Introduction - Katedra anglického jazyka
... a) lexical (content) morphemes – nouns, adjectives, verbs which we think of as words which carry the “content” of messages we convey b) functional morphemes – this set consists largely of the functional words in the language such as conjunctions, prepositions, articles and pronouns. They signal gram ...
... a) lexical (content) morphemes – nouns, adjectives, verbs which we think of as words which carry the “content” of messages we convey b) functional morphemes – this set consists largely of the functional words in the language such as conjunctions, prepositions, articles and pronouns. They signal gram ...
Ling200 Jan. 3, 2001
... – The two “p sounds” are not really the same sounds. – [p] with an extra puff of air occurs at the beginning of a word (roughly) – [p] without a puff of air occurs elsewhere – So their occurrences in English are rulegoverned. ...
... – The two “p sounds” are not really the same sounds. – [p] with an extra puff of air occurs at the beginning of a word (roughly) – [p] without a puff of air occurs elsewhere – So their occurrences in English are rulegoverned. ...
Overview Computational Linguistics I: Introduction and Machine Translation What is it?
... • We can treat each sentence as a bag of words = unordered collection of words. What does is align with? ⇒ In cases like this, a word can be mapped to a “null” element in the other ...
... • We can treat each sentence as a bag of words = unordered collection of words. What does is align with? ⇒ In cases like this, a word can be mapped to a “null” element in the other ...
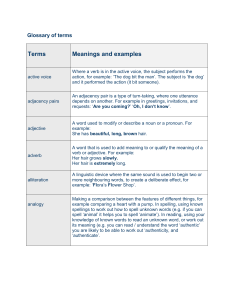
Grammar Terms - Duxbury Public Schools
... Adverb A word that modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. An adverb tells how, when, where, why, how often, or how much. Adverbs can be cataloged in four basic ways: time, place, manner, and degree. See Adjective, Noun, Verb, Adverbial phrase Adverbial phrase A phrase that modifies a verb ...
... Adverb A word that modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. An adverb tells how, when, where, why, how often, or how much. Adverbs can be cataloged in four basic ways: time, place, manner, and degree. See Adjective, Noun, Verb, Adverbial phrase Adverbial phrase A phrase that modifies a verb ...
Tennessee Academic Vocabulary – 4th grade
... omnipresence for a greater intimacy with one character. It allows the reader to see what the focus character is thinking 3rd person limited – s style of narrator is similar to the first person narrator, except for the notable use of the third person pronouns, he, she and it. The character is not the ...
... omnipresence for a greater intimacy with one character. It allows the reader to see what the focus character is thinking 3rd person limited – s style of narrator is similar to the first person narrator, except for the notable use of the third person pronouns, he, she and it. The character is not the ...
12.1 phrases and clauses
... Grammar is a complex – as you know – and controversial area of language study! Prescriptive approach/attitude = tends to see other varieties of language other than ‘standard’ English as incorrect or bad and is highly critical to uses of language that ‘deviates’ from established grammatical rules. De ...
... Grammar is a complex – as you know – and controversial area of language study! Prescriptive approach/attitude = tends to see other varieties of language other than ‘standard’ English as incorrect or bad and is highly critical to uses of language that ‘deviates’ from established grammatical rules. De ...
ppt
... • Some general properties associated with inflection, generalizations which hold for the most part: – Inflection does not change syntactic categories. E.g. kick-s is still a verb, even with its inflectional suffix – Inflection expresses grammatically required features or ...
... • Some general properties associated with inflection, generalizations which hold for the most part: – Inflection does not change syntactic categories. E.g. kick-s is still a verb, even with its inflectional suffix – Inflection expresses grammatically required features or ...
Ling 001, Week 4
... • Some general properties associated with inflection, generalizations which hold for the most part: – Inflection does not change syntactic categories. E.g. kick-s is still a verb, even with its inflectional suffix – Inflection expresses grammatically required features or ...
... • Some general properties associated with inflection, generalizations which hold for the most part: – Inflection does not change syntactic categories. E.g. kick-s is still a verb, even with its inflectional suffix – Inflection expresses grammatically required features or ...
