
Insertion of SO2 into the Metal−Carbon Bonds of Rhodium and
... also investigated previously. In the case of Mn compounds, this has been accomplished by oxidative demetalation.6 The SO2-inserted species was reacted with H2O2, leading to the formation of MnO2 and a mixture of sulfinate and sulfonate products. The breaking of the metal-sulfur bond can also be indu ...
... also investigated previously. In the case of Mn compounds, this has been accomplished by oxidative demetalation.6 The SO2-inserted species was reacted with H2O2, leading to the formation of MnO2 and a mixture of sulfinate and sulfonate products. The breaking of the metal-sulfur bond can also be indu ...
Molybdenum-Pterin Chemistry. 3. Use of X
... supported by spectroscopic and microanalytical data. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS). This method allows the determination of the oxidation state of a metal ion provided the compound is reasonably stable and standard compounds are available. The energy scale of the spectra can be shifted due ...
... supported by spectroscopic and microanalytical data. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS). This method allows the determination of the oxidation state of a metal ion provided the compound is reasonably stable and standard compounds are available. The energy scale of the spectra can be shifted due ...
+ H 2
... Net Ionic Equation (NIE) • Cross out Spectator Ions (no change) (same state) (same charge) • only species left are those that react (change) during the course of the reaction. ...
... Net Ionic Equation (NIE) • Cross out Spectator Ions (no change) (same state) (same charge) • only species left are those that react (change) during the course of the reaction. ...
Precipitation Reactions
... • The driving force of all reactions is related to energy • The driving force is not “make everything achieve its lowest possible energy,” although that often happens • The driving force is not “increase the entropy of the system,” although that often happens. • We use a bookkeeping technique called ...
... • The driving force of all reactions is related to energy • The driving force is not “make everything achieve its lowest possible energy,” although that often happens • The driving force is not “increase the entropy of the system,” although that often happens. • We use a bookkeeping technique called ...
this PDF file - Journal of the Indian Institute of Science
... compounds which otherwise require many cumbersome steps, as shall be shown later. In this paper, the mechanism of vinylidene reamngement, a few preparative methods, thc structure and several reactions of the vinylidene complexes will be discusqed. For the sake of brevity, we restrict ourselves to th ...
... compounds which otherwise require many cumbersome steps, as shall be shown later. In this paper, the mechanism of vinylidene reamngement, a few preparative methods, thc structure and several reactions of the vinylidene complexes will be discusqed. For the sake of brevity, we restrict ourselves to th ...
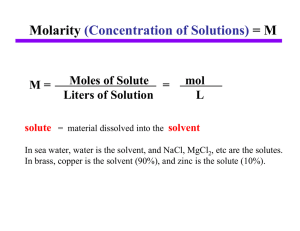
Molarity = M (Concentration of Solutions)
... Gas Law Stoichiometry - I - NH3 + HCl Problem: A slide separating two containers is removed, and the gases are allowed to mix and react. The first container with a volume of 2.79 L contains Ammonia gas at a pressure of 0.776 atm and a temperature of 18.7 oC. The second with a volume of 1.16 L conta ...
... Gas Law Stoichiometry - I - NH3 + HCl Problem: A slide separating two containers is removed, and the gases are allowed to mix and react. The first container with a volume of 2.79 L contains Ammonia gas at a pressure of 0.776 atm and a temperature of 18.7 oC. The second with a volume of 1.16 L conta ...
Entropy
... • Standard free energy of formation (Gof) is change in free energy that accompanies the formation of 1 mol of that substance from reactants and products in their standard state Gof • The standard free energy of formation for any element in its standard state is 0, (see table on p.A19) • Use the fo ...
... • Standard free energy of formation (Gof) is change in free energy that accompanies the formation of 1 mol of that substance from reactants and products in their standard state Gof • The standard free energy of formation for any element in its standard state is 0, (see table on p.A19) • Use the fo ...
Physical chemistry advanced laboratory course
... In this work, the solubility curve at temperatures between 313–273 K and the differential heat of solution at T = 298 K are determined for succinic acid in water. For a succesful experiment it is important that the system is in dynamic equilibrium at all temperatures, so that the solution is saturat ...
... In this work, the solubility curve at temperatures between 313–273 K and the differential heat of solution at T = 298 K are determined for succinic acid in water. For a succesful experiment it is important that the system is in dynamic equilibrium at all temperatures, so that the solution is saturat ...
Final exam questions for Chemical Engineer BSc
... constant and its relation to the standard reaction Gibbs energy. Definition of Kp, Kx and Kc, their relationships. Determining equilibrium constant from thermochemical data. 13. The response of equilibria to conditions: Le Chatalier’s principle. The response of equilibria to pressure, temperature an ...
