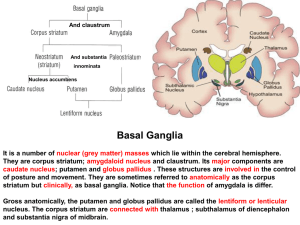
21. Basal ganglion
... Originates from the pars compacta of the ipsilateral substantia nigra of the midbrain tegmentum to caudate nucleus and putamen. The neurons of pars compacta contain the dark pigment neuromelanin. Their transmitter is the monoamine dopamine which has both excitatory and inhibitory effects upon striat ...
... Originates from the pars compacta of the ipsilateral substantia nigra of the midbrain tegmentum to caudate nucleus and putamen. The neurons of pars compacta contain the dark pigment neuromelanin. Their transmitter is the monoamine dopamine which has both excitatory and inhibitory effects upon striat ...
Cell Assembly Sequences Arising from Spike
... model was driven by temporally and spatially unstructured noise I(t); different instances of Figure 1. Time prediction from sequential neural activity in a memory task. A, Average raster over 18 s for a population of noise was thus the only difference between trisimultaneously recorded neurons durin ...
... model was driven by temporally and spatially unstructured noise I(t); different instances of Figure 1. Time prediction from sequential neural activity in a memory task. A, Average raster over 18 s for a population of noise was thus the only difference between trisimultaneously recorded neurons durin ...
Lecture 4 : Nervous System
... Unlike other body cells, neurons stop reproducing shortly after birth. Because of this, some parts of the brain have more neurons at birth than later in life because neurons die but are not replaced. While neurons do not reproduce, research has shown that new connections between neurons form through ...
... Unlike other body cells, neurons stop reproducing shortly after birth. Because of this, some parts of the brain have more neurons at birth than later in life because neurons die but are not replaced. While neurons do not reproduce, research has shown that new connections between neurons form through ...
Untitled
... membranes by zippering into a tight four-helix bundle between membranes. Most SM proteins interact directly with the Qa-SNARE or syntaxin, although different binding modes have been proposed. Upon phylogenetic analysis of the SM protein family, we came across a new member of the family, named Scfd2 ...
... membranes by zippering into a tight four-helix bundle between membranes. Most SM proteins interact directly with the Qa-SNARE or syntaxin, although different binding modes have been proposed. Upon phylogenetic analysis of the SM protein family, we came across a new member of the family, named Scfd2 ...
Regents Biology
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom more and gland ...
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom more and gland ...
Nervous System
... receptors information on the senses of balance, smell, sight, taste, and hearing. Cranial nerves also carry information from general sensory receptors in the body, mostly from the head region. This information is processed in the CNS; the resulting orders travel back through the cranial nerves to th ...
... receptors information on the senses of balance, smell, sight, taste, and hearing. Cranial nerves also carry information from general sensory receptors in the body, mostly from the head region. This information is processed in the CNS; the resulting orders travel back through the cranial nerves to th ...
Physiopathology – Motor prostheses
... Non-intuitive control requires concentration, has high rejection rate in practice Although more active joints than commercial alternatives, motion is still limited by under-actuation ...
... Non-intuitive control requires concentration, has high rejection rate in practice Although more active joints than commercial alternatives, motion is still limited by under-actuation ...
Estimating Fast Neural Input Using Anatomical and
... stimulation of a single postsynaptic neuron (Prakash et al., 2012). A small number of postsynaptic neurons can now be activated, and even decorrelated, in similar ways using light patterning methods (see references above). The sparse activation practically eliminates the problem of common source inp ...
... stimulation of a single postsynaptic neuron (Prakash et al., 2012). A small number of postsynaptic neurons can now be activated, and even decorrelated, in similar ways using light patterning methods (see references above). The sparse activation practically eliminates the problem of common source inp ...
Reading_Nervous_System
... transmit from special sensory receptors information on the senses of balance, smell, sight, taste, and hearing. Cranial nerves also carry information from general sensory receptors in the body, mostly from the head region. This information is processed in the CNS; the resulting orders travel back th ...
... transmit from special sensory receptors information on the senses of balance, smell, sight, taste, and hearing. Cranial nerves also carry information from general sensory receptors in the body, mostly from the head region. This information is processed in the CNS; the resulting orders travel back th ...
The Visual Perception System
... Bipolar cells are like ‘spark plugs’ once ignited by photoreceptors they trigger the firing of the ganglion cells. The axons the fibres that take neural impulses away from the cells of the ganglion cells, collect from all over the retina and converge to make a bundle of about one million fibres call ...
... Bipolar cells are like ‘spark plugs’ once ignited by photoreceptors they trigger the firing of the ganglion cells. The axons the fibres that take neural impulses away from the cells of the ganglion cells, collect from all over the retina and converge to make a bundle of about one million fibres call ...
Understanding Glial Differentiation in Vertebrate Nervous - J
... of Notch1 did not promote glial differentiation from cultured crest cells, based on the expression of P0 (Wakamatsu et al. 2000). In contrast, there is a report showing that a transient treatment of cultured crest-derived cells with a soluble form of Delta1 instructively promotes differentiation of ...
... of Notch1 did not promote glial differentiation from cultured crest cells, based on the expression of P0 (Wakamatsu et al. 2000). In contrast, there is a report showing that a transient treatment of cultured crest-derived cells with a soluble form of Delta1 instructively promotes differentiation of ...
An oscillation-based model for the neuronal basis
... We here present a model where the temporal tagging (Crick & Koch, 1990b) is implemented at the single cell level using an oscillatory signal in the 3&50 Hz range. We have also investigated to what extent temporal tagging can be achieved by synchronizing the firing rate of a group of neurons without ...
... We here present a model where the temporal tagging (Crick & Koch, 1990b) is implemented at the single cell level using an oscillatory signal in the 3&50 Hz range. We have also investigated to what extent temporal tagging can be achieved by synchronizing the firing rate of a group of neurons without ...
Class 10: Other Senses
... receptors are found in the back of the nasal cavity. ¢ Olfactory receptors are neurons. ¢ Olfactory receptor neurons have cilia suspended in a mucous fluid. ¢ Olfactory 7-TM receptors similar to NT metabotropic receptors. ...
... receptors are found in the back of the nasal cavity. ¢ Olfactory receptors are neurons. ¢ Olfactory receptor neurons have cilia suspended in a mucous fluid. ¢ Olfactory 7-TM receptors similar to NT metabotropic receptors. ...
Chapter 15 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... – alpha adrenergic receptors (often excitatory) – beta adrenergic receptors (often inhibitory) ...
... – alpha adrenergic receptors (often excitatory) – beta adrenergic receptors (often inhibitory) ...
Which Model to Use for the Liquid State Machine?
... work we perform a systematic analysis and comparison of LSM computational performance for various neuron models. The integrate-and-fire, resonate-and-fire, FitzHugh-Nagumo, Morris-Lecar, both versions of Hindmarsh-Rose and Izikevich’s neural models are examined and assessed. Beata J. Grzyb and Eris ...
... work we perform a systematic analysis and comparison of LSM computational performance for various neuron models. The integrate-and-fire, resonate-and-fire, FitzHugh-Nagumo, Morris-Lecar, both versions of Hindmarsh-Rose and Izikevich’s neural models are examined and assessed. Beata J. Grzyb and Eris ...
ppt - University of Connecticut
... but it should be considered that sometime tools and computational strategies that work for analyzing bulk-cell population RNA-seq data cannot successfully applied to study of gene expression at sing-cell level. So, we need to develop new tools for analyzing them. At this work, we look at application ...
... but it should be considered that sometime tools and computational strategies that work for analyzing bulk-cell population RNA-seq data cannot successfully applied to study of gene expression at sing-cell level. So, we need to develop new tools for analyzing them. At this work, we look at application ...
VISCERAL SENSORY NEURONS THAT INNERVATE BOTH
... mediate the response to putative nociceptive signals. They continue to respond to P2X3 and TRPV1 agonists, mimicking in vivo activation. ATP release from tissues during pathological conditions that cause tissue damage or inflammation activates P2X3 receptors on primary afferent fibers innervating th ...
... mediate the response to putative nociceptive signals. They continue to respond to P2X3 and TRPV1 agonists, mimicking in vivo activation. ATP release from tissues during pathological conditions that cause tissue damage or inflammation activates P2X3 receptors on primary afferent fibers innervating th ...
Granger causality analysis of state dependent functional connectivity
... cycles has not been well investigated. Furthermore, how changes in networks of neurons can be assessed is a research in network science itself. In this study, we simultaneously recorded jaw kinematics and spiking activity of neuronal ensemble in the orofacial area of MI and used the generalized line ...
... cycles has not been well investigated. Furthermore, how changes in networks of neurons can be assessed is a research in network science itself. In this study, we simultaneously recorded jaw kinematics and spiking activity of neuronal ensemble in the orofacial area of MI and used the generalized line ...
Synaptic Transmission
... potassium out instead of sodium in, which makes the neuron even more negative! ...
... potassium out instead of sodium in, which makes the neuron even more negative! ...
Efficient gene delivery to the adult and fetal CNS using
... DNA into sensitive areas of the host genome in large animals and humans.1–3 However, recent studies have also identified this risk using lentiviruses.4 Non-integrating lentiviruses (NILVs) have been developed by introducing class 1 mutations into the integrase gene, and may obviate some of these dif ...
... DNA into sensitive areas of the host genome in large animals and humans.1–3 However, recent studies have also identified this risk using lentiviruses.4 Non-integrating lentiviruses (NILVs) have been developed by introducing class 1 mutations into the integrase gene, and may obviate some of these dif ...
motor systems
... studies a foreign object. In area 7, some neurons increase their activity only when the monkey stretches the hand toward an object that it also looks at. In humans, lesions of the posterior parietal cortex may, for example, make them unable to open a door or to handle previously familiar tools. Such ...
... studies a foreign object. In area 7, some neurons increase their activity only when the monkey stretches the hand toward an object that it also looks at. In humans, lesions of the posterior parietal cortex may, for example, make them unable to open a door or to handle previously familiar tools. Such ...
Transcript
... lectures are exciting but they can't cover everything, so let me draw you attention to a website, one of our websites that helps supplement some of this. It's called www.biointeractive.org, biointeractive.org. if you go there you'll find streaming videos of all the Holiday Lectures and animations an ...
... lectures are exciting but they can't cover everything, so let me draw you attention to a website, one of our websites that helps supplement some of this. It's called www.biointeractive.org, biointeractive.org. if you go there you'll find streaming videos of all the Holiday Lectures and animations an ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.