Lady Bankes Infant and Nursery School
... do not end in -ly. Note too that some -ly words are adjectives, not adverbs (eg lovely, silly, friendly). In many cases, adverbs tell us: how (manner) slowly, happily, dangerously, carefully where (place) here, there, away, home, outside when (time) now, yesterday, later, soon how often (frequency) ...
... do not end in -ly. Note too that some -ly words are adjectives, not adverbs (eg lovely, silly, friendly). In many cases, adverbs tell us: how (manner) slowly, happily, dangerously, carefully where (place) here, there, away, home, outside when (time) now, yesterday, later, soon how often (frequency) ...
Document
... Eliminate clutter in language by eliminating needless words and redundancies. For example: we don’t need to say “each and every” or “free gift” or “surrounded on all sides” or “past history” and so forth. Any excessively wordy phrase only serves to bog down the idea and frustrate the audience. ...
... Eliminate clutter in language by eliminating needless words and redundancies. For example: we don’t need to say “each and every” or “free gift” or “surrounded on all sides” or “past history” and so forth. Any excessively wordy phrase only serves to bog down the idea and frustrate the audience. ...
Example - WordPress.com
... of the sentence Examples: O A word processor is, in my opinion, all I need for my work. O A computer, on the other hand, has many more uses. O To mark off words like ‘therefore’ ‘however’ ‘consequently’ ‘unfortunately’ at the beginning or in the middle of sentence. Examples: O Unfortunately, I have ...
... of the sentence Examples: O A word processor is, in my opinion, all I need for my work. O A computer, on the other hand, has many more uses. O To mark off words like ‘therefore’ ‘however’ ‘consequently’ ‘unfortunately’ at the beginning or in the middle of sentence. Examples: O Unfortunately, I have ...
Commonly Made French Mistakes
... • If a direct object comes before the subject, the verb must ALWAYS agree with the direct object. NOT the subject. ...
... • If a direct object comes before the subject, the verb must ALWAYS agree with the direct object. NOT the subject. ...
PSSA English Language Arts Glossary Grade 4
... idiom - An expression that is peculiar to itself grammatically and cannot be understood from the individual meanings of its elements (e.g., raining cats and dogs). illustration - To clarify by using examples. inference - A judgment based on reasoning rather than on a direct or explicit statement. A ...
... idiom - An expression that is peculiar to itself grammatically and cannot be understood from the individual meanings of its elements (e.g., raining cats and dogs). illustration - To clarify by using examples. inference - A judgment based on reasoning rather than on a direct or explicit statement. A ...
Parts of Speech - cloudfront.net
... Compound - made up of two or more words; it may be written as one word (baseball), separate words (parking lot), or as a hyphenated word (runner-up) Collective - refers to a group of people of things (audience, crowd) ...
... Compound - made up of two or more words; it may be written as one word (baseball), separate words (parking lot), or as a hyphenated word (runner-up) Collective - refers to a group of people of things (audience, crowd) ...
Year 6 Vocabulary, Grammar and Punctuation
... Use of the passive to affect the presentation of information in a sentence [for example, I broke the window in the greenhouse versus The window in the greenhouse was broken (by me)]. The difference between structures typical of informal speech and structures appropriate for formal speech and writing ...
... Use of the passive to affect the presentation of information in a sentence [for example, I broke the window in the greenhouse versus The window in the greenhouse was broken (by me)]. The difference between structures typical of informal speech and structures appropriate for formal speech and writing ...
Grammar Mechanics, Style, and the Rules of Language
... • Words that sound the same but mean different things and are used in different circumstances are often spelled differently- big problem for non-readers or phonetic language learning. • Problems with contractions & usage. ...
... • Words that sound the same but mean different things and are used in different circumstances are often spelled differently- big problem for non-readers or phonetic language learning. • Problems with contractions & usage. ...
Rhetorical Devices Definitions
... Assonance: The repetition o identical or similar vowel sounds in the syllables of neighboring words. Consonance: The repetition of identical or similar consonants in neighboring words whose vowel sounds are usually different. Allusion: An indirect or passing reference to some event, person, place, o ...
