • The Main Sequence is just a manifestation of the relationship between Mass and Luminosity: L ~ M3.5 • The more massive the star the larger its weight • The larger the weight, the larger the pressure • The larger the pressure, the higher the temperature • The higher the temperature, the more energe ...
... • The Main Sequence is just a manifestation of the relationship between Mass and Luminosity: L ~ M3.5 • The more massive the star the larger its weight • The larger the weight, the larger the pressure • The larger the pressure, the higher the temperature • The higher the temperature, the more energe ...
etlife_exoplanets - University of Glasgow
... We can tell that planets are there by the effect they have on their star. ...
... We can tell that planets are there by the effect they have on their star. ...
Slide 1
... The Planetary Nebula (show) Glowing gaseous shrouds shed by dying sun-like stars trying to stabilize as they run out of nuclear fuel.. Typically 1,000 times the size of our solar system These Ten have names like Owl, the Cat's Eye, the Ghost of Jupiter, Ring. This glorious final phase in the life of ...
... The Planetary Nebula (show) Glowing gaseous shrouds shed by dying sun-like stars trying to stabilize as they run out of nuclear fuel.. Typically 1,000 times the size of our solar system These Ten have names like Owl, the Cat's Eye, the Ghost of Jupiter, Ring. This glorious final phase in the life of ...
What is a “Planet”?
... smaller ones around. Some are ejected from the system. There must be “lost” planets. This has also been suggested as a means of making brown dwarfs. ...
... smaller ones around. Some are ejected from the system. There must be “lost” planets. This has also been suggested as a means of making brown dwarfs. ...
this PDF file
... rements, allows us to estimate the size. This is particularly important for Near Earth Asteroids, that can pose threats to the Earth. (ii) Polarimetry is also a very useful diagnostic tool for the planet atmospheres, providing unique information on their structure and the scattering properties of pa ...
... rements, allows us to estimate the size. This is particularly important for Near Earth Asteroids, that can pose threats to the Earth. (ii) Polarimetry is also a very useful diagnostic tool for the planet atmospheres, providing unique information on their structure and the scattering properties of pa ...
BIO 10 Lecture 2
... – Most of the H and He are found in the sun; rocky planets made of heavier elements (like Earth) are found close to the sun, while gaseous planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune) are found further out ...
... – Most of the H and He are found in the sun; rocky planets made of heavier elements (like Earth) are found close to the sun, while gaseous planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune) are found further out ...
Our Solar System
... medium in size & life span compared to other stars primary energy source for all processes on Earth much closer to Earth than any other star! about 4 ½ billion years old ...
... medium in size & life span compared to other stars primary energy source for all processes on Earth much closer to Earth than any other star! about 4 ½ billion years old ...
NCEA Level 2 Earth and Space Science (91192) 2015
... The star started life as a cloud of dust and gas that is called nebula or a Giant Molecular Cloud (GMC). The dust and gas can be caused to condense together by an outside force, such as a nearby star going supernova, or just the gravity of a near star. As the GMC condenses under gravity, it forms a ...
... The star started life as a cloud of dust and gas that is called nebula or a Giant Molecular Cloud (GMC). The dust and gas can be caused to condense together by an outside force, such as a nearby star going supernova, or just the gravity of a near star. As the GMC condenses under gravity, it forms a ...
NCEA Level 2 Earth and Space Science (91192) 2015
... The star started life as a cloud of dust and gas that is called nebula or a Giant Molecular Cloud (GMC). The dust and gas can be caused to condense together by an outside force, such as a nearby star going supernova, or just the gravity of a near star. As the GMC condenses under gravity, it forms a ...
... The star started life as a cloud of dust and gas that is called nebula or a Giant Molecular Cloud (GMC). The dust and gas can be caused to condense together by an outside force, such as a nearby star going supernova, or just the gravity of a near star. As the GMC condenses under gravity, it forms a ...
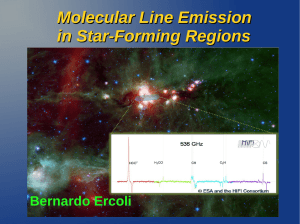
Molecular Line Emission in Star
... dense cores can be traced with ammonia (NH3). The concentration of dust is normally sufficient to block light from background stars so that there appear “dark nebulae”. ...
... dense cores can be traced with ammonia (NH3). The concentration of dust is normally sufficient to block light from background stars so that there appear “dark nebulae”. ...
The Planets in our Solar System Solar System Basics
... • Temperature and distance from the Sun influenced the condensation of various substances within the evolving solar system. • Eventually, the condensing material merged to form large bodies hundreds of kilometers in diameter. ...
