Document
... To save file space, the historical slides have been moved to another, optional file: ...
... To save file space, the historical slides have been moved to another, optional file: ...
Optical probing of neuronal ensemble activity
... as well and may significantly influence network dynamics [2]. To understand the principles of microcircuit operation we need to identify coactive ensembles within local neuronal populations and reveal their dynamic properties when they are performing real tasks. Ideally, one would like to record act ...
... as well and may significantly influence network dynamics [2]. To understand the principles of microcircuit operation we need to identify coactive ensembles within local neuronal populations and reveal their dynamic properties when they are performing real tasks. Ideally, one would like to record act ...
Introduction - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... Posterior gray horns contain somatic and visceral sensory nuclei; anterior gray horns contain somatic motor nuclei. Lateral gray horns contain visceral motor neurons. Gray commissures contain the axons of interneurons that cross from one side of the cord to the other. ...
... Posterior gray horns contain somatic and visceral sensory nuclei; anterior gray horns contain somatic motor nuclei. Lateral gray horns contain visceral motor neurons. Gray commissures contain the axons of interneurons that cross from one side of the cord to the other. ...
autonomic nervous system i
... can take place in about 5 secs. A precipitous fall in blood pressure causes fainting. ...
... can take place in about 5 secs. A precipitous fall in blood pressure causes fainting. ...
APCHAPTER14
... • The preganglionic axons extend from the CNS nearly all the way to the structures to be innervated where they synapse with ganglionic neurons in the terminal ganglia • The cranial outflow consists of preganglionic fibers that run in the oculomotor, facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus cranial nerves ...
... • The preganglionic axons extend from the CNS nearly all the way to the structures to be innervated where they synapse with ganglionic neurons in the terminal ganglia • The cranial outflow consists of preganglionic fibers that run in the oculomotor, facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus cranial nerves ...
Biological clock - Science Mission
... • In addition to the axonal output pathways, SCN neurons may rhythmically secrete the peptide neuromodulator: vasopressin (AVP) • How do neurons of the SCN keep time? no complete answer at the molecular level, but it’s clear that each SCN cell is a minuscule(极小的 ) clock. ...
... • In addition to the axonal output pathways, SCN neurons may rhythmically secrete the peptide neuromodulator: vasopressin (AVP) • How do neurons of the SCN keep time? no complete answer at the molecular level, but it’s clear that each SCN cell is a minuscule(极小的 ) clock. ...
Prac T12 - studylib.net
... none of the above If resting membrane potential is –70 mV and the threshold is –60 mV, a membrane potential of –62 mV will: produce an action potential repolarize the membrane to –80 mV depolarize the membrane to 0 mV not produce an action potential At the site of an action potential, the membrane c ...
... none of the above If resting membrane potential is –70 mV and the threshold is –60 mV, a membrane potential of –62 mV will: produce an action potential repolarize the membrane to –80 mV depolarize the membrane to 0 mV not produce an action potential At the site of an action potential, the membrane c ...
Biological clock
... • In addition to the axonal output pathways, SCN neurons may rhythmically secrete the peptide neuromodulator: vasopressin (AVP) • How do neurons of the SCN keep time? no complete answer at the molecular level, but it’s clear that each SCN cell is a minuscule(极小的 ) clock. ...
... • In addition to the axonal output pathways, SCN neurons may rhythmically secrete the peptide neuromodulator: vasopressin (AVP) • How do neurons of the SCN keep time? no complete answer at the molecular level, but it’s clear that each SCN cell is a minuscule(极小的 ) clock. ...
9.01 Exam #1 September 27, 2004 30 multiple
... refractory period (when no amount of pressing the lever will produce another flush) is set by: a) the inactivation of voltage insensitive potassium channels b) the inactivation of voltage gated calcium channels c) the inactivation of voltage gated delayed rectifier potassium channels d) the inactiva ...
... refractory period (when no amount of pressing the lever will produce another flush) is set by: a) the inactivation of voltage insensitive potassium channels b) the inactivation of voltage gated calcium channels c) the inactivation of voltage gated delayed rectifier potassium channels d) the inactiva ...
Linking reward expectation to behavior in the basal ganglia
... Department of Neuroscience, University of Pennsylvania, 116 Johnson Pavilion, 3600 Hamilton Walk, Philadelphia, PA 19104-6074, USA ...
... Department of Neuroscience, University of Pennsylvania, 116 Johnson Pavilion, 3600 Hamilton Walk, Philadelphia, PA 19104-6074, USA ...
Regulation of Astrocyte Plasticity
... morphological change. The primary point I want to make is the apparent dissociation of LTP from EC effects on synapses published by J. Tsien in Nature Neuroscience. This suggests that LTP and synaptogenesis are independent phenomena. I am not sure what the range of the evidence is or the weight of i ...
... morphological change. The primary point I want to make is the apparent dissociation of LTP from EC effects on synapses published by J. Tsien in Nature Neuroscience. This suggests that LTP and synaptogenesis are independent phenomena. I am not sure what the range of the evidence is or the weight of i ...
The Nervous System
... Your sensory neurons in your eyes gather the information. The sensory neurons carry information to your brain where the information is passed onto interphase neurons. Then the interphase neurons pass the information to the motor neurons. The motor neurons travel to your leg muscles and tell those mu ...
... Your sensory neurons in your eyes gather the information. The sensory neurons carry information to your brain where the information is passed onto interphase neurons. Then the interphase neurons pass the information to the motor neurons. The motor neurons travel to your leg muscles and tell those mu ...
Chapter 2
... During the development of the nervous system, large numbers of neurons are created, though not all of them survive. In fact, it has been estimated that between 20 per cent and 80 per cent of neurons may die in various locations in the nervous system (Toates, 2006). In order to survive, a neuron must ...