... constant and its relation to the standard reaction Gibbs energy. Definition of Kp, Kx and Kc, their relationships. Determining equilibrium constant from thermochemical data. 13. The response of equilibria to conditions: Le Chatalier’s principle. The response of equilibria to pressure, temperature an ...
Kémiai technológia I
... constant and its relation to the standard reaction Gibbs energy. Definition of Kp, Kx and Kc, their relationships. Determining equilibrium constant from thermochemical data. 13. The response of equilibria to conditions: Le Chatalier’s principle. The response of equilibria to pressure, temperature an ...
... constant and its relation to the standard reaction Gibbs energy. Definition of Kp, Kx and Kc, their relationships. Determining equilibrium constant from thermochemical data. 13. The response of equilibria to conditions: Le Chatalier’s principle. The response of equilibria to pressure, temperature an ...
CHAPTER 23 THE TRANSITION ELEMENTS AND THEIR
... a) The cation is tetramminezinc ion. The tetraammine indicate four NH3 ligands. Zinc has an oxidation state of +2, so the charge on the cation is +2. The anion is SO42-. Only one sulfate is needed to make a neutral salt. The formula of the compound is [Zn(NH3)4]SO4. b) The cation is pentaamminechlor ...
... a) The cation is tetramminezinc ion. The tetraammine indicate four NH3 ligands. Zinc has an oxidation state of +2, so the charge on the cation is +2. The anion is SO42-. Only one sulfate is needed to make a neutral salt. The formula of the compound is [Zn(NH3)4]SO4. b) The cation is pentaamminechlor ...
materials: metals and non—metals
... Zinc with dilute sulphuric acid is often used for the laboratory preparation of hydrogen. The reaction is slow at room temperature, but its rate can be increased by the addition of a little copper (II) sulphate. Zinc displaces copper metal, which acts as a catalyst. In general, ...
... Zinc with dilute sulphuric acid is often used for the laboratory preparation of hydrogen. The reaction is slow at room temperature, but its rate can be increased by the addition of a little copper (II) sulphate. Zinc displaces copper metal, which acts as a catalyst. In general, ...
Department of Chemistry, IIT-Delhi CY110N Tutorial
... 17. Calculate the maximum work and the maximum non-expansion work that can be obtained from the freezing of supercooled water at −5 o C and 1.0 atm. The densities of water and ice are 0.999 and 0.917 g cm−3 , respectively at −5 o C. 18. One mole of He is heated from 200 o C to 400 o C at a constant ...
... 17. Calculate the maximum work and the maximum non-expansion work that can be obtained from the freezing of supercooled water at −5 o C and 1.0 atm. The densities of water and ice are 0.999 and 0.917 g cm−3 , respectively at −5 o C. 18. One mole of He is heated from 200 o C to 400 o C at a constant ...
Absolute Electronegativity and Hardness: Application to Inorganic
... Results for Cations It is necessary to show that (I- A ) indeed does correlate with earlier assignments of hardness and softness for various systems. At the same time ( I A ) must correlate with behavior as Lewis acids or bases. Large values of x characterize Lewis acids, and small values apply to b ...
... Results for Cations It is necessary to show that (I- A ) indeed does correlate with earlier assignments of hardness and softness for various systems. At the same time ( I A ) must correlate with behavior as Lewis acids or bases. Large values of x characterize Lewis acids, and small values apply to b ...
Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry Hybrid Orbitals Hybridization
... 6-coordinated complex ions These are complex ions in which the central metal ion is forming six bonds. In the simple cases we are talking about, that means that it will be attached to six ligands. These ions have an octahedral shape. Four of the ligands are in one plane, with the fifth one above the ...
... 6-coordinated complex ions These are complex ions in which the central metal ion is forming six bonds. In the simple cases we are talking about, that means that it will be attached to six ligands. These ions have an octahedral shape. Four of the ligands are in one plane, with the fifth one above the ...
Side-on binding of p-sulphonatocalix[4]arene to the
... 03. The structures of free s-CX[4] and di-Pt were minimised individually before they were manually docked together in the sideon model of binding and then energy minimised together. The 2+ charge of di-Pt and the addition of two sodium cations maintains the bowl-like shape of s-CX[4] (Fig. 5). On bi ...
... 03. The structures of free s-CX[4] and di-Pt were minimised individually before they were manually docked together in the sideon model of binding and then energy minimised together. The 2+ charge of di-Pt and the addition of two sodium cations maintains the bowl-like shape of s-CX[4] (Fig. 5). On bi ...





















![Side-on binding of p-sulphonatocalix[4]arene to the](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007757151_1-b9f6314a49efc7cd3b627b958f629ca7-300x300.png)