... • Temperature and distance from the Sun influenced the condensation of various substances within the evolving solar system. • Eventually, the condensing material merged to form large bodies hundreds of kilometers in diameter. ...
Temperature and Formation of Our Solar System
... is the region where the temperature in the early Solar System was below 273K, the freezing point of water. 6) Over what range of distances from the Sun would you expect to find solid, rocky material collecting together to form a terrestrial planet? Explain your reasoning. Terrestrial planets could f ...
... is the region where the temperature in the early Solar System was below 273K, the freezing point of water. 6) Over what range of distances from the Sun would you expect to find solid, rocky material collecting together to form a terrestrial planet? Explain your reasoning. Terrestrial planets could f ...
formation of the outer planets
... reason to believe that the collapse process that leads to stars cannot also produce substellar objects (Wuchterl and Tscharnuter, 2003), strongly implies that most isolated (or distant companion) brown dwarfs∗ and isolated high planetary mass objects formed via the same collapse process as do stars. ...
... reason to believe that the collapse process that leads to stars cannot also produce substellar objects (Wuchterl and Tscharnuter, 2003), strongly implies that most isolated (or distant companion) brown dwarfs∗ and isolated high planetary mass objects formed via the same collapse process as do stars. ...
Gravity in the Solar System Quiz
... 9) If you are on the top of a mountain and drop an apple, it will fall to the ground, even though the apple is gravitationally attracted to you. Why? a) Earth is larger and has a much stronger gravitational pull. b) Apples always fall down. c) Centrifugal forces pull the apple to the Earth and that ...
... 9) If you are on the top of a mountain and drop an apple, it will fall to the ground, even though the apple is gravitationally attracted to you. Why? a) Earth is larger and has a much stronger gravitational pull. b) Apples always fall down. c) Centrifugal forces pull the apple to the Earth and that ...
Two obvious differences between the exoplanets and the giant
... Two obvious differences between the exoplanets and the giant planets in the Solar System: A) Existence of planets at small orbital radii, where our previous theory suggested formation was very difficult. B) Substantial eccentricity of many of the orbits. No clear answers to either of these surprises ...
... Two obvious differences between the exoplanets and the giant planets in the Solar System: A) Existence of planets at small orbital radii, where our previous theory suggested formation was very difficult. B) Substantial eccentricity of many of the orbits. No clear answers to either of these surprises ...
Slide 1
... Kuiper belt objects more than 300 km in diameter, smaller asteroids, comets, and meteoroids ...
... Kuiper belt objects more than 300 km in diameter, smaller asteroids, comets, and meteoroids ...
Formation of Planets III
... cycles of newly forming stars. Before the fusion of hydrogens to form helium begins, the star emits a large wind, called a ________________, named after the star where it was first observed. This wind would push out all the gas from the solar system and also cause the spin of the sun to slow down. W ...
... cycles of newly forming stars. Before the fusion of hydrogens to form helium begins, the star emits a large wind, called a ________________, named after the star where it was first observed. This wind would push out all the gas from the solar system and also cause the spin of the sun to slow down. W ...
Stars, Planets, Moons, too Doing the Solar System
... The star nearest Earth is the Sun, It provides energy for everyone. The energy comes in the form of heat and light, It’s a ball of gases that burns just right. ...
... The star nearest Earth is the Sun, It provides energy for everyone. The energy comes in the form of heat and light, It’s a ball of gases that burns just right. ...
Red Giant Sun May Not Destroy Earth
... Fortney is a scientist at the NASA Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, California, who was not involved in the new paper. Stars like the sun become red giants when the hydrogen in their cores burns fully into helium. At that point they expand, becoming large enough to engulf any inner planets. Mo ...
... Fortney is a scientist at the NASA Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, California, who was not involved in the new paper. Stars like the sun become red giants when the hydrogen in their cores burns fully into helium. At that point they expand, becoming large enough to engulf any inner planets. Mo ...
Final Exam Practice Part I
... 4. What caused its shape to become a disk? 5. Today’s planets formed from dust and gases that clumped together. What caused this clumping into actual planets? 6. The inner planets of our solar system are rocky, while the outer planets are “gas giants.” Why are the inner and outer planets different? ...
... 4. What caused its shape to become a disk? 5. Today’s planets formed from dust and gases that clumped together. What caused this clumping into actual planets? 6. The inner planets of our solar system are rocky, while the outer planets are “gas giants.” Why are the inner and outer planets different? ...