UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION Objective:
... The transmission of information-bearing signal over a band pass communication channel, such as telephone line or a satellite channel usually requires a shift of the range of frequencies contained in the signal to another frequency range suitable for transmission. A shift in the signal frequency rang ...
... The transmission of information-bearing signal over a band pass communication channel, such as telephone line or a satellite channel usually requires a shift of the range of frequencies contained in the signal to another frequency range suitable for transmission. A shift in the signal frequency rang ...
Nanocrystlline Oxide Semiconductor Materials for Future Semiconductor and Display Technology
... HIZO(200Å )-IZO Bi-layer IZO: 100Å IZO: 200Å IZO: 400Å IZO: 600Å HIZO:400Å Single Layer ...
... HIZO(200Å )-IZO Bi-layer IZO: 100Å IZO: 200Å IZO: 400Å IZO: 600Å HIZO:400Å Single Layer ...
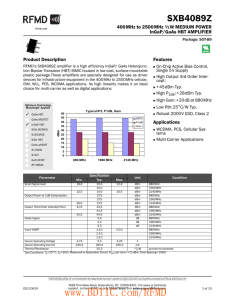
AD831 Low Distortion Mixer Data Sheet (REV. C)
... mixer for use in such applications as RF to IF downconversion in HF and VHF receivers, the second mixer in DMR base stations, direct-to-baseband conversion, quadrature modulation and demodulation, and doppler shift detection in ultrasound imaging applications. The mixer includes an LO driver and a l ...
... mixer for use in such applications as RF to IF downconversion in HF and VHF receivers, the second mixer in DMR base stations, direct-to-baseband conversion, quadrature modulation and demodulation, and doppler shift detection in ultrasound imaging applications. The mixer includes an LO driver and a l ...
Compact infrared continuous-wave double-pass single
... periods ranging from 29.75 to 30:75 μm with a 0:25 μm step. With a pump wavelength equal to 1:064 μm, this enables to cover the 3:2–3:8 μm spectral range for the idler wavelength, by choosing the poling period and the temperature. The nested cavity is based on the use of three mirrors M1, M2, and M3 ...
... periods ranging from 29.75 to 30:75 μm with a 0:25 μm step. With a pump wavelength equal to 1:064 μm, this enables to cover the 3:2–3:8 μm spectral range for the idler wavelength, by choosing the poling period and the temperature. The nested cavity is based on the use of three mirrors M1, M2, and M3 ...
Modulation Schemes for Single-Laser 100 Gb/s Links
... digital-to-analog and analog-to-digital converters (ADC and DAC) on system performance. We evaluate the performance based on required optical power for achieving a target bit-error ratio (BER) as a function of the modulator bandwidth. For optical powers near the ideal receiver sensitivity, the domin ...
... digital-to-analog and analog-to-digital converters (ADC and DAC) on system performance. We evaluate the performance based on required optical power for achieving a target bit-error ratio (BER) as a function of the modulator bandwidth. For optical powers near the ideal receiver sensitivity, the domin ...
3 Noise in Physical Systems
... 3.3 N O I S E M E C H A N I S M S Now that we’ve seen something about how to describe random systems we will turn to a quantitative discussion of some of the most important fundamental noise mechanisms: shot noise, Johnson noise, and 1/f noise. Chapter 14 will consider other practical sources of noi ...
... 3.3 N O I S E M E C H A N I S M S Now that we’ve seen something about how to describe random systems we will turn to a quantitative discussion of some of the most important fundamental noise mechanisms: shot noise, Johnson noise, and 1/f noise. Chapter 14 will consider other practical sources of noi ...
SG-2020 Transceiver
... The SGC factory test procedures as well as the test procedures detailed in the ARRL Handbook chapter 26 can be used to fully measure the performance of the radio. The following are simple tests which do not require laboratory test equipment and can be used to determine if the unit is generally opera ...
... The SGC factory test procedures as well as the test procedures detailed in the ARRL Handbook chapter 26 can be used to fully measure the performance of the radio. The following are simple tests which do not require laboratory test equipment and can be used to determine if the unit is generally opera ...
Noise-related resolution limit of dispersion measurements with white
... under identical conditions, even though this requires multiple Fourier transforms. Note that the averaging of original (wrapped) phases obtained from the FT leads to the strong artificial oscillations of D2 at the wrapping point. Averaging the unwrapped phase requires the phase noise 关兴 Ⰶ ; this ...
... under identical conditions, even though this requires multiple Fourier transforms. Note that the averaging of original (wrapped) phases obtained from the FT leads to the strong artificial oscillations of D2 at the wrapping point. Averaging the unwrapped phase requires the phase noise 关兴 Ⰶ ; this ...