... Assonance: The repetition o identical or similar vowel sounds in the syllables of neighboring words. Consonance: The repetition of identical or similar consonants in neighboring words whose vowel sounds are usually different. Allusion: An indirect or passing reference to some event, person, place, o ...
Six Common Problems in an Sentence
... Run a spell check. Remember to check for commonly confused words that computer spell-checkers miss (it/it's, their/there, etc.). Also, keep in mind that computers often don't "know" technical terms and recently invented words, so you'll have to check those yourself. ...
... Run a spell check. Remember to check for commonly confused words that computer spell-checkers miss (it/it's, their/there, etc.). Also, keep in mind that computers often don't "know" technical terms and recently invented words, so you'll have to check those yourself. ...
formato Word
... arguments to nonterminal symbols: you can use the additional information in the parameters to associate meanings with strings and to achieve contextsensitivity. The context-sensitive grammars are grammars that take the word's context into account (not the sentence's context - this would lead to disc ...
... arguments to nonterminal symbols: you can use the additional information in the parameters to associate meanings with strings and to achieve contextsensitivity. The context-sensitive grammars are grammars that take the word's context into account (not the sentence's context - this would lead to disc ...
here - Teaching and Training Pathways
... A group of words, consisting of a subject and, usually, a verb. It does not necessarily constitute a sentence. The way the text hangs together or flows. It is connected with the overall effect of the text. For example, in a CV a sentence about hobbies in the middle of a paragraph explaining previous ...
... A group of words, consisting of a subject and, usually, a verb. It does not necessarily constitute a sentence. The way the text hangs together or flows. It is connected with the overall effect of the text. For example, in a CV a sentence about hobbies in the middle of a paragraph explaining previous ...
into the house - Dipartimento di Lingue, Letterature e Culture Straniere
... stative – states of being or processes in which there is no obvious action o Cf. I’m seeing the doctor at ten o’clock. // I see what you mean. lexical – express meaning in the verb phrase and can function only as the main verb o auxiliary – used to construct different timescales, questions and n ...
... stative – states of being or processes in which there is no obvious action o Cf. I’m seeing the doctor at ten o’clock. // I see what you mean. lexical – express meaning in the verb phrase and can function only as the main verb o auxiliary – used to construct different timescales, questions and n ...
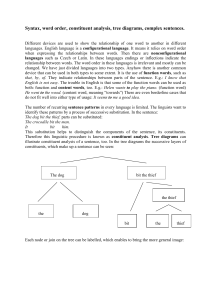
Syntax, word order, constituent analysis, tree diagrams
... languages. English language is a configurational language. It means it relies on word order when expressing the relationships between words. Then there are nonconfigurational languages such as Czech or Latin. In these languages endings or inflections indicate the relationship between words. The word ...
... languages. English language is a configurational language. It means it relies on word order when expressing the relationships between words. Then there are nonconfigurational languages such as Czech or Latin. In these languages endings or inflections indicate the relationship between words. The word ...
THE “IMPERSONAL SE” Pattern: The word se can be used to
... Pattern: The word se can be used to express an impersonal, non-specific instance of a verb. Basics of the “impersonal se” The common phrase se habla español does NOT mean “Spanish speaks itself.” It looks like a reflexive verb phrase, but in cases like this, se expresses a different feeling. Its mea ...
... Pattern: The word se can be used to express an impersonal, non-specific instance of a verb. Basics of the “impersonal se” The common phrase se habla español does NOT mean “Spanish speaks itself.” It looks like a reflexive verb phrase, but in cases like this, se expresses a different feeling. Its mea ...
Rhetoric: The Art of Persuasion
... Repetition of the same word or words at the beginning or successive phrases, clauses, or sentences, commonly in conjunction with climax and with parallelism Often used in conjunction with rhetorical questions ...
... Repetition of the same word or words at the beginning or successive phrases, clauses, or sentences, commonly in conjunction with climax and with parallelism Often used in conjunction with rhetorical questions ...