Skymapper and Kepler K2: Finding the Origin of Hot Gas Giants
... determine which stars are young. • Data/pretty images prior to May 1 would really help the proposal for K2 targets! • This is standard “fast” survey data. ...
... determine which stars are young. • Data/pretty images prior to May 1 would really help the proposal for K2 targets! • This is standard “fast” survey data. ...
Slide 1
... class to get notes on the stages. We’ll add a bit more to this in “official” notes later, but this poster will be your main source of notes for this topic! ...
... class to get notes on the stages. We’ll add a bit more to this in “official” notes later, but this poster will be your main source of notes for this topic! ...
Our Solar System
... that cannot, and between problems that can be solved by technology and those that cannot with regards to solar system formation. -Estimate quantities of distances in parsec. Estimate the age of the solar system. -Describe and apply classification systems and nomenclature used in the sciences. Classi ...
... that cannot, and between problems that can be solved by technology and those that cannot with regards to solar system formation. -Estimate quantities of distances in parsec. Estimate the age of the solar system. -Describe and apply classification systems and nomenclature used in the sciences. Classi ...
Excellence
... White dwarfs form when a star dies. They don’t have a fuel source so are slowly cooling over time. They range in temperature from 7, 500 – 30, 000 K. This is quite hot compared to the red giants which are still burning fuel but it makes sense when you compare their surface area and mass. White dwarf ...
... White dwarfs form when a star dies. They don’t have a fuel source so are slowly cooling over time. They range in temperature from 7, 500 – 30, 000 K. This is quite hot compared to the red giants which are still burning fuel but it makes sense when you compare their surface area and mass. White dwarf ...
Name the eight planets in order by increasing distance from the sun:
... 1. Name the eight planets in order by increasing distance from the sun: A: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune 2. What are two pieces of technology that have helped scientists explore the solar system? A: space shuttles, probes, telescopes 3. What two things combine/balance ...
... 1. Name the eight planets in order by increasing distance from the sun: A: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune 2. What are two pieces of technology that have helped scientists explore the solar system? A: space shuttles, probes, telescopes 3. What two things combine/balance ...
File
... Massive stars have much _______ gravitational pressure on the core... they consume hydrogen much __________ (7-10 million years) the core temperatures are very ________ the outer surface is very large...a ______________ ________ when fuel runs out the star collapses and explodes...__________ ...
... Massive stars have much _______ gravitational pressure on the core... they consume hydrogen much __________ (7-10 million years) the core temperatures are very ________ the outer surface is very large...a ______________ ________ when fuel runs out the star collapses and explodes...__________ ...
Lecture #27: The Next 100 Years
... coronagraphy (meaning blocking out the light of the central star to observe fainter objects around it) TPF will survey 250 of the closest stars as a follow up for Kepler and SIM ...
... coronagraphy (meaning blocking out the light of the central star to observe fainter objects around it) TPF will survey 250 of the closest stars as a follow up for Kepler and SIM ...
PowerPoint - Chandra X
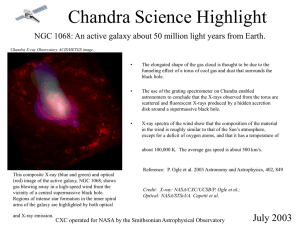
... The elongated shape of the gas cloud is thought to be due to the funneling effect of a torus of cool gas and dust that surrounds the black hole. ...
... The elongated shape of the gas cloud is thought to be due to the funneling effect of a torus of cool gas and dust that surrounds the black hole. ...
Test 2 Overview
... Too cold for optical emission but some radio spectral lines from molecules. Doppler shifts of lines indicate clouds rotate at a few km/s. Clumps within such clouds collapse to form stars or clusters of stars. They are spinning at about 1 km/s. ...
... Too cold for optical emission but some radio spectral lines from molecules. Doppler shifts of lines indicate clouds rotate at a few km/s. Clumps within such clouds collapse to form stars or clusters of stars. They are spinning at about 1 km/s. ...
Star Formation/Llfe Cycle Notes
... d. Center of protostar gets dense enough and therefore hot enough (3000K+) to become luminous, however not visible due to exterior of gas and dust surrounding it. 3) Phophids- YSO’s starting to disk a. start to get charged particles 4) Early star- Does a stutter step with nuclear fusion which blows ...
... d. Center of protostar gets dense enough and therefore hot enough (3000K+) to become luminous, however not visible due to exterior of gas and dust surrounding it. 3) Phophids- YSO’s starting to disk a. start to get charged particles 4) Early star- Does a stutter step with nuclear fusion which blows ...
Lecture 1
... Rapidly developing subject - first extrasolar planet around an ordinary star only discovered in 1995 by Mayor & Queloz. Observations are secure, but theory is still developing ... http://star-www.st-and.ac.uk/~srk1/as3012/ ...
... Rapidly developing subject - first extrasolar planet around an ordinary star only discovered in 1995 by Mayor & Queloz. Observations are secure, but theory is still developing ... http://star-www.st-and.ac.uk/~srk1/as3012/ ...
chapter10
... If an accreting white dwarf exceeds the Chandrasekhar mass limit, it collapses, triggering a type Ia supernova. ...
... If an accreting white dwarf exceeds the Chandrasekhar mass limit, it collapses, triggering a type Ia supernova. ...
How Big Is Big
... 12. Scientists are discovering more __________ in our Solar System. They are all small _______ rocky worlds similar to Pluto. They are found in a region that includes Pluto called the Kuiper ________. The Kuiper Belt reaches from 30 – 50 ________ from the Sun and includes comets and all the newly di ...
... 12. Scientists are discovering more __________ in our Solar System. They are all small _______ rocky worlds similar to Pluto. They are found in a region that includes Pluto called the Kuiper ________. The Kuiper Belt reaches from 30 – 50 ________ from the Sun and includes comets and all the newly di ...
Gemini South telescope makes the case for multiple Earth
... companions to the primary “host” star, to within a distance that is less than that of Mercury from our Sun. Faint “M-class” stars such as TRAPPIST-1 are of great interest to astronomers: their diminutive size allows easier detection of small, terrestrial planets. In the TRAPPIST-1 system, two of the ...
... companions to the primary “host” star, to within a distance that is less than that of Mercury from our Sun. Faint “M-class” stars such as TRAPPIST-1 are of great interest to astronomers: their diminutive size allows easier detection of small, terrestrial planets. In the TRAPPIST-1 system, two of the ...
24exoplanets5s
... The planets are detected by measuring the motions they induce in the central star The period and velocity of the motions allows the determination of the mass and orbit of the planet New missions in the next 20 years will allow for the detection of many new planets, including Earth-like, habitable ...
... The planets are detected by measuring the motions they induce in the central star The period and velocity of the motions allows the determination of the mass and orbit of the planet New missions in the next 20 years will allow for the detection of many new planets, including Earth-like, habitable ...