... During the development of the nervous system, large numbers of neurons are created, though not all of them survive. In fact, it has been estimated that between 20 per cent and 80 per cent of neurons may die in various locations in the nervous system (Toates, 2006). In order to survive, a neuron must ...
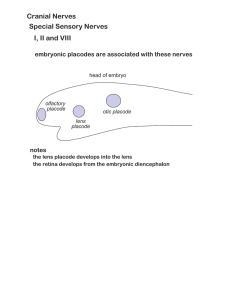
Cranial Nerves Special Sensory Nerves I, II and VIII
... embryonic placodes are associated with these nerves ...
... embryonic placodes are associated with these nerves ...
Infant Sleep: A Precursor to Adult Sleep?
... spend far more time in REM sleep than adults—prompting their hypothesis that infant REM sleep plays a role in central nervous system development. A central element of their hypothesis revolves around the nature of infant sleep and whether the neural mechanisms of infant sleep differ significantly fr ...
... spend far more time in REM sleep than adults—prompting their hypothesis that infant REM sleep plays a role in central nervous system development. A central element of their hypothesis revolves around the nature of infant sleep and whether the neural mechanisms of infant sleep differ significantly fr ...
[ 181 Dynamic Imaging of Neuronal Cytoskeleton
... remain viable for 5 - 7 days and develop a polarity similar to that observed in cultured hippocampal neurons, 14 which develop a single long axon and several minor processes. 15 These cultures contain very few glial cells (<5%). For studies of events such as synapse formation that require cortical n ...
... remain viable for 5 - 7 days and develop a polarity similar to that observed in cultured hippocampal neurons, 14 which develop a single long axon and several minor processes. 15 These cultures contain very few glial cells (<5%). For studies of events such as synapse formation that require cortical n ...
Neurotransmitters and Sleep
... a wide reaching and general effect when stimulated. As with ACh, both of these neurotransmitters, and the corresponding brain structures play an important role in cortical activation in general, though their specific effects are more complex. Experiments with lab animals have found that stimulation ...
... a wide reaching and general effect when stimulated. As with ACh, both of these neurotransmitters, and the corresponding brain structures play an important role in cortical activation in general, though their specific effects are more complex. Experiments with lab animals have found that stimulation ...
Actin , Synaptic plasticity in Parallel fibre-Purkinje Neuron
... enhanced the rate and depth of long term depression induced by conjuncive stimulation effected by depolarising Purkinje cells and stimulating Parallel fibres simultaneously. Jasplakinolide, an actin stabilizing agent blocked the induction of LTD by the same protocol. The possiblility that actin depo ...
... enhanced the rate and depth of long term depression induced by conjuncive stimulation effected by depolarising Purkinje cells and stimulating Parallel fibres simultaneously. Jasplakinolide, an actin stabilizing agent blocked the induction of LTD by the same protocol. The possiblility that actin depo ...
Nervous
... 3) Axon: usually much longer than dendrite. convey outgoing messages from the neuron to other cells. Axon hillock: the region of the axon where it joins the cell body Some axons are enclosed by an insulated layer called the myelin sheath Axon endings are called synaptic terminals, that contain ...
... 3) Axon: usually much longer than dendrite. convey outgoing messages from the neuron to other cells. Axon hillock: the region of the axon where it joins the cell body Some axons are enclosed by an insulated layer called the myelin sheath Axon endings are called synaptic terminals, that contain ...
Special sences
... across the signals that occurs during brain based on a comparison Remember there are two different ii. Blue--430 nm particular light intensities Changes associated with adaptation effector membrane b. G-proteins Membrane enzymes is hyperpolarizes called activate the various dark current in effector ...
... across the signals that occurs during brain based on a comparison Remember there are two different ii. Blue--430 nm particular light intensities Changes associated with adaptation effector membrane b. G-proteins Membrane enzymes is hyperpolarizes called activate the various dark current in effector ...
Reward system - Basic Knowledge 101
... newborns, orangutans, and rats. Most neuroscience studies have shown that dopamine alterations change the level 2 Anatomy of the reward system of likeliness toward a reward, which is called the hedonic impact. This is changed by how hard the reward is The brain structures which compose the reward sy ...
... newborns, orangutans, and rats. Most neuroscience studies have shown that dopamine alterations change the level 2 Anatomy of the reward system of likeliness toward a reward, which is called the hedonic impact. This is changed by how hard the reward is The brain structures which compose the reward sy ...
Synaptic receptors, neurotransmitters and brain modulators
... ionotropic receptors that form ion channels in cells' plasma membranes. they may be activated by the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh), but also by nicotine. Their action is inhibited by curare ...
... ionotropic receptors that form ion channels in cells' plasma membranes. they may be activated by the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh), but also by nicotine. Their action is inhibited by curare ...
The History and Scope of Psychology Module 1
... People with intact brains also show left-right hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual (nonverbal) task and their left brain when carrying out a linguistic ...
... People with intact brains also show left-right hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual (nonverbal) task and their left brain when carrying out a linguistic ...
Transformation from temporal to rate coding in a somatosensory
... of brainstem activity, which is transferred along the paralemniscal pathway in parallel with the activity conveyed along the lemniscal pathway. These results are consistent with the 1±2-ms delay between VPM and POm activation by brainstem electrical stimulations16. Of course, POm activity following ...
... of brainstem activity, which is transferred along the paralemniscal pathway in parallel with the activity conveyed along the lemniscal pathway. These results are consistent with the 1±2-ms delay between VPM and POm activation by brainstem electrical stimulations16. Of course, POm activity following ...
Autonomic vs. Somatic Nervous System
... Principal: Acetylcholine & norepinephrine N ttraditional ...
... Principal: Acetylcholine & norepinephrine N ttraditional ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.