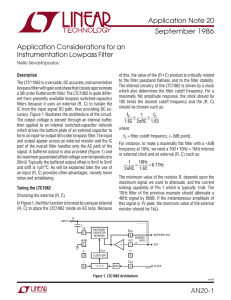
Application Considerations for an Instrumentation Lowpass Filter
... filters because it uses an external (R, C) to isolate the IC from the input signal DC path, thus providing DC accuracy. Figure 1 illustrates the architecture of the circuit. The output voltage is sensed through an internal buffer, then applied to an internal switched-capacitor network which drives th ...
... filters because it uses an external (R, C) to isolate the IC from the input signal DC path, thus providing DC accuracy. Figure 1 illustrates the architecture of the circuit. The output voltage is sensed through an internal buffer, then applied to an internal switched-capacitor network which drives th ...
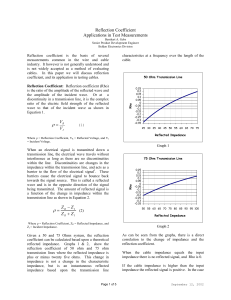
Reflection Coefficient Applications in Test Measurements
... of an open circuit the impedance is infinitely high and the reflected signal is equals the input signal and has the same polarity. Thus VR and VI are equal in magnitude and of the same polarity so the resultant Rho is 1. If the cable impedance is lower than the input impedance the reflected signal ...
... of an open circuit the impedance is infinitely high and the reflected signal is equals the input signal and has the same polarity. Thus VR and VI are equal in magnitude and of the same polarity so the resultant Rho is 1. If the cable impedance is lower than the input impedance the reflected signal ...
Montgomery self-imaging effect using computer
... were used. In [14], it is shown that – under suitable conditions – quasi-periodic and aperiodic ring pupils generate self-imaging wavefields. Here, a relationship to Bessel or ‘‘nondiffracting’’ beams [15] is of interest: each ring in the pupil is the source of a Bessel beam whose intensity distributi ...
... were used. In [14], it is shown that – under suitable conditions – quasi-periodic and aperiodic ring pupils generate self-imaging wavefields. Here, a relationship to Bessel or ‘‘nondiffracting’’ beams [15] is of interest: each ring in the pupil is the source of a Bessel beam whose intensity distributi ...
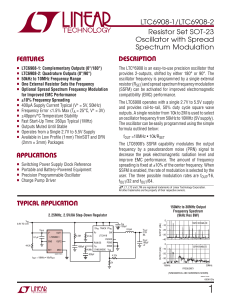
LTC6908-1/LTC6908-2 - Resistor Set SOT-23
... outputs. A single resistor from 10k to 2M is used to select an oscillator frequency from 50kHz to 10MHz (5V supply). The oscillator can be easily programmed using the simple formula outlined below: fOUT =10MHz • 10k/RSET The LTC6908’s SSFM capability modulates the output frequency by a pseudorandom ...
... outputs. A single resistor from 10k to 2M is used to select an oscillator frequency from 50kHz to 10MHz (5V supply). The oscillator can be easily programmed using the simple formula outlined below: fOUT =10MHz • 10k/RSET The LTC6908’s SSFM capability modulates the output frequency by a pseudorandom ...
Fundamental Noise and Fundamental Constants
... Given the white spectrum of Johnson and shot noise, one must take the frequency response of the measuring system into careful consideration whenever making measurements of this kind of noise. In this experiment, our task is greatly eased by the use of a sophisticated piece of gear— an FFT spectrum a ...
... Given the white spectrum of Johnson and shot noise, one must take the frequency response of the measuring system into careful consideration whenever making measurements of this kind of noise. In this experiment, our task is greatly eased by the use of a sophisticated piece of gear— an FFT spectrum a ...
Spectrum analyzer

A spectrum analyzer measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument. The primary use is to measure the power of the spectrum of known and unknown signals. The input signal that a spectrum analyzer measures is electrical, however, spectral compositions of other signals, such as acoustic pressure waves and optical light waves, can be considered through the use of an appropriate transducer. Optical spectrum analyzers also exist, which use direct optical techniques such as a monochromator to make measurements.By analyzing the spectra of electrical signals, dominant frequency, power, distortion, harmonics, bandwidth, and other spectral components of a signal can be observed that are not easily detectable in time domain waveforms. These parameters are useful in the characterization of electronic devices, such as wireless transmitters.The display of a spectrum analyzer has frequency on the horizontal axis and the amplitude displayed on the vertical axis. To the casual observer, a spectrum analyzer looks like an oscilloscope and, in fact, some lab instruments can function either as an oscilloscope or a spectrum analyzer.