Chapter 4 - profpaz.com
... Many ionic solids dissolve in water and are called soluble salts. However, some ionic solids do not dissolve in water and do not form ions in solution. These salts are called insoluble salts and remain solid in solution. ...
... Many ionic solids dissolve in water and are called soluble salts. However, some ionic solids do not dissolve in water and do not form ions in solution. These salts are called insoluble salts and remain solid in solution. ...
Press here to hemy 102 lab manual
... determine the number of valence electrons on each atom. For an anion, add an electron to the total for each negative charge. For a cation, subtract an electron for each positive charge. 2- Write the symbols for the atoms to show which atoms are attached to which, and connect them with a single bond ...
... determine the number of valence electrons on each atom. For an anion, add an electron to the total for each negative charge. For a cation, subtract an electron for each positive charge. 2- Write the symbols for the atoms to show which atoms are attached to which, and connect them with a single bond ...
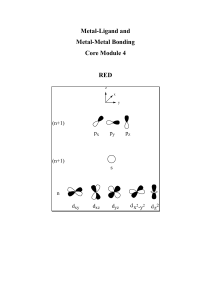
Introduction to Coordination Chemistry
... The chemistry of coordination compounds comprises an area of chemistry that spans the entire spectrum from theoretical work on bonding to the synthesis of organometallic compounds. The essential feature of coordination compounds is that they involve coordinate bonds between Lewis acids and bases. Me ...
... The chemistry of coordination compounds comprises an area of chemistry that spans the entire spectrum from theoretical work on bonding to the synthesis of organometallic compounds. The essential feature of coordination compounds is that they involve coordinate bonds between Lewis acids and bases. Me ...
Learn more - Cube Biotech
... trivalent ligand (coordination number 3), IDA exhibits higher leaching of metal ions, particularly in the equilibration and wash steps(1). Elution fractions from NTA-based resins also contain leached metal ions, but substantially less than observed from IDA(1). Secondly, while some variation is at ...
... trivalent ligand (coordination number 3), IDA exhibits higher leaching of metal ions, particularly in the equilibration and wash steps(1). Elution fractions from NTA-based resins also contain leached metal ions, but substantially less than observed from IDA(1). Secondly, while some variation is at ...
Oxidation Chemistry of Metal(II) Salen-Type Complexes
... the phenoxyl radical characteristics and that the radical electron is delocalized on the two phenolate moieties. Indeed, the XPS and K-edge XANES of an oxidized Ni complex showed the same binding energies and pre-edge peak of nickel ion as those of the complex before oxidation [40]. These results su ...
... the phenoxyl radical characteristics and that the radical electron is delocalized on the two phenolate moieties. Indeed, the XPS and K-edge XANES of an oxidized Ni complex showed the same binding energies and pre-edge peak of nickel ion as those of the complex before oxidation [40]. These results su ...
Carbohydrate-Metal Complexes : Structural Chemistry of Stable
... and polysaccharides are viewed. The nucleosides are the only non-O-glycosides considered in this review. Structures of simple addition products of carbohydrates and metal salts are not included either. Structures which should be included in this review, according to the requirements stated above, bu ...
... and polysaccharides are viewed. The nucleosides are the only non-O-glycosides considered in this review. Structures of simple addition products of carbohydrates and metal salts are not included either. Structures which should be included in this review, according to the requirements stated above, bu ...
PROPERTIES OF SOLUTIONS
... The expected freezing point depression is .2 m x 1.86 C/m =.372 C. The actual depression is .348 C. Ions in solution form ion pairs ( the oppositely charged ions associate with each other for a short period) which reduces the number of independent particles The van’t Hoff factor (i) is a measu ...
... The expected freezing point depression is .2 m x 1.86 C/m =.372 C. The actual depression is .348 C. Ions in solution form ion pairs ( the oppositely charged ions associate with each other for a short period) which reduces the number of independent particles The van’t Hoff factor (i) is a measu ...
Polysulfane Antitumor Agents from o
... error with the o-benzyne precursors o-C6H4ClLi or o-C6H4CO2-N2+, which provide evidence for thermodynamic product ratios. Pentathiepin 2 displayed a weak molecular ion peak m/z 236 [M+] and a base peak at m/z 172 [M+ - 2S] representing the loss of two sulfur atoms. The molecular ion of trithiole 6 i ...
... error with the o-benzyne precursors o-C6H4ClLi or o-C6H4CO2-N2+, which provide evidence for thermodynamic product ratios. Pentathiepin 2 displayed a weak molecular ion peak m/z 236 [M+] and a base peak at m/z 172 [M+ - 2S] representing the loss of two sulfur atoms. The molecular ion of trithiole 6 i ...
Descriptive Chemistry of Elements d-Block
... The oxidation number of a metal centre is the charge left on the metal when all the ligands are removed. For example, removal of three Br ions and three neutral ammonia molecules from [CoBr3(NH3)3] leaves three positive charges on cobalt. Therefore, the oxidation number of cobalt in [CoBr3(NH3)3] i ...
... The oxidation number of a metal centre is the charge left on the metal when all the ligands are removed. For example, removal of three Br ions and three neutral ammonia molecules from [CoBr3(NH3)3] leaves three positive charges on cobalt. Therefore, the oxidation number of cobalt in [CoBr3(NH3)3] i ...
