General classification of peripheral nervous system
... (in contrast to those of the sensory-somatic system). It also differs from the sensory-somatic system is using two groups of motor neurons to stimulate the effectors instead of one. The first, the preganglionic neurons, arise in the CNS and run to a ganglion in the body. Here they synapse with postg ...
... (in contrast to those of the sensory-somatic system). It also differs from the sensory-somatic system is using two groups of motor neurons to stimulate the effectors instead of one. The first, the preganglionic neurons, arise in the CNS and run to a ganglion in the body. Here they synapse with postg ...
The Distribution and Morphological Characteristics of
... Serial 50-Ìm sections of the brains were made in coronal and sagittal planes. A one in five series of stains was made for Nissl, fibers [Gallyas, 1979], choline acetyltransferase (ChAT), tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and serotonin. The results of ChAT and serotonin immunohistochemistry are presented els ...
... Serial 50-Ìm sections of the brains were made in coronal and sagittal planes. A one in five series of stains was made for Nissl, fibers [Gallyas, 1979], choline acetyltransferase (ChAT), tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and serotonin. The results of ChAT and serotonin immunohistochemistry are presented els ...
File
... Motor programs require conscious directions from the frontal lobes. Movement is initiated when commands are received by the primary motor cortex from the motor association areas. The cerebellum is critically important in coordinating movements because it specifies the exact timing of control signals ...
... Motor programs require conscious directions from the frontal lobes. Movement is initiated when commands are received by the primary motor cortex from the motor association areas. The cerebellum is critically important in coordinating movements because it specifies the exact timing of control signals ...
6 BIO Neurotransmitters - Appoquinimink High School
... a neuron fires its message, there is a brief period of time before it can fire again. This is called a neuron’s refractory period. During the refractory period, excess neurotransmitters are reabsorbed by the sending neuron, called re-uptake, as well as the cell becoming polarized once again. ...
... a neuron fires its message, there is a brief period of time before it can fire again. This is called a neuron’s refractory period. During the refractory period, excess neurotransmitters are reabsorbed by the sending neuron, called re-uptake, as well as the cell becoming polarized once again. ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... --Activation of nicotinic receptors leads to depolarization & excitation of postganglionic neuron and skeletal muscles. --Activation of muscarinic receptors by Ach: may lead to depolarization & hyperpolarization depending on the presence of these receptors. --Effects of cholinergic fibers are brief ...
... --Activation of nicotinic receptors leads to depolarization & excitation of postganglionic neuron and skeletal muscles. --Activation of muscarinic receptors by Ach: may lead to depolarization & hyperpolarization depending on the presence of these receptors. --Effects of cholinergic fibers are brief ...
this worksheet - (canvas.brown.edu).
... On the left side of the screen is a group of skin cells. On the right side of the screen is a group of muscle fibers. In the middle are different types of neurons. One is a sensory neuron, one is a motorneuron, and there is also one each of an excitatory and inhibitory interneuron. Excitatory neurot ...
... On the left side of the screen is a group of skin cells. On the right side of the screen is a group of muscle fibers. In the middle are different types of neurons. One is a sensory neuron, one is a motorneuron, and there is also one each of an excitatory and inhibitory interneuron. Excitatory neurot ...
Bioinspired Computing Lecture 5
... Thus, we would expect to find very few ‘redundant’ neurons with co-varying outputs in that network. Accordingly, an optimal temporal coding circuit might tend to eliminate redundancy in the pattern of inputs to different neurons. On the other hand, if neural information is carried by a noisy rate-ba ...
... Thus, we would expect to find very few ‘redundant’ neurons with co-varying outputs in that network. Accordingly, an optimal temporal coding circuit might tend to eliminate redundancy in the pattern of inputs to different neurons. On the other hand, if neural information is carried by a noisy rate-ba ...
Neuro Quiz 4 – Notes from April 9 to April 16 First order neurons
... 77. T or F: Interneurons have many interconnections amongst themselves, but have little to do with the anterior motor neurons. 78. Most incoming signals are transmitted first through _______ , where they are appropriately processed. These neurons integrate all the incoming and outgoing information. ...
... 77. T or F: Interneurons have many interconnections amongst themselves, but have little to do with the anterior motor neurons. 78. Most incoming signals are transmitted first through _______ , where they are appropriately processed. These neurons integrate all the incoming and outgoing information. ...
The Nervous System - Solon City Schools
... • Includes the brain and the spinal cord • The main control center, controls your body’s actions • Brain- gets, interprets, and sends responses • Spinal Cord- bunch of nerve tissue - organized into segments for each muscle, organ, and function/job ...
... • Includes the brain and the spinal cord • The main control center, controls your body’s actions • Brain- gets, interprets, and sends responses • Spinal Cord- bunch of nerve tissue - organized into segments for each muscle, organ, and function/job ...
Lecture #13 – Animal Nervous Systems
... • Form the myelin sheath around axons • Cells are rectangular and tile-shaped, wrapped spirally around the axons • High lipid content insulates the axon – prevents electrical signals from escaping • Gaps between the cells (Nodes of Ranvier) speed up signal transmission ...
... • Form the myelin sheath around axons • Cells are rectangular and tile-shaped, wrapped spirally around the axons • High lipid content insulates the axon – prevents electrical signals from escaping • Gaps between the cells (Nodes of Ranvier) speed up signal transmission ...
Lecture #13 * Animal Nervous Systems
... • Form the myelin sheath around axons • Cells are rectangular and tile-shaped, wrapped spirally around the axons • High lipid content insulates the axon – prevents electrical signals from escaping • Gaps between the cells (Nodes of Ranvier) speed up signal transmission ...
... • Form the myelin sheath around axons • Cells are rectangular and tile-shaped, wrapped spirally around the axons • High lipid content insulates the axon – prevents electrical signals from escaping • Gaps between the cells (Nodes of Ranvier) speed up signal transmission ...
Neural Networks 2 - Monash University
... how such topology-preserving mappings might arise in neural networks It is probable that in biological systems that much of the organization of such maps is genetically determined, BUT: The brain is estimated to have ~1013 synapses (connections), so it would be impossible to produce this organiz ...
... how such topology-preserving mappings might arise in neural networks It is probable that in biological systems that much of the organization of such maps is genetically determined, BUT: The brain is estimated to have ~1013 synapses (connections), so it would be impossible to produce this organiz ...
A true science of consciousness explains
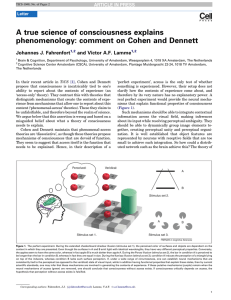
... generating the contents of experience, and therefore it has little power to explain phenomenology [10]. Now if it turns out that the neural mechanisms of perception established in our perfect experiment subside when their contents cannot be accessed- as when the green connections in Figure 1 are les ...
... generating the contents of experience, and therefore it has little power to explain phenomenology [10]. Now if it turns out that the neural mechanisms of perception established in our perfect experiment subside when their contents cannot be accessed- as when the green connections in Figure 1 are les ...
ABSTRACT BOOK CHAMPALIMAUD NEUROSCIENCE
... networks like those controlling eye movements, expression of emotions, respirations and locomotion. These networks are to a large degree conserved through a vertebrate phylum. The neural mechanisms underlying the control of goal directed locomotion will be in focus. The propulsive locomotor synergy ...
... networks like those controlling eye movements, expression of emotions, respirations and locomotion. These networks are to a large degree conserved through a vertebrate phylum. The neural mechanisms underlying the control of goal directed locomotion will be in focus. The propulsive locomotor synergy ...
What Are They Thinking? Understanding Your Child’s Brain
... •Synapses(connections) are created in the brain while the fetus is still in the womb. ...
... •Synapses(connections) are created in the brain while the fetus is still in the womb. ...
nervous system text b - powerpoint presentation
... A. Axons are myelinated by the activities of oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system and Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. B. Perhaps the most important reason for this is that myelination allows for higher velocities of nervous impulse or action potential conduction. C. Action ...
... A. Axons are myelinated by the activities of oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system and Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. B. Perhaps the most important reason for this is that myelination allows for higher velocities of nervous impulse or action potential conduction. C. Action ...
Impacts of Marijuana Use on Adolescents
... neurons in the brain. They are very abnormal in schizophrenia and other brain disorders. ...
... neurons in the brain. They are very abnormal in schizophrenia and other brain disorders. ...
neurons
... receives visual information from the visual area and recodes into auditory form • Damage to different language areas will result in differing forms of aphasia. • Main Point: The mind’s subsystems are localized in particular brain regions (specialization), yet the brain acts as a unified whole (integ ...
... receives visual information from the visual area and recodes into auditory form • Damage to different language areas will result in differing forms of aphasia. • Main Point: The mind’s subsystems are localized in particular brain regions (specialization), yet the brain acts as a unified whole (integ ...
Doktryna neuronu
... Sodium channels are dense at the node of Ranvier but sparse or absent in the internodal regions of the axon membrane. The K+ channels are located beneath the myelin sheath in internodal regions. There are about 700 000 sodium channels per node, i.e., 12,000 per um2 of nodal membrane. Internodal memb ...
... Sodium channels are dense at the node of Ranvier but sparse or absent in the internodal regions of the axon membrane. The K+ channels are located beneath the myelin sheath in internodal regions. There are about 700 000 sodium channels per node, i.e., 12,000 per um2 of nodal membrane. Internodal memb ...
Full Material(s)-Please Click here
... They were considered to be the passive bystanders of neural transmission. However, recent studies have shown this to be untrue. For example, astrocytes are crucial in clearance of neurotransmitter from within the synaptic cleft, which provides distinction between arrival of action potentials and pre ...
... They were considered to be the passive bystanders of neural transmission. However, recent studies have shown this to be untrue. For example, astrocytes are crucial in clearance of neurotransmitter from within the synaptic cleft, which provides distinction between arrival of action potentials and pre ...
Slide 1
... vasopressin (AVP) and oxytocin (OT). The vascular organ of the lamina terminalis (OVLT) is especially sensitive to hyperosmolality. Hyperosmolality also activates other neurons in the anterior hypothalamus, such as those in the subfornical organ (SFO) and median preoptic nucleus (MnPO), and magnocel ...
... vasopressin (AVP) and oxytocin (OT). The vascular organ of the lamina terminalis (OVLT) is especially sensitive to hyperosmolality. Hyperosmolality also activates other neurons in the anterior hypothalamus, such as those in the subfornical organ (SFO) and median preoptic nucleus (MnPO), and magnocel ...
So it is the number of action potentials per second
... inhibitory. Between a neuron and a muscle cell it is excitatory but the receptors on cardiac muscle cells generate an inhibitory responses to reduce strength of contraction and rate of heart beat. 2. Epinephrine and norepinephrine a) can be both excitatory or inhibitory 3. Dopamine a) lack of dopami ...
... inhibitory. Between a neuron and a muscle cell it is excitatory but the receptors on cardiac muscle cells generate an inhibitory responses to reduce strength of contraction and rate of heart beat. 2. Epinephrine and norepinephrine a) can be both excitatory or inhibitory 3. Dopamine a) lack of dopami ...
Chapter 14
... and composed primarily of muscle tissue. – Muscle tissues are classified into three types: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Collectively, muscle and bone tissues form the functional analog of the cytoskeleton in tissues. – Skeletal muscle cells are multinucleated, terminallydifferentiated cells ...
... and composed primarily of muscle tissue. – Muscle tissues are classified into three types: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Collectively, muscle and bone tissues form the functional analog of the cytoskeleton in tissues. – Skeletal muscle cells are multinucleated, terminallydifferentiated cells ...
INTRODUCTION - Faculty & Staff Webpages
... – The first autonomic neuron motor has its cell body in the CNS and its myelinated axon extends to an autonomic ganglion. • It may extend to the adrenal medullae rather than an autonomic ganglion ...
... – The first autonomic neuron motor has its cell body in the CNS and its myelinated axon extends to an autonomic ganglion. • It may extend to the adrenal medullae rather than an autonomic ganglion ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.