SNC 1D1 Space Unit Review Answers How long does it take the
... 23. Why is the length of a year on Earth different from the length of a year on other planets? Because they have different lengths of time that they take to orbit the Sun. 24. Name and describe the predominant scientific theory on how the universe was formed. -Big Bang Theory: 14 billion years ago, ...
... 23. Why is the length of a year on Earth different from the length of a year on other planets? Because they have different lengths of time that they take to orbit the Sun. 24. Name and describe the predominant scientific theory on how the universe was formed. -Big Bang Theory: 14 billion years ago, ...
Sample exam 2
... Essay questions — choose three of the following questions; circle the numbers of the ones chosen, so I know which ones to grade. Please answer each question in sentence/paragraph format or a drawing, depending on what is asked. 11. The Sun started off its trajectory on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagra ...
... Essay questions — choose three of the following questions; circle the numbers of the ones chosen, so I know which ones to grade. Please answer each question in sentence/paragraph format or a drawing, depending on what is asked. 11. The Sun started off its trajectory on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagra ...
the solar system and the universe - Colegio Nuestra Señora del Prado
... The outer planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. These are the furthest planets from the sun and they have got many satellites. They are often called the gas giants, because they are gigantic gas balls. ...
... The outer planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. These are the furthest planets from the sun and they have got many satellites. They are often called the gas giants, because they are gigantic gas balls. ...
galctr
... Fix the problem of slow migration by increasing mass: star cluster Fix the problem of tidal disruption before reaching center by high central density Fix the problem of core collapse/evaporation by putting a massive object in cluster • Massive object (103-104 M) could have formed by physical ...
... Fix the problem of slow migration by increasing mass: star cluster Fix the problem of tidal disruption before reaching center by high central density Fix the problem of core collapse/evaporation by putting a massive object in cluster • Massive object (103-104 M) could have formed by physical ...
The Structure of Our Solar System
... the sun was in the center and all the planets except for the moon orbited around it. He thought that the moon orbited around the Earth. No one believed him at the time because A) They didn’t think the Earth could be moving and people wouldn’t feel it. ...
... the sun was in the center and all the planets except for the moon orbited around it. He thought that the moon orbited around the Earth. No one believed him at the time because A) They didn’t think the Earth could be moving and people wouldn’t feel it. ...
15_LectureOutline
... Planets orbiting within 0.1 AU of their stars are called “hot Jupiters”; they are not included in the previous figure but are numerous. Stars with composition like our Sun are much more likely to have planets, showing that the “dusty disk” theory is plausible. Some of these “planets” may actually be ...
... Planets orbiting within 0.1 AU of their stars are called “hot Jupiters”; they are not included in the previous figure but are numerous. Stars with composition like our Sun are much more likely to have planets, showing that the “dusty disk” theory is plausible. Some of these “planets” may actually be ...
Astronomy Review - Cockeysville Middle
... because it travels so quickly, all light takes time to go any distance. Light travels at 3 x 108 m/s. To the right, are some light travel times. Even when I look at you, I see what was! The further away we look, the further back in time we see. ...
... because it travels so quickly, all light takes time to go any distance. Light travels at 3 x 108 m/s. To the right, are some light travel times. Even when I look at you, I see what was! The further away we look, the further back in time we see. ...
lecture9 Solar System1
... 3) Gravity-enhanced accretion: objects now have significant gravity => faster growth ...
... 3) Gravity-enhanced accretion: objects now have significant gravity => faster growth ...
ph709-08-3b - Centre for Astrophysics and Planetary Science
... there's too little solid material in the vicinity to build protoplanet's core of 10 ME (applies to r~1 AU as well). ...
... there's too little solid material in the vicinity to build protoplanet's core of 10 ME (applies to r~1 AU as well). ...
And let there be light!
... Ptolemy explained planet orbits and rotations. • The greatest difficulties he had to overcome were explaining the changing speeds and the occasional east-to-west, or retrograde, motion of the planets. He accomplished this by having each planet move along a small circle, called an epicycle, whose ce ...
... Ptolemy explained planet orbits and rotations. • The greatest difficulties he had to overcome were explaining the changing speeds and the occasional east-to-west, or retrograde, motion of the planets. He accomplished this by having each planet move along a small circle, called an epicycle, whose ce ...
Quiz CH 8 solution 1. An extrasolar planet is
... b. The amount of radioactive material is measured. Using this with the radioactive material’s half-life, the age c. The amount of decay material is measured. Using this with the radioactive material’s half-life, the age can b d. The amount of heat generated by radioactive dating is measured to deter ...
... b. The amount of radioactive material is measured. Using this with the radioactive material’s half-life, the age c. The amount of decay material is measured. Using this with the radioactive material’s half-life, the age can b d. The amount of heat generated by radioactive dating is measured to deter ...
public_lector_10
... The dark halo was built up from mergers of smaller sub-halos Saw spiral structure developing in the gas Merging of galaxies is still going on now ...
... The dark halo was built up from mergers of smaller sub-halos Saw spiral structure developing in the gas Merging of galaxies is still going on now ...
Methods Of Discovering Extra solar Planets.
... • The average temperature of this hot giants range from 1,700 to 1,200 degrees F. • The hot Jupiters can orbit the wrong way. What it means the star will be going one way while the planet goes the other way. • To make thing even weirder the jupiters rotation is in tide lock. • Tide lock means they d ...
... • The average temperature of this hot giants range from 1,700 to 1,200 degrees F. • The hot Jupiters can orbit the wrong way. What it means the star will be going one way while the planet goes the other way. • To make thing even weirder the jupiters rotation is in tide lock. • Tide lock means they d ...
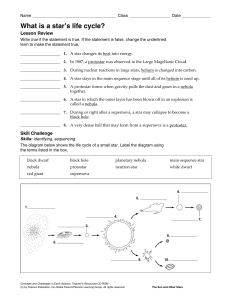
Stellar Evolution Lab
... Stage 1- Stars are born in clouds of gas and dust called Nebulas. Stage 2- The gas and dust spiral together and contract under their own gravity. The gas and dust will begin to heat up and start to glow forming Protostars. Stage 3- If a protostar contains enough matter, the central temperature will ...
... Stage 1- Stars are born in clouds of gas and dust called Nebulas. Stage 2- The gas and dust spiral together and contract under their own gravity. The gas and dust will begin to heat up and start to glow forming Protostars. Stage 3- If a protostar contains enough matter, the central temperature will ...