MC84 - Southchemistry.com
... compound results in the appearance of a brown color. When this solution is shaken with the organic solvent, methylene dichloride, the organic solvent layer turns purple. The unknown compound probably contains (A) K+ (B) Br¯ (C) NO3¯ (D) I¯ (E) Co2+ 36. CuO(s) + H2(g) <===> Cu(s) + H2O(g); H = - 2.0 ...
... compound results in the appearance of a brown color. When this solution is shaken with the organic solvent, methylene dichloride, the organic solvent layer turns purple. The unknown compound probably contains (A) K+ (B) Br¯ (C) NO3¯ (D) I¯ (E) Co2+ 36. CuO(s) + H2(g) <===> Cu(s) + H2O(g); H = - 2.0 ...
11_chapter 1
... research on the photoreaction in the micro heterogeneous environment provided by the polymer has been reported (Mathur et al 1980). Metalloenzyme is a kind of polymer-metal complex present in nature, where metal ions are surrounded by a giant protein molecule of definite three dimensional structures ...
... research on the photoreaction in the micro heterogeneous environment provided by the polymer has been reported (Mathur et al 1980). Metalloenzyme is a kind of polymer-metal complex present in nature, where metal ions are surrounded by a giant protein molecule of definite three dimensional structures ...
OXIDATIVE ADDITION OF POLAR REAGENTS
... oxidative additions of strong acids, which occur basically through the same mechanism (with replacement of hydrogen for carbon). During these so-called “ionic mechanisms,” protonation of the metal center usually occurs first, followed by ligand substitution or simple coordination of the conjugate ba ...
... oxidative additions of strong acids, which occur basically through the same mechanism (with replacement of hydrogen for carbon). During these so-called “ionic mechanisms,” protonation of the metal center usually occurs first, followed by ligand substitution or simple coordination of the conjugate ba ...
Examples
... The second approach, known as Lewis theory, is introduced in the second year of the course. It involves transfer of electron-pairs. ...
... The second approach, known as Lewis theory, is introduced in the second year of the course. It involves transfer of electron-pairs. ...
Ministry of Education and Science of the Ukraine
... Chemical bonding. Chemical bonds: covalent, ionic, metallic. Electronegativity. Types of complex compounds. Chemical bonds in complex compounds. Central ion and coordination sphere. Stability constants. Complex formation in biological systems. 4. Solutions. Electrolytic dissociation. The dissolving ...
... Chemical bonding. Chemical bonds: covalent, ionic, metallic. Electronegativity. Types of complex compounds. Chemical bonds in complex compounds. Central ion and coordination sphere. Stability constants. Complex formation in biological systems. 4. Solutions. Electrolytic dissociation. The dissolving ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... The Common Ion Effect explains why there is a reduction in the solubility of a salt due to the presence of a common ion. Example: Think about the solubility of CaF2(s) in NaF(aq)…. The CaF2(s) can’t breakdown as easily because there is already F- ions in solution. ...
... The Common Ion Effect explains why there is a reduction in the solubility of a salt due to the presence of a common ion. Example: Think about the solubility of CaF2(s) in NaF(aq)…. The CaF2(s) can’t breakdown as easily because there is already F- ions in solution. ...
Full answers
... If Step 2 is assumed to be very slow compared to the equilibrium of Step 1, derive the overall rate equation you would expect to see for this mechanism. If step 1 is at equilibrium, with equilibrium constant, K: K = [N2O2(g)]/[NO(g)]2 [N2O2(g)] = K [NO(g)]2 Step 2 involves the bimolecular reaction o ...
... If Step 2 is assumed to be very slow compared to the equilibrium of Step 1, derive the overall rate equation you would expect to see for this mechanism. If step 1 is at equilibrium, with equilibrium constant, K: K = [N2O2(g)]/[NO(g)]2 [N2O2(g)] = K [NO(g)]2 Step 2 involves the bimolecular reaction o ...
Dr. Arrington Exam 3
... (b) Make a solution drawing that indicates which species are present in significant quantities (not obtained from an equilibrium calculation) at the point on the titration curve indicated by the arrow. Do not show spectator ions in your drawing. ...
... (b) Make a solution drawing that indicates which species are present in significant quantities (not obtained from an equilibrium calculation) at the point on the titration curve indicated by the arrow. Do not show spectator ions in your drawing. ...
Chapter
... • coordination number range from 2 to 12, with the most common being 6 and 4 CoCl36H2O = [Co(H2O)6]Cl3 Tro, Chemistry: A Molecular Approach ...
... • coordination number range from 2 to 12, with the most common being 6 and 4 CoCl36H2O = [Co(H2O)6]Cl3 Tro, Chemistry: A Molecular Approach ...
K c
... 1. The concentrations of the reacting species in the condensed phase are expressed in mol/L (M). In the gaseous phase, the concentrations can be expressed in M. 2. The concentrations of pure solids, pure liquids and solvents do not appear in the equilibrium constant expressions. 3. The equilibrium c ...
... 1. The concentrations of the reacting species in the condensed phase are expressed in mol/L (M). In the gaseous phase, the concentrations can be expressed in M. 2. The concentrations of pure solids, pure liquids and solvents do not appear in the equilibrium constant expressions. 3. The equilibrium c ...