PDF
... How many adverbs are in this sentence: 'She ran quickly and quietly down the stairs, carefully avoiding the dog who was sleeping soundly at the bottom.' A ...
... How many adverbs are in this sentence: 'She ran quickly and quietly down the stairs, carefully avoiding the dog who was sleeping soundly at the bottom.' A ...
D.L.P. – Week Four Grade eight Day One – Skills Correction of a
... Another, anybody, anyone, anything, everybody, everyone, everything, much, nobody, no one, nothing, one, somebody, someone, and something are singular. That means these words would pair with an action verb that ends in an s or a linking verb like “is” or “was.” Both, few, many, and several are plura ...
... Another, anybody, anyone, anything, everybody, everyone, everything, much, nobody, no one, nothing, one, somebody, someone, and something are singular. That means these words would pair with an action verb that ends in an s or a linking verb like “is” or “was.” Both, few, many, and several are plura ...
Description of Editing Symbols
... pn ant error or lack of clarity in pronoun-antecedent agreement—be especially careful not to use indefinite demonstrative pronouns (this, that, they, their, it, its ) in place of the nouns and/or details necessary to maintain clarity vt error or awkwardness in verb tense ...
... pn ant error or lack of clarity in pronoun-antecedent agreement—be especially careful not to use indefinite demonstrative pronouns (this, that, they, their, it, its ) in place of the nouns and/or details necessary to maintain clarity vt error or awkwardness in verb tense ...
Grammar Terms and what they mean…
... Plural – means two or more things or people. Examples – tables, places, feelings Gender – in foreign languages nouns are divided up into feminine, masculine or neuter. We do have some nouns that are marked by gender in English. Examples - poet (male) poetess ( female), fiancé ( male) Fiancée (female ...
... Plural – means two or more things or people. Examples – tables, places, feelings Gender – in foreign languages nouns are divided up into feminine, masculine or neuter. We do have some nouns that are marked by gender in English. Examples - poet (male) poetess ( female), fiancé ( male) Fiancée (female ...
Correct Word Choice
... A and An. Use the article a before an initial h pronounced even slightly (a historian, a hypothesis, a horse). Use of an in such cases is considered affected or archaic in this country. Affect, effect. In common usage affect is always a verb. It is used as a noun only in fields like psychology and p ...
... A and An. Use the article a before an initial h pronounced even slightly (a historian, a hypothesis, a horse). Use of an in such cases is considered affected or archaic in this country. Affect, effect. In common usage affect is always a verb. It is used as a noun only in fields like psychology and p ...
Grammar rules and common mistakes File
... Three frequently used adjectives are irregular in their comparative and superlative forms. They are: ...
... Three frequently used adjectives are irregular in their comparative and superlative forms. They are: ...
Literacy glossary - Professional skills tests
... Luckily, all the children were happy with the arrangements - modifies a whole sentence. Adverbs are often (but not always) formed by adding the letters 'ly' to the end of an adjective. Adverbs of manner are used to describe the way in which something is done (slowly, noisily); adverbs of place descr ...
... Luckily, all the children were happy with the arrangements - modifies a whole sentence. Adverbs are often (but not always) formed by adding the letters 'ly' to the end of an adjective. Adverbs of manner are used to describe the way in which something is done (slowly, noisily); adverbs of place descr ...
Grammar for parents Part 1
... Root words are helpful because: You can use a root word to help you with other spellings. If you recognise the root of a word when you are reading it can help you to work out what the word is and what it means. There are spelling rules for adding suffixes and prefixes to root words. ...
... Root words are helpful because: You can use a root word to help you with other spellings. If you recognise the root of a word when you are reading it can help you to work out what the word is and what it means. There are spelling rules for adding suffixes and prefixes to root words. ...
to see more detailed instructions, along with the chart needed
... Another way to identify the part of speech of a word is to look at its placement in a sentence. For example, in English, we put adjectives before the nouns they describe. We say, “Look at the blue sky,” and we do NOT say, “Look at the sky blue.” If I wrote, “Look at the shmorkle sky,” you could gues ...
... Another way to identify the part of speech of a word is to look at its placement in a sentence. For example, in English, we put adjectives before the nouns they describe. We say, “Look at the blue sky,” and we do NOT say, “Look at the sky blue.” If I wrote, “Look at the shmorkle sky,” you could gues ...
04. English - Year 5 and 6 Spelling
... applicable/applicably (application), considerable/considerably (consideration), tolerable/tolerably (toleration) ...
... applicable/applicably (application), considerable/considerably (consideration), tolerable/tolerably (toleration) ...
Analyzing Word Parts
... part of speech of a word. For example, by adding different suffixes to the adjective short you can create shorten (verb), shortness (noun), and shortly (adverb). ...
... part of speech of a word. For example, by adding different suffixes to the adjective short you can create shorten (verb), shortness (noun), and shortly (adverb). ...
Every Child Matters – key aims
... words for vocab and pronouns for other words. • Ensure that you have positive and negative forms clear • Build out from there using your judgement, with the emphasis on structures rather than vocab. ...
... words for vocab and pronouns for other words. • Ensure that you have positive and negative forms clear • Build out from there using your judgement, with the emphasis on structures rather than vocab. ...
Diapositiva 1 - Roma Tre University
... Terms extracted from special language texts represent a limited number of parts of speech: nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, phraseological material are combined with general language connective material to produce subject-specific discourse. ...
... Terms extracted from special language texts represent a limited number of parts of speech: nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, phraseological material are combined with general language connective material to produce subject-specific discourse. ...
Key Stage 3 Framework for languages
... was thirsty/she wanted a drink). It usually contains a subject (she in the examples) and verb (drank/was/wanted). A clause differs from a phrase (see definition of 'phrase'). A sentence is made up of one or more clauses: It was raining. (one clause) It was raining and we were cold. (two main clauses ...
... was thirsty/she wanted a drink). It usually contains a subject (she in the examples) and verb (drank/was/wanted). A clause differs from a phrase (see definition of 'phrase'). A sentence is made up of one or more clauses: It was raining. (one clause) It was raining and we were cold. (two main clauses ...
Grammar Glossary for Parents Please find below a glossary of the
... A determiner is used to modify a noun. It indicates reference to something specific or something of a particular type. There are different types of determiners: articles (a, an, the), demonstratives (this, that, these and those), possessives (my, your, his, her, its, our, your, their, mine, his, her ...
... A determiner is used to modify a noun. It indicates reference to something specific or something of a particular type. There are different types of determiners: articles (a, an, the), demonstratives (this, that, these and those), possessives (my, your, his, her, its, our, your, their, mine, his, her ...
English Year 6 - Tewkesbury C of E Primary
... develop their understanding of the concepts set out in English Appendix 2 by: recognising vocabulary and structures that are appropriate for formal speech and writing, including subjunctive forms using passive verbs to affect the presentation of information in a sentence using the perfect form of ve ...
... develop their understanding of the concepts set out in English Appendix 2 by: recognising vocabulary and structures that are appropriate for formal speech and writing, including subjunctive forms using passive verbs to affect the presentation of information in a sentence using the perfect form of ve ...
English – Year 6 – Tracker - Statutory Age Expected Requirement
... develop their understanding of the concepts set out in English Appendix 2 by: recognising vocabulary and structures that are appropriate for formal speech and writing, including subjunctive forms using passive verbs to affect the presentation of information in a sentence using the perfect form of ve ...
... develop their understanding of the concepts set out in English Appendix 2 by: recognising vocabulary and structures that are appropriate for formal speech and writing, including subjunctive forms using passive verbs to affect the presentation of information in a sentence using the perfect form of ve ...
LITERARY TERMS 1. onomatopoeia: The use of words whose
... 12. idiom: when the phrase is not taken literally (We were just shooting the breeze – meaning not talking about anything important) 13. symbol: when something stands for something else. (The pearl represents avarice or greed in THE PEARL) 14. flashback: interruption in the present action to show wha ...
... 12. idiom: when the phrase is not taken literally (We were just shooting the breeze – meaning not talking about anything important) 13. symbol: when something stands for something else. (The pearl represents avarice or greed in THE PEARL) 14. flashback: interruption in the present action to show wha ...
Literacy overview y56
... degrees of possibility using adverbs [for example, perhaps, surely] or modal verbs [for example, might, should, will, must] Year 6: Use of the passive to affect the presentation of information in a sentence [for example, I broke the window in the greenhouse versus The window in the greenhouse was br ...
... degrees of possibility using adverbs [for example, perhaps, surely] or modal verbs [for example, might, should, will, must] Year 6: Use of the passive to affect the presentation of information in a sentence [for example, I broke the window in the greenhouse versus The window in the greenhouse was br ...
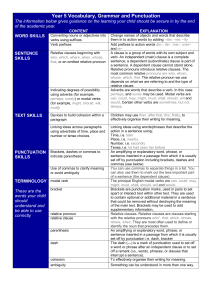
Year 5 Vocabulary Grammar and Punctuation
... Tense, i.e. he had seen her before An amplifying or explanatory word, phrase, or sentence inserted in a passage from which it is usually set off by punctuation including brackets, dashes and commas (see below) You can use commas to separate things in a list. You can also use them to mark out the les ...
... Tense, i.e. he had seen her before An amplifying or explanatory word, phrase, or sentence inserted in a passage from which it is usually set off by punctuation including brackets, dashes and commas (see below) You can use commas to separate things in a list. You can also use them to mark out the les ...
GRAMMAR SKILLS QUESTIONNAIRE
... only his most recent thought. She might have the best memory in the world. He could very well have the worst. “My memory flows like a movie—nonstop and uncontrollable,” says AJ. She remembers that on Sunday, August 3, 1986, a young man called her on the phone. She remembers what happened on Murphy B ...
... only his most recent thought. She might have the best memory in the world. He could very well have the worst. “My memory flows like a movie—nonstop and uncontrollable,” says AJ. She remembers that on Sunday, August 3, 1986, a young man called her on the phone. She remembers what happened on Murphy B ...
Day 5 presentation
... So Maria played in the outfield. Jed pitched, like he always does. He struck out several players. No one minded because Jed let everyone play ball. ...
... So Maria played in the outfield. Jed pitched, like he always does. He struck out several players. No one minded because Jed let everyone play ball. ...
All our dreams can come true – if we have the courage to pursue them.
... phrase that the preposition is showing the relationship between another part of a sentence. KEY Preposition – red word Prepositional phrase – underlined Object of the preposition - green word ...
... phrase that the preposition is showing the relationship between another part of a sentence. KEY Preposition – red word Prepositional phrase – underlined Object of the preposition - green